2412
The value of whole volume radiomics machine learning model based on multi-parameter MRI in predicting triple negative breast cancer1Radiology, Shanghai Tenth People’s Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Radiomics, Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Triple-negative breast cancer. DCE-MRI. ADC maps
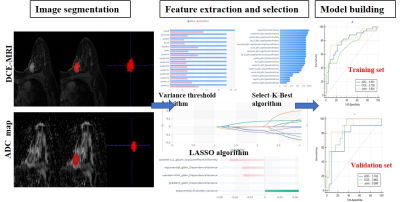
43 TNBCs and 84 Non-TNBCs were allocated in this retrospective study.The lesions were manually segmented with ITK-SNAP software then whole volume radiomics features were extracted with Radcloud radiomics platform based on DCE-MRI and ADC maps, respectively. Three prediction models were constructed by using support vector machine (SVM) classifier, including Model A (based on the selected features of ADC maps), Model B (based on the selected features of DCE-MRI), and Model C (based on the selected features of both combined). The radiomics features model combining DCE-MRI and ADC maps can improve the diagnostic performance of predicting TNBC.Introduction
Breast cancer has been the leading malignancy worldwide with an increasing incidence in recent decades. It is a heterogeneous disease with various clinical behaviors, subtypes, and treatment responses 1. According to their gene expression, there are four molecular subtypes: luminal A, luminal B, human epidermal growth factor receptor2- (HER2-) overexpressing, and triple negative (TN) 2, 3. Triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC) have the worst prognosis, lowest survival rate and lack of effective targeted therapy, but some of the tumors may respond well to chemotherapy 3-6. If we can accurately differentiate TNBC from non-TNBC, it will aid our treatment decision-making. However, molecular subtypes are confirmed by IHC analyses on sample tissues that are invasive and cannot be obtained before operation. Thus, the accurate diagnosis of TNBC is important for the patient’s therapeutic schedule and prognosis. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) has an excellent sensitivity and good specificity for breast cancer diagnosis 7. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) has been used for breast imaging as an adjunct to DCE-MRI increasingly 8. DWI measures the Brownian motion of free water in tissue, therefore can be used to assess cellular density the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) [9]. Multi-parametric breast MRI, that combining DCE-MRI and DWI (or ADC maps), has been widely used in routine clinical practice and recommended to enhance the accuracy of diagnosis, tumor characterization, and response assessment 10-12. Recent studies suggested that radiomics analysis could provide promising conclusions for the diagnosis of breast cancer and was a better discrimination ability than conventional parameters 13. Radiomics is a noninvasive imaging technology which is promising in obtaining hidden data and evaluating the imaging features of entire tumor 14-16, therefore it has been considered as predictive tool for differential diagnosis and pathological classification, as well as the evaluation of gene expression, response to treatment, and prognosis. During the past five years, radiomics has also been applied to breast imaging actively. Numerous radiomics analyses have been used to differentiate breast malignant from benign lesions as well as to predict the pathological subtypes, axillary lymph node metastasis and tumor response to chemotherapy 17-24. However, studies focusing on the value of radiomics analysis based on the whole volume data of breast cancer of both DCE-MRI and ADC maps for the prediction of TNBCs were relatively rare. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to evaluate the differences of whole volume radiomics features of breast cancer between TNBC and non-TNBC based on DCE-MRI and ADC maps in order to make a precise diagnosis of TNBC.Methods
127 patients with pathological proven breast cancer (TNBC: 43, non-TNBC: 84) were allocated in this retrospective study. The lesions were manually segmented with ITK-SNAP software then whole volume radiomics features were extracted with Radcloud radiomics platform. Radiomics features were obtained from DCE-MRI and ADC maps, respectively. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression method was employed for feature selection. Three prediction models were constructed by using support vector machine (SVM) classifier, including Model A (based on the selected features of ADC maps), Model B (based on the selected features of DCE-MRI), and Model C (based on the selected features of both combined). The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to evaluate the diagnostic performance of conventional MR image model and the three radiomics models in predicting TNBC.Results
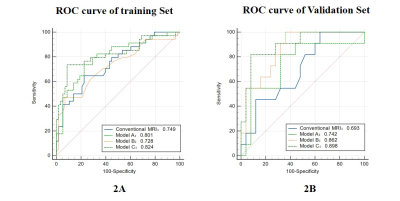
The optimal radiomics features were 5, 6, and 5 for DCE-MRI, ADC maps, and combination of both, respectively. In the training dataset, the AUCs for conventional MR image model and the three radiomics models were 0.749, 0.728, 0.801 and 0.824, respectively. In the validation dataset, the AUCs for conventional MR image model and the three radiomics models were 0.693, 0.862, 0.742 and 0.898, respectively.Conclusions
Radiomics from the combination of DCE-MRI and ADC maps is a promising tool to distinguish TNBC from non-TNBC.Acknowledgements
The authors thank Xiance Zhao and Huiying Medical Technology Co., Ltd. for his technical support.
References
1. Tan J, Le A. (2021) The Heterogeneity of Breast Cancer Metabolism. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1311:89-101.
2. Cancer Genome Atlas N. (2012) Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 490(7418):61-70.
3. Huber KE, Carey LA, Wazer DE. (2009) Breast cancer molecular subtypes in patients with locally advanced disease: impact on prognosis, patterns of recurrence, and response to therapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 19(4):204-10.
4. Lam SW, Jimenez CR, Boven E. (2014) Breast cancer classification by proteomic technologies: current state of knowledge. Cancer Treat Rev. 40(1):129-38.
5. Yin L, Duan JJ, Bian XW, Yu SC. (2020) Triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment progress. Breast Cancer Res. 22(1):61.
6. Li X, Yang J, Peng L, et al. (2017) Triple-negative breast cancer has worse overall survival and cause-specific survival than non-triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 161(2):279-87. 7. Pinker K, Helbich TH, Morris EA. (2017) The potential of multiparametric MRI of the breast. Br J Radiol. 90(1069):20160715.
8. El Ameen NF, Abdel Gawad EA, Abdel Ghany HS. (2021) Diffusion-weighted imaging versus dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI: a new horizon for characterisation of suspicious breast lesions. Clin Radiol. 76(1):80 e1- e8.
9. Thomassin-Naggara I, De Bazelaire C, Chopier J, Bazot M, Marsault C, Trop I. (2013) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the breast: advantages and pitfalls. Eur J Radiol. 82(3):435-43.
10. Niu S, Wang X, Zhao N, et al. (2021) Radiomic Evaluations of the Diagnostic Performance of DM, DBT, DCE MRI, DWI, and Their Combination for the Diagnosisof Breast Cancer. Front Oncol.11:725922. 11. Yuan C, Jin F, Guo X, Zhao S, Li W, Guo H. (2019) Correlation Analysis of Breast Cancer DWI Combined with DCE-MRI Imaging Features with Molecular Subtypes and Prognostic Factors. J Med Syst. 43(4):83.
12. Choi BB. (2021) Dynamic contrast enhanced-MRI and diffusion-weighted image as predictors of lymphovascular invasion in node-negative invasive breast cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 19(1):76.
13. Zhang L, Tang M, Min Z, Lu J, Lei X, Zhang X. (2016) Accuracy of combined dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and diffusion-weighted imaging for breast cancer detection: a meta-analysis. Acta Radiol. 57(6):651-60.
14. Kumar V, Gu Y, Basu S, et al. (2012) Radiomics: the process and the challenges. Magn Reson Imaging. 30(9):1234-48.
15. Limkin EJ, Sun R, Dercle L, et al. (2017) Promises and challenges for the implementation of computational medical imaging (radiomics) in oncology. Ann Oncol. 28(6):1191-1206.
16. Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H. Radiomics: (2016) Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology. 278(2):563-77.
17. Bickelhaupt S, Jaeger PF, Laun FB, et al. (2018)nRadiomics Based on Adapted Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Helps to Clarify Most Mammographic Findings Suspicious for Cancer. Radiology. 287(3):761-70. 18. Whitney HM, Drukker K, Edwards A, Papaioannou J, Giger ML. (2019) Effect of biopsy on the MRI radiomics classification of benign lesions and luminal A cancers. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 6(3):031408.
19. Ma W, Ji Y, Qi L, Guo X, Jian X, Liu P. (2018) Breast cancer Ki67 expression prediction by DCE-MRI radiomics features. Clin Radiol. 73(10):909 e1- e5.
20. Fan M, Zhang P, Wang Y, et al. (2019) Radiomic analysis of imaging heterogeneity in tumours and the surrounding parenchyma based on unsupervised decomposition of DCE-MRI for predicting molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Eur Radiol. 29(8):4456-67.
21. Braman NM, Etesami M, Prasanna P, et al. (2017) Intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics for the pretreatment prediction of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy based on breast DCE-MRI. Breast Cancer Res. 19(1):57.
22. Kim JH, Ko ES, Lim Y, et al. (2017) Breast Cancer Heterogeneity: MR Imaging Texture Analysis and Survival Outcomes. Radiology. 282(3):665-75.
23. Mazurowski MA, Zhang J, Grimm LJ, Yoon SC, Silber JI. (2014) Radiogenomic analysis of breast cancer: luminal B molecular subtype is associated with enhancement dynamics at MR imaging. Radiology. 273(2):365-72.
24. Dong Y, Feng Q, Yang W, et al. (2018) Preoperative prediction of sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer based on radiomics of T2-weighted fat-suppression and diffusion-weighted MRI. Eur Radiol. 28(2):582-91.