2243
A Radiomics Nomogram for the Prediction of Microvascular Invasion of HCC and Patients’ Benefit from Postoperative Adjuvant TACE
Kun Zhang1, Zhi Wei Shen2, and Wen Shen1
1Department of Radiology, Tianjin First Central Hospital, Tianjin Institute of imaging medicine, Tianjin, China, 2Philips healthcare,Beijing,China, Beijing, China
1Department of Radiology, Tianjin First Central Hospital, Tianjin Institute of imaging medicine, Tianjin, China, 2Philips healthcare,Beijing,China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Liver, Cancer, Hepatocellular carcinoma · Neoplasm invasion
• The novel radiomics nomogram developed based on Gd-EOB-DTPA MRI achieved preoperative non-invasive MVI risk prediction.• An m-score based on the radiomics nomogram could stratify HCC patients and further identify individuals who may benefit from the PA-TACE.• The radiomics nomogram could help clinicians to implement more appropriate interventions and perform individualized precision therapies.Objectives
To evaluate the performance of a radiomics nomogram developed based on gadolinium-ethoxybenzyl-diethylenetriamine penta-acetic acid (Gd-EOB-DTPA) MRI for preoperative prediction of microvascular invasion (MVI) of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and to identify patients who may benefit from the postoperative adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization (PA-TACE).Methods
A total of 260 eligible patients were retrospectively enrolled from three hospitals (140, 65, and 55 in training, standardized external, and non-standardized external validation cohort). Radiomics features and image characteristics were extracted from Gd-EOB-DTPA MRI image before hepatectomy for each lesion. In the training cohort, a radiomics nomogram incorporated the radiomics signature and radiological predictors was developed. The performance of radiomics nomogram was assessed with respect to discrimination calibration, and clinical usefulness with external validation. A score (m-score) was constructed to stratify the patients and explored whether it could accurately predict patient who benefit from PA-TACE.Results
A radiomics nomogram integratied with the radiomics signature, max-D(iameter) >5.1 cm, peritumoral low intensity (PTLI), incomplete capsule, and irregular morphology had favorable discrimination in the training cohort (AUC=0.982), with an accuracy of 93.6%, sensitivity of 94.1%, and specificity of 93.3%. Decision curve analysis confirmed the clinical usefulness of the novel radiomics nomogram. The log-rank test revealed that PA-TACE significantly decreased the early recurrence in the high-risk group (P=0.006) with no significant effect in the low-risk group (P=0.270).Conclusions
The novel radiomics nomogram combining the radiomics signature and clinical radiological features achieved preoperative non-invasive MVI risk prediction and patients benefit assessment after PA-TACE, which may help clinicians implement more appropriate interventions.Acknowledgements
The author (Zhi-Wei Shen) is an employee of Philips Healthcare. Part of the work on radiomics analysis was supported by Ding Chengyu, an employee of Philips Healthcare. The remaining authors declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.References
1Marrero JA, Kulik LM, Sirlin C et al (2018) Diagnosis, staging, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2018 practice guidance by the American association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology 68:723-7502Erstad DJ, Tanabe KK (2019) Prognostic and therapeutic implications of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 26:1474-1493
3Tang A (2020) Using MRI to Assess Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Radiology 297:582-583
4Server S, Sabet S, Yaghouti K Namal E, Inan N, Tokat Y (2019) Value of imaging findings in the prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Transplant Proc 51:2403-2407
5Kim H, Park MS, Choi JY et al (2009) Can microvessel invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma be predicted by pre-operative MRI. Eur Radiol 19: 1744-1751
6Kristina IR, Daniela BH, Claude BS, Elmar MM (2010) Gadoxetate Disodium-Enhanced MRI of the Liver: Part 1, Protocol Optimization and Lesion Appearance in the Noncirrhotic Liver. Am J Roentgenol 195:13-28
7Nishie A, Asayama Y, Ishigami K et al (2014) Clinicopathological significance of the peritumoral decreased uptake area of gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 29:561-567
8Lambin P, Leijenaar RTH, Deist TM et al (2017) Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14:749-762
9Bowen SR, Yuh WTC, Hippe DS et al (2018) Tumor radiomic heterogeneity: Multiparametric functional imaging to characterize variability and predict response following cervical cancer radiation therapy. J Magnet Resonance Imaging 47:1388-1396
10Zhang S, Xu G, Duan CF et al (2021) Radiomics analysis of MR imaging with Gd-EOB-DTPA for preoperative prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: investigation and comparison of different hepatobiliary phase delay times. BioMed research international. Doi:10.1155/2021/6685723
11Feng ST, Jia YM, Liao B et al (2019) Preoperative prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular cancer: a radiomics model using Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced MRI. Eur Radiol 29:4648-4659
12Isabella FW, Hitesh M, Christoph JA et al (2020) Reliability and prognostic value of radiomic features are highly dependent on choice of feature extraction platform. Eur Radiol 30:6241-6250
13Yang L, Gu DS, Wei JW et al (2019) A radiomics nomogram for preoperative prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver cancer 8:373-386
14Wang Z, Ren Z, Chen Y et al (2018) Adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization for HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma after resection: a randomized controlled study. Clin Cancer Res 24:2074-2081
15Qi YP, Zhong JH, Liang ZY et al (2019) Adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma involving microvascular invasion. Am J Surg 217:739-744
16Liu S, Li H, Guo L et al (2019) Tumor size affects efficacy of adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and microvascular invasion. Oncologist 24:513-520
17Wang YY, Wang LJ, Xu D et al (2019) Postoperative adjuvant transcatheter arterial chemoembolization should be considered selectively in patients who have hepatocellular carcinoma with microvascular invasion. HPB (Oxford) 21:425-433
18Dai HJ, Lu MH, Huang BS et al (2021) Considerable effects of imaging sequences, feature extraction, feature selection, and classifiers on radiomics-based prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma using magnetic resonance imaging. Quant Imag Med Surg 11:1836-1853
19Nebbia G, Zhang Q, Arefan D, Zhao XX, Wu SD (2020) Pre-operative Microvascular Invasion Prediction Using Multi-parametric Liver MRI Radiomics. J Digit Imaging 33:1376-1386
20Hong SB, Choi SH, Kim SY et al (2021) MRI Features for Predicting Microvascular Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Liver Cancer 10:94-106
21Renzulli M, Brocchi S, Cucchetti A et al (2016) Can current preoperative imaging be used to detect microvascular invasion of hepatocellular Carcinoma? Radiology 279: 432-442
22Zhang L, Yu X, Wei WX et al (2020) Prediction of HCC microvascular invasion with gadobenate-enhanced MRI: correlation with pathology. Eur Radiol 30:5327-5336
23Kim KA, Kim MJ, Jeon HM et al (2012) Prediction of microvascular invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma: Usefulness of peritumoral hypointensity seen on gadoxetate disodium-enhanced hepatobiliary phase images. J Magn Reson Imaging 35: 629-634
24Wu TH, Hatano E, Yamanaka K et al (2016) A non-smooth tumor margin on preoperative imaging predicts microvascular invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Surg Today 46: 1275-1281
25Alexeya S, Macieja P, Jazana O et al (2021) Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Reflects Tumor Grading and Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver cancer 10:10-24
26Zhang K, Xie SS, Li WC, Ye ZX, Shen ZW, Shen W (2022) Prediction of microvascular invasion in HCC by a scoring model combining Gd-EOB-DTPA MRI and biochemical indicators. Eur Radiol 32:4186-4197
27Kang I, Jang M, Lee JG et al (2020) Subclassification of Microscopic Vascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Annals of surgery 274: e1170-e1178
28Uno H, Cai T, Pencina MJ, D’Agostino RB, Wei LJ (2011) On the C-statistics for evaluating overall adequacy of risk prediction procedures with censored survival data. Stat Med 30:1105-1117
29Balachandran VP, Gonen M, Smith JJ, DeMatteo RP (2015) Nomograms in oncology: more than meets the eye. Lancet Oncol 16:e173-e180.
30Kramer AA, Zimmerman JE (2007) Assessing the calibration of mortality benchmarks in critical care: the HosmerLemeshow test revisited. Crit Care Med 35:2052-2056
31Vickers AJ, Elkin EB (2006) Decision curve analysis: a novel method for evaluating prediction models. Med Decis Making 26:565-574
32Wang Q, Li CF, Zhang JX et al (2021) Radiomics Models for Predicting Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Radiomics Quality Score Assessment.Cancers 13:5864
33Ahn SJ, Kim JH, Park SJ, Kim ST, Han JK (2019) Hepatocellular carcinoma: preoperative gadoxetic acid -enhanced MR imaging can predict early recurrence after curative resection using image features and texture analysis. Abdom Radiol 44:539-548
34Levi Sandri GB, Spoletini G, Vennarecci G et al (2018) Laparoscopic liver resection for large HCC: short- and long-term outcomes in relation to tumor size. Surg Endosc 32: 4772-4779
35Huang JC, Tian WW, Zhang LL et al (2020) Preoperative prediction power of imaging methods for microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol 10:887
36Wang H, Wu MC, Cong WM (2019) Microvascular invasion predicts a poor prognosis of solitary hepatocellular carcinoma up to 2 cm based on propensity score matching analysis. Hepatol Res 49: 344-354
37Bruix J, Sherman M (2011) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology 53:1020-1022
38Liao M, Zhu Z, Wang H, Huang J (2017) Adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization for patients after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Scand J Gastroenterol 52):624-634
39Liang L, Li C, Diao YK et al (2020) Survival benefits from adjuvant transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in patients undergoing liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther Adv Gastroenter. Doi:10.1177/ 1756284820977693
40Chen W, Ma T, Zhang J et al (2020) A systematic review and meta-analysis of adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization after curative resection for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB : the official journal of the International Hepato Pancreato Biliary Association 22:795-808
41Ma XH, Wei JW, Gu DS et al (2019) Preoperative radiomics nomogram for microvascular invasion prediction in hepatocellular carcinoma using contrast-enhanced CT. Eur Radiol 29:3595-3605
42Lei Z, Li J, Wu D et al (2016) Nomogram for Preoperative Estimation of Microvascular Invasion Risk in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Within the Milan Criteria. JAMA Surg 151:356-363
43Zhang Y, Shu ZY, Ye Q et al (2021) Preoperative Prediction of Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Multi-Parametric MRI Radiomics. Front Oncol 11:633596
44Li L, Su Q, Yang H (2022) Preoperative prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: a radiomic nomogram based on MRI. Clin Radiol. Doi:10.1016/j.crad.2021.12.008
45Huang MQ, Shen SL, Cai HS et al (2021) Regional liver function analysis with gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI and virtual hepatectomy: prediction of postoperative short-term outcomes for HCC. Eur Radiol 31:4720-4730
46Bernard EVB, Catherine MP, Hero KH (2012) Primovist, eovist: What to expect? J Hepatol 57:421-429
Figures
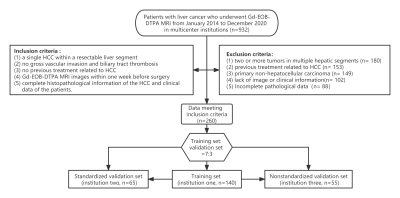
Flowchart of the recruitment of the modeling and validation cohorts
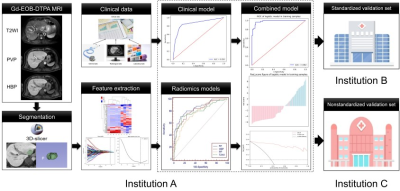
Workflow of model establishment
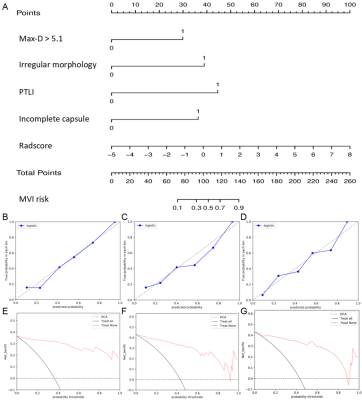
Nomogram for predicting MVI probability, nomogram calibration and decision curve analysis of the patients.
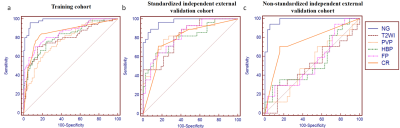
Comparison of the ROCs of the clinical radiological, radiomics and radiomics nomogram models in the training, standardized validation, and non-standardized validation cohorts.
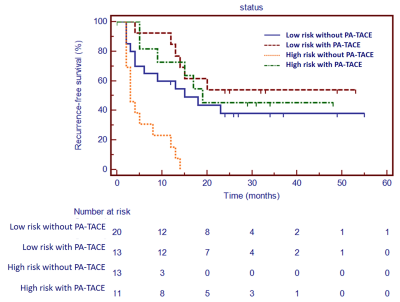
Kaplan-Meier survival curves compaing PA-TACE with no-PA-TACE by risk group
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/2243