2411
MRI Radiomics Signature to Predict Lymph Node Metastasis after Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation Therapy in locally advanced Rectal Cancer1Department of Radiology, Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences and Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital, Chengdu, China, 2Department of Radiology, Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Medical School, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Sichuan Cancer Hospital, Chengdu, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Radiomics, Radiomics
To develop and validate clinical-radiomics models for predicting lymph node metastasis following neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy in locally advanced rectal cancer .83 patients were retrospectively enrolled.pre-,post- and delta radiomics signatures of T2WI and ADC images were constructed by support vector machine model.These models were applied to predict LNM and 5-year disease-free survival.The clinical-deltaADC radiomics combined model presented good performance for predicting post-CRT LNM in the training cohort (AUC=0.895) and validation cohort (AUC=0.900). In ypT0-T2 stage, this model could predict 5-year RFS. Clinical-deltaADC radiomics combined model has good performance to predict LNM after nCRT and helped identify patients with poor prognosis.Purpose
To develop and validate models based on MRI-radiomics and clinical parameters for predicting lymph node status following neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy (nCRT) in locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC).Methods
Eighty-three patients (59 men, 24 women; mean age, 58.3 ± 11.1 years) with LARC between June 2018 and December 2021were retrospectively enrolled. The inclusion criteria consisted of (a) non-mucinous rectal adenocarcinoma proven by endoscopic biopsy; (b) locally advanced disease (either staged on MRI as ≥T3 or regional LNM); (c) being scheduled for nCRT before surgical resection; (d) availability of pre- and post-nCRT MRI results; (e) documentation of the histopathological examination after surgical resection.35 patients were excluded for the following reasons: (a) insufficient image quality due to gas-induced susceptibility artifacts or movement artifacts (n= 19) ;(b) an interval longer than 2 months between post-nCRT MRI and surgery (n= 8); (c) mucinous adenocarcinoma detected at pathologic examination(n=8).MRI was performed with a 1.5-T scanner (MAGNETOM Aera, Siemens Healthineers). The conventional MRI protocol included sagittal, axial (perpendicular to the long axis of the rectum), oblique coronal T2WI with no fat saturation, and diffusion weighted imaging (DWI). The acquisition parameters for T2WI were as follows: TR/TE, 4590/73; field of view, 220 mm2; matrix size, 256mm× 512mm; section thickness, 3.5mm; and intersection gap, 0.7 mm. Axial DWI of the pelvis were performed with the following parameters: 4600/59; number of signals acquired, eight; field of view, 360 mm2; section thickness, 5 mm; and b values, 0 and 800 s/mm2. All the radiomics features were extracted from T2WI and apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC) images before and after nCRT. Delta-radiomics feature was defined as the difference in radiomics feature before and after nCRT. The radiomics signatures of T2WI and ADC images were constructed by support vector machine (SVM) model. The clinical-radiomics model was developed by combining the most predictive radiomics signatures and clinical parameters in SVM models. Receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was used to evaluate the differentiation performance of models. These models were applied to predict 5-year disease-free survival (RFS) using Kaplan-Meier analysis.Results
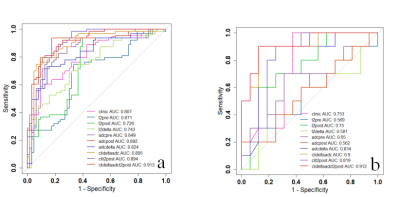
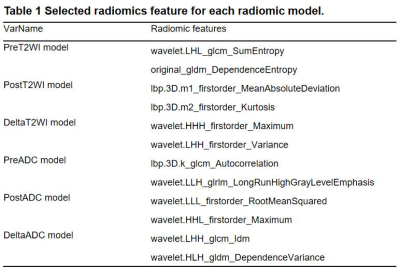
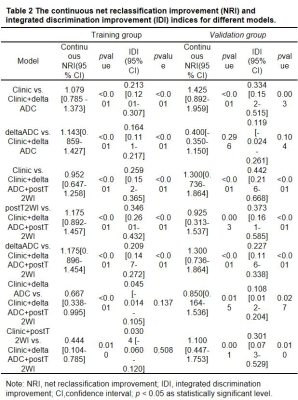
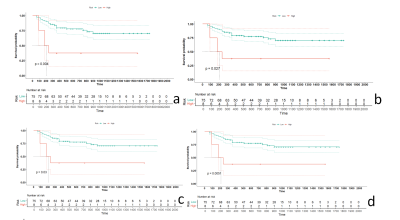
The characteristics of the patients in the primary and validation cohorts are given in Table1. The model performance in the training (Table 2) and validation cohort (Table 3) was summarized in Figure 3. The independent clinical model was constructed by CA199 and post-nCRT tumor thickness. And the radiomic features finally retained in each radiomic model were listed as Table 4.The clinical-deltaADC radiomics combined model presented good performance for predicting post-CRT LNM in the training cohort (AUC=0.895, 95% CI: 0.838-0.953) and validation cohort (AUC=0.900, 95% CI: 0.771-1.000). Clinical-deltaADC radiomic-postT2WI radiomic combined model also showed good diagnostic performances (AUC=0.913, 95% CI: 0.838-0.953) in the training cohort and (AUC=0.912; 95% CI: 0.771-1.000) validation cohort. The NRI and IDI analyses results were summarized in Table 5.The calibration curves with Hosmer–Lemeshow test showed good calibration for clinical-deltaADC-postT2WI combined model and clinical-delta ADC combined model in the training cohort (P=0.51 and 0.12, respectively) and validation cohort (P=0.821 and 0.783, respectively) (Figure 4). Decision curve analysis (DCA) of each model in the training cohort and validation cohort are shown in the Figure 4. Both clinical-deltaADC-postT2WI combined model and clinical-deltaADC combined model had a greater advantage compared with the treat-all-patients scheme or the treat-none scheme for predicting post-nCRT LNM. As for subgroup analysis, clinical-deltaADC radiomics combined model showed good performance in the ypT0-2 (AUC=0.827;95% CI:0.649-1.000) and ypT3-4 stage (AUC=0.934;95% CI:0.864-1.000). In ypT0-T2 stage, clinical-deltaADC radiomic combined model could predict 5-year RFS (P=0.03).Dissussion
At present, morphological methods are not effective in assessing lymph nodes status after nCRT[1-2]. Most previous studies used the pre-nCRT image data to establish a radiomics model and the results are controversial[3-4].Pre-nCRT images do not contain all the information regarding tumor response after nCRT and may not enough to provide useful information for predicting post-nCRT LNM in rectal cancer.Delta-radiomic features have been reported to be associated with treatment response or outcome [5, 6]. As for rectal cancer, some studies indicated delta-radiomics features can predict tumor response patient with rectal cancer after nCRT [7-9]. Our study shows the clinical-deltaADC radiomics combined model presented good performance for predicting post-CRT LNM in the training cohort (AUC=0.895, 95% CI: 0.838-0.953) and validation cohort (AUC=0.900, 95% CI: 0.771-1.000). Delta-radiomics provided rich information on the changes in heterogeneity that might be discarded by single-time-point radiomics [10]. Therefore, delta radiomics approach has the advantage of providing information about the treatment course and the progressive response to multimodal therapies, allowing a real personalization of the treatment before its own end.Local excision or wait-and-watch is typically considered for ypT0-ypT2 with lymph node negative patients. Our study showed clinical-deltaADC combined model could predict 5-year RFS in ypT0-2 rectal cancer after nCRT. This may help contribute to identify high risk patients amenable to treatment intensification with view of personalized medicine.Conclusion
Clinical-deltaADC radiomics combined model could predict post-nCRT LNM in LARC and help identify which patients are at the highest risk for disease recurrence and metastasis.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Ryu KH, Kim SH, Yoon JH, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging for evaluating lymph node eradication after neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy in locally advanced rectal cancer. Acta Radiol. 2016;57(2):133-141.
2. Ogawa S, Itabashi M, Inoue Y, et al. Lateral pelvic lymph nodes for rectal cancer: A review of diagnosis and management. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021;13(10):1412-1424.
3. Zhu H, Zhang X, Li X, et al. Prediction of pathological nodal stage of locally advanced rectal cancer by collective features of multiple lymph nodes in magnetic resonance images before and after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. Chin J Cancer Res. 2019;31(6):984-992.
4. Zhou X, Yi Y, Liu Z, et al. Radiomics-Based Preoperative Prediction of Lymph Node Status Following Neoadjuvant Therapy in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. Front Oncol. 2020;10:604.
5. Fave X, Zhang L, Yang J, et al. Delta-radiomics features for the prediction of patient outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):588.
6. Goh V, Ganeshan B, Nathan P, et al. Assessment of response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in metastatic renal cell cancer: CT texture as a predictive biomarker. Radiology. 2011;261(1):165-171.
7. Boldrini L, Cusumano D, Chiloiro G, et al. Delta radiomics for rectal cancer response prediction with hybrid 0.35 T magnetic resonance-guided radiotherapy (MRgRT): a hypothesis-generating study for an innovative personalized medicine approach. Radiol Med. 2019;124(2):145-153.
8. Jeon SH, Song C, Chie EK, et al. Delta-radiomics signature predicts treatment outcomes after preoperative chemoradiotherapy and surgery in rectal cancer. Radiat Oncol. 2019;14(1):43.
9. Bulens P, Couwenberg A, Intven M, et al. Predicting the tumor response to chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer: Model development and external validation using MRI radiomics. Radiother Oncol. 2020;142:246-252.10. Lin P, Yang PF, Chen S, et al. A Delta-radiomics model for preoperative evaluation of Neoadjuvant chemotherapy response in high-grade osteosarcoma. Cancer Imaging. 2020;20(1):7.
Figures