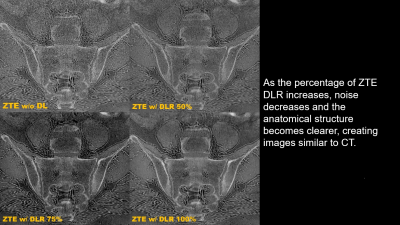
2267
Deep learning reconstruction of zero echo time imaging: bone erosion detection in axial spondyloarthritis1Department of Radiology, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea, Republic of, 2Department of Radiology, IHaeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea, Republic of, 3Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea, Republic of, 4Department of Radiology, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea, Republic of, 5GE Healthcare, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 6GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, United Kingdom, 7GE Healthcare, New York, NJ, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Joints, MSK, sacroiliac joint, zero echo time imaging, deep learning reconstruction
The aim of this study was to compare the diagnostic performance of DLR of ZTE imaging for bone erosion in axial spondyloarthritis, using CT as the reference standard. Twenty-three patients with suspicion of sacroiliitis underwent both CT and MR scans of sacroiliac joints included for analysis. ZTE with or with DLR showed higher correlation coefficients than T1WI for two readers. Inter-reader agreements showed moderate to substantial agreement. ZTE DLR improves diagnostic performance in the detection of SIJ bone erosion in patients with axial spondyloarthritis compared with T1WI and ZTE without DLR.Introduction
Deep learning–based reconstruction (DLR) of MRI enables image denoising with sharp edges and reduced artifacts, which improves the image quality [1-2]. The aim of this study was to compare the diagnostic performance of DLR of zero echo time (ZTE) imaging for bone erosion in axial spondyloarthritis (SpA) compared T1-weighted fast spin echo (T1FSE) imaging, using CT as the reference standard.Methods
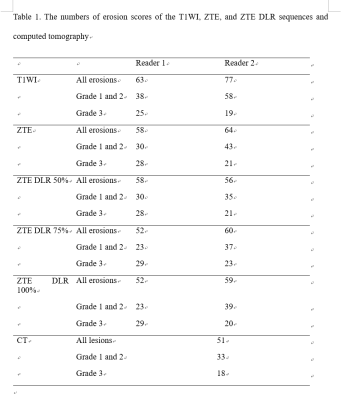
A prototype ZTE DLR pipeline was used to sharpen and denoise the images. The model effectively eliminates ringing while the denoising level is adjustable and independent of the ringing reduction. Twenty-three patients with suspicion of sacroiliitis underwent both CT and MR scans of sacroiliac joints (SIJs, 92 quadrants) from February 2021 to May 2022 included for analysis. Two musculoskeletal radiologists (with 7 and 6 years of subspecialty experience, respectively) independently scored SIJs for bone erosion on MR images including T1FSE oblique coronal images, ZTE oblique coronal reformation images without DLR, ZTE DLR 50%, 75% and 100%. Each of the five sequences were reviewed at time intervals of 2 weeks. Other musculoskeletal radiologist (with 11 years of subspecialty experience) scored the erosion seen in CT, which was used as the reference standard [3]. Diagnostic confidence in axial SpA was measured based on a five-point confidence score [4]. Correlation of erosion scores between CT and MRIs were evaluated using Spearman’s correlation test. Sensitivities, specificities, and accuracies were calculated. Weighted kappa coefficients were calculated by the quadratic method to assess the inter-reader agreements for bone erosion. Confidence scores were compared using the Wilcoxon sum rank test.Results
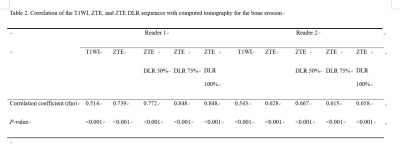
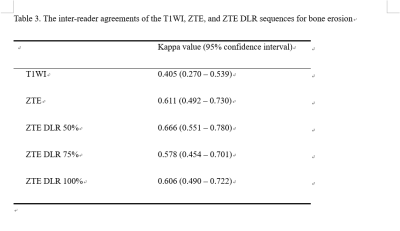
Compared with erosion scores of CT, the correlation coefficients for each MRI showed significant moderate to high positive correlations. ZTE with or with DLR showed higher correlation coefficients than T1WI for two readers. The sensitivities, specificities, accuracies were 88.2%, 68.3%, and 79.3% for T1WI and ZTE without DLR; 90.2%, 70.7%, and 81.5% for ZTE DLR 50%, 92.2%, 87.8%, and 90.2% for ZTE DLR 75% and 100% in reader 1 and 88.2%, 22.0%, and 58.7% for T1WI; 86.3%, 51.2%, and 70.7% for ZTE without DLR; 84.3%, 68.3%, and 77.2% for ZTE DLR 50%; 86.3%, 61.0%, and 75.0% for ZTE DLR 75%; 84.3%, 61.0%, and 73.9% for ZTE DLR 100% in reader 2. Inter-reader agreements showed moderate to substantial agreement. ZTE DLR 50% showed highest kappa value. The mean confidence score of SpA was 3.8 for ZTE DL 70% and 100%, the highest value in reader 1. The mean confidence score of SpA was 4.4 for T1WI, the highest value in reader 2.Discussion
The present study showed that ZTE DLR were highly correlated with CT findings in terms of subchondral bone erosion. ZTE allowed the bone cortex to be well delineated from cartilage, ligament, and medullary bone, which resulted in the production of a CT-like image and good delineation of subchondral bone erosion [5-6]. However, in clinical practice, it is difficult to distinguish bone erosion from artifacts caused by low signal-to-noise ratio. ZTE DLR provided better diagnostic performance for identifying bone erosion compared to conventional MRI and ZTE without DLR. ZTE DLR also increases confidence in the diagnosis of SpA.Conclusion
ZTE DLR improves diagnostic performance in the detection of SIJ bone erosion in patients with SpA compared with T1WI and ZTE without DLR.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Lebel RM: Performance characterization of a novel deep learning-based MR image reconstruction pipeline. arXiv:2008.06559
2. Hahn S, Yi J, Lee HJ, et al. Image Quality and Diagnostic Performance of Accelerated Shoulder MRI With Deep Learning-Based Reconstruction. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2022;218(3):506-516.
3. Diekhoff T, Hermann K-GA, Greese J, et al. Comparison of MRI with radiography for detecting structural lesions of the sacroiliac joint using CT as standard of reference: results from the SIMACT study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:1502–1508.
4. Hahn S, Song JS, Choi EJ, et al. Can Bone Erosion in Axial Spondyloarthropathy be Detected by Ultrashort Echo Time Imaging? A Comparison With Computed Tomography in the Sacroiliac Joint. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022;56(5):1580-1590.
5. Li Y, Xiong Y, Hou B, et al. Comparison of zero echo time MRI with T1‑weighted fast spin echo for the recognition of sacroiliac joint structural lesions using CT as the reference standard. Eur Radiol. 2022;32(6):3963-3973.
6. Jans LBO, Chen M, Elewaut D, et al. MRI-based Synthetic CT in the Detection of Structural Lesions in Patients with Suspected Sacroiliitis: Comparison with MRI. Radiology. 2021 Feb;298(2):343-349.
Figures