2292
Diagnostic efficacy of combined fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean kurtosis (MK) in detecting the Parkinson disease (PD) model rat
Yanchao Dong1, Yansheng Chen2, and Lanxiang Liu2
1Qinhuangdao Municipal No.1 Hospital, Qinhuandao, China, 2Qinhuangdao Municipal No.1 Hospital, Qinhuangdao, China
1Qinhuangdao Municipal No.1 Hospital, Qinhuandao, China, 2Qinhuangdao Municipal No.1 Hospital, Qinhuangdao, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Parkinson's Disease, Parkinson's Disease, DKI
Both FA and MK in DKI have value in the diagnosis of PD. We here investigated the sensitivity and specificity of FA and MK in the early diagnosis of PD rat model. PD and control group, 20 in each group. The FA, MK and FA+MK in PD group were statistically significantly different from that of the control group (P < 0.01). The Youden’s index of FA+MK value was higher than the two alone. The optimal cut-off FA+MK value was 1.404. The diagnostic efficiency of the FA+MK values were better relative to that two alone in diagnosing PD.Objectives: Both fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean kurtosis (MK) in diffusion kurtosis
imaging (DKI) have value in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease(PD). However, it
remains unclear whether the combined FA and MK values are better than the two
alone in diagnosing PD. Thus, we here investigated the sensitivity and specificity of FA
and MK to explore which of these methods were more efficient in the early diagnosis of
6-OHDA-induced PD in a rat model. Methods: 20 male SD rats were injected with 6-
OHDA into the right substantia nigra (SN) for modeling, and other 20 rat for control
group. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed 5th weeks after modeling.
The FA, MK and FA+MK values of the right SN were measured and analyzed.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the sensitivity and
specificity of the above two values for identifying PD. Immunohistochemistry of tyrosine
hydroxylase (TH), Tunel, and Nissl staining in the SN was performed. Results: The FA,
MK and FA+MK values in PD group obtained in the 5th week were statistically
significantly different from that of the control group (P < 0.01). The optimal cut-off FA+MK value (with
respective area under the curve, sensitivity, specificity) was 1.404 (0.925, 95%, 75%),
the Youden index of FA+MK was higher than the two alone. The FA, MK and FA+MK
values correlated positively with the Tunel staining (r = 0.47, r = 0.60, r = 0.61,
respectively), while they correlated negatively with the TH and Nissl staining (r = -0.62,
r = -0.57, r = -0.67; r = -0.67, r = -0.71, r = -0.78, respectively). Conclusions: At the 5th
week, the diagnostic efficiency of the FA+MK values were better relative to that two
alone in diagnosing PD.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
No reference found.Figures
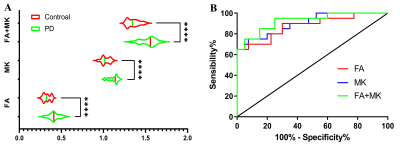
Figure 1A shows that the FA, MK and FA+MK values of the PD group were significantly higher than those of the control group at the 5th week after modeling, and the difference was statistically significant. 1B shows ROC curve analysis, and the area under FA+MK curve was the largest.
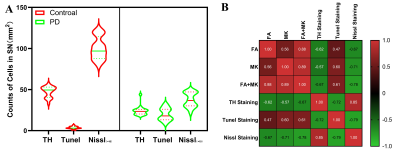
Figure 2A shows that at the 5th week
after modeling, the number of TH and Nissl stained positive cells in PD group
was significantly lower than that in control group, while the number of Tunel
stained positive cells was significantly higher than that in control group. 2B
showed that FA, MK and FA+MK were positively correlated with the number of
Tunel positive cells and negatively correlated with the number of TH and Nissl
positive cells.
Transverse axial DKI image of rat brain
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/2292