2245
Value of texture analysis based on R2* map for predicting early recurrence of HCC after hepatectomy1Department of Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Engineering Research Center for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging, Dalian, China, 3GE Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Liver, Cancer
Hepatectomy is an important therapeutic method for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The overall survival rate of patients with early recurrence is often lower than that of patients without early recurrence. Therefore, this worked aimed at investigating the value of texture analysis based on R2* map for predicting early recurrence of HCC after hepatectomy. Eleven optimal texture features were obtained to predict early recurrence of HCC. This research suggested that R2* map texture analysis had certain predictive value for early recurrence of HCC after hepatectomy, which was valuable for noninvasively, preoperatively and accurately predicting the prognostic factors during clinical practice.Purpose
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common malignant tumor and the third leading cause of cancer death in the world [1]. Hepatectomy is an important therapeutic method for HCC and the first choice for HCC patients with good liver function [2]. However, the HCC recurrence rate after hepatectomy is 40-70%[3]. For HCC with high recurrence probability, postoperative neoadjuvant therapy and other methods can be used to prevent tumor recurrence [4]. The overall survival rate of patients with early recurrence is often lower than that of patients without early recurrence [5]. Therefore, accurate preoperative prediction of early HCC relapse is very important for the selection of the best treatment plan. Enhanced T2* weighted angiography (ESWAN) is a heavy T2* weighted sequence developed based on magnetic sensitive weighted imaging. After post-processing, R2* maps can be obtained to reflect changes in local tissue oxygen content. By delineating all tumor layers and conducting texture analysis to extract texture features, the overall heterogeneity within the lesion can be quantitatively evaluated. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to investigate the feasibility of predicting early postoperative recurrence of HCC based on R2* map texture analysis of ESWAN sequence.Materials and Methods
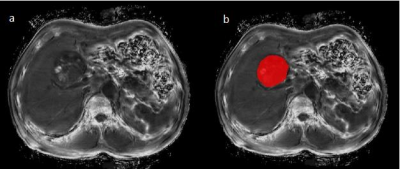
A retrospective analysis was performed of all 46 patients who underwent hepatectomy and were pathologically confirmed between November 2011 and May 2020. According to whether there were new intrahepatic HCC lesions or extrahepatic metastases (confirmed by enhanced CT or MRI or surgical pathology) within 2 years after hepatectomy, HCC patients were divided into the early recurrence group (ER, n=26) and the non-early recurrence group (NER, n=20). All patients underwent conventional 3.0T MRI and ESWAN sequence scan of upper abdomen within 1 month before surgery. ESWAN image was postprocessed by Functool software (GE AW 4.6 workstation) to obtain R2* graph. Radiologists with 3 and 7 years of MRI diagnosis experience delineate all layers of the tumor along the tumor edge on R2* maps(Figure1), and then extracted 107 texture features using AK software (GE Healthcare). It includes first-order features, shape features, Gray Level co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM), Gray Level Dependence Matrix (GLDM),Gray Level Size Zone Matrix(GLSZM), Gray Level Run Length Matrix (GLRLM) and Neighbouring Gray Tone Difference Matrix(NGTDM). Inter-class correlation coefficient (ICC), Spearman correlation test and Gradient boosting decision tree (GBDT) were used for feature dimension reduction. Logistic regression model was established, receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was drawn to predict the efficacy of relapse, and area under the curve (AUC), precision, sensitivity and specificity were calculated.Results
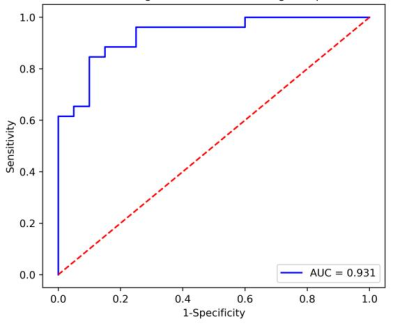
Eleven optimal texture features were obtained, including two first-order features: Kurtosis, Range and Skewness, one GLCM features: MaximumProbability, three GLDM features: DependenceVariance, GrayLevelNonUniformity, LargeDependenceEmphasis, and four GLSZM features: LargeAreaLowGrayLevelEmphasis, LowGrayLevelZoneEmphasis, SizeZoneNonUniformityNormalized and SmallAreaLowGrayLevelEmphasis. Logistic regression model was established to predict AUC, accuracy, sensitivity and specificity of ER after hepatectomy for HCC were 0.931[95%CI(0.867,0.983)]、84.80%、80.80% and 90.00%(Figure2).Discussion and conclusion
The regression model established by the 11 texture features more accurately and comprehensively reflects the deep tumor heterogeneity information such as the intensity, depth, direction, uniformity, spatial arrangement relationship, complexity, and smooth roughness of the R2 * map texture, and has high predictive efficiency. In conclusion, this study preliminarily demonstrated that the R2 * plot texture analysis based on the ESWAN sequence can multiparametric, comprehensively, objective, and non-invasively predict the early recurrence of HCC after hepatectomy.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1]. Torimura T, Iwamoto H. Treatment and the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia[J]. Liver Int. 2021.DOI: 10.1111/liv.15130.
[2]. Mocan L. Multimodal therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: the role of surgery[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021,25(13):4470-4477.DOI: 10.26355/eurrev_202107_26238.
[3]. Tampaki M, Papatheodoridis G, Cholongitas E. Intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection: an update[J]. Clin J Gastroenterol.2021,14(3):699-713.DOI: 10.1007/s12328-021-01394-7.
[4]. Liu D, Song T. Changes in and challenges regarding the surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in China[J]. Biosci Trends. 2021,15(3):142-147.DOI: 10.5582/bst.2021.01083.
[5]. Cheng Z, Yang P, Qu S, et al. Risk factors and management for early and late intrahepatic recurrence of solitary hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection[J]. HPB (Oxford). 2015,17(5):422-427