2401
Automated High Order Shim for Neuroimaging Studies
Jia Xu1, Baolian Yang2, Douglas Kelley2, and Vincent A. Magnotta1,3,4
1Radiology, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, United States, 2GE Healthcare, Waukesha, WI, United States, 3Psychiatry, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, United States, 4Biomedical Engineering, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, United States
1Radiology, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, United States, 2GE Healthcare, Waukesha, WI, United States, 3Psychiatry, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, United States, 4Biomedical Engineering, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Software Tools, Shims
In this work, we proposed an automated High Order Shim procedure for neuroimaging studies. The proposed shimming procedure is fully automated and hence eliminates variability between operators. The procedure performs automated real-time brain extraction to define the region of interest (ROI) of the field map to be used in the shimming algorithm. Automated High Order Shim has fewer image distortions and narrower spectral linewidths than linear shimming and manual high-order shimming, suggesting its superior performance in correcting B0 field homogeneity. The shimming performance was assessed by acquiring EPI-based images and MR spectroscopy at both 3T and 7T field strengths.Introduction
Robust and automated shimming procedures are fundamental to the success of MR techniques sensitive to B0 inhomogeneity, such as magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) and echo-planar imaging (EPI). B0 inhomogeneity can cause unwanted signal loss, image distortion, and spectral line broadening. There are mainly two classes of automatic shimming techniques: projection-based shimming and image-based shimming. Image-based shimming methods are suitable for arbitrary-shaped volumes such as human brains1. High-order shimming is usually used at high field strengths, e.g., 3T and above, to overcome increased field inhomogeneity. For example, the High Order Shim (HOS) software on GE MRI scanners calculates third-order shim currents to minimize the B0 inhomogeneity within a given region of interest (ROI) of the acquired gradient-echo-based field maps2. To date, most automatic shimming methods need a manually defined shim ROI, which introduces intra- and inter-operator variability. In this work, we propose an automated High Order Shim (autoHOS) prototype to perform objective and automated high-order shimming based on automated brain extraction3 for neuroimaging studies.Methods
Fig. 1 shows the flowchart of automated HOS. The autoHOS prototype is developed in Python 3.8 and Tcl/Tk and depends on HD-BET3 and GE HOS software2. First, a 3D field map covering the whole brain (e.g., 25.6×25.6×25.6 cm3 box) with 128×128×64 pixel resolution is acquired using a 3D gradient-echo pulse sequence. The magnitude images of the 3D field map are transferred to Volume Recon Engine (VRE), the image reconstruction architecture of GE MRI scanners for automated brain extraction with GPU. Alternatively, the magnitude images can be transferred to a remote computer for automated brain extraction. Brain masks are generated by HD-BET in GPU mode and applied to magnitude images of the field map. The obtained skull-stripped magnitude images are then transferred back to the MRI host computer for least-squares calculation of shim currents. By default, the autoHOS procedure will automatically adjust the high order shims over the whole brain. However, it also supports selection of smaller ROIs based on voxel placement for single-voxel MRS applications (Fig. 2).Results
At 3T, HOS and autoHOS have fewer distortions than linear shimming, while HOS and autoHOS perform similarly (Fig. 3). At 7T, autoHOS has fewer distortions compared to HOS and linear shimming (Fig. 4). Notably, autoHOS is superior to HOS for MRS at 7T, as exemplified by the narrower linewidth of both nonlocalized 31P MRS (Fig. 5A, ~48% improvement) and 31P MRSI (Fig. 5B, ~12% improvement).Discussion
Among several popular automated brain extraction tools, we chose the HD-BET prediction algorithm because it needs little parameter tuning and is robust to cavities and abnormalities such as tumors. The use of GPU on modern MRI hardware (e.g., SIGNA 7.0T, GE Healthcare) or on a remote server has enabled real-time MRI reconstruction based on deep learning, such as HD-BET. AutoHOS with a high-resolution 3D field map (128×128×64) can be finished within 1~2 minutes. For EPI-based diffusion tensor images (DTI) or gradient-echo EPI BOLD images, autoHOS is evidently better than linear shimming but does not show considerable improvement compared to HOS at 3T and 7T. This is because brain extraction does not remove all pixels with possible phase offsets1, although the erroneous extracranial lipid pixels are already stripped. While for both nonlocalized MRS and multivoxel MRSI at 7T, autoHOS significantly improves the lineshapes, suggesting a better global B0 homogeneity can be achieved by this fully automated method.Conclusion
The autoHOS we present in this work eliminates the need for additional user interaction while providing better B0 homogeneity than the existing HOS method. In the future, we will improve the field map for shim calculation by utilizing brain masks generated as part of the automated prescription algorithm on the scanner eliminating the need for the most time-consuming aspect of our current solution. In the future, we hope to integrate this into the Pre-scan process, similar to coil calibration and center frequency adjustment.Acknowledgements
This work was conducted on an MRI instrument funded by S10OD025025 and S10RR028821.References
(1) Juchem, C.; Cudalbu, C.; de Graaf, R. A.; Gruetter, R.; Henning, A.; Hetherington, H. P.; Boer, V. O. B0 shimming for in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy: Experts' consensus recommendations. NMR Biomed 2021, 34 (5), e4350. DOI: 10.1002/nbm.4350.
(2) Kim, D. H.; Adalsteinsson, E.; Glover, G. H.; Spielman, D. M. Regularized higher-order in vivo shimming. Magn Reson Med 2002, 48 (4), 715-722. DOI: 10.1002/mrm.10267.
(3) Isensee, F.; Schell, M.; Pflueger, I.; Brugnara, G.; Bonekamp, D.; Neuberger, U.; Wick, A.; Schlemmer, H. P.; Heiland, S.; Wick, W.; et al. Automated brain extraction of multisequence MRI using artificial neural networks. Hum Brain Mapp 2019, 40 (17), 4952-4964. DOI: 10.1002/hbm.24750.
Figures
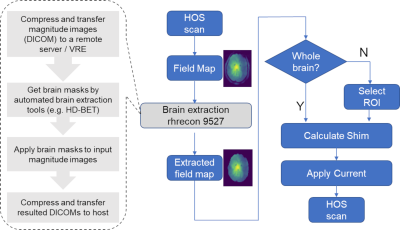
Figure
1. Flowchart of Automated
HOS
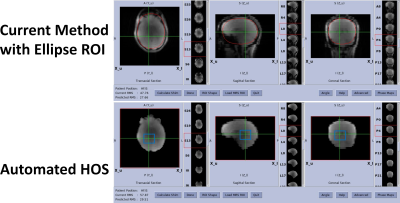
Figure
2. Selection of
shim ROI. The current HOS software needs manual selection of ellipse or
rectangular ROI (top). autoHOS (bottom) automatically shims the whole brain
(red box). It also supports the manual selection of smaller ROI (blue box) for
applications such as single-voxel MRS.
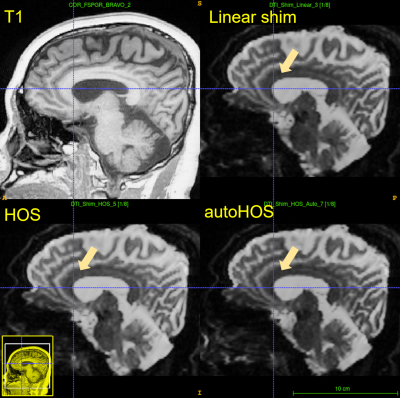
Figure
3. Single-Spin Echo
DTI images on a Premier 3.0T scanner (GE Healthcare). HOS and autoHOS have
fewer distortions compared to linear shimming.
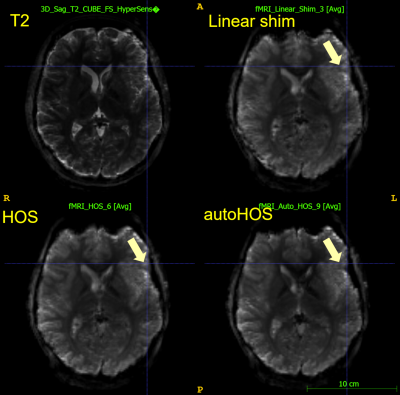
Figure
4. Single Shot
Gradient-Echo EPI images on a SIGNA 7.0T (GE Healthcare). autoHOS shows fewer
distortions compared to linear shimming and HOS.
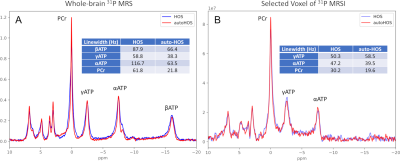
Figure
5. Lineshape
comparison between HOS and autoHOS on a SIGNA 7.0T (GE Healthcare) scanner. The
linewidths are fitted by AMARES. (A) Non-localized 31P MRS (real
spectra) using a free induction decay (FID) sequence. (B) Selected voxel (8.3×8.3×8
cm3) of 31P MRSI (magnitude spectra) using FID sequence.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/2401