2114
The application of MTP synthetic sequence in the diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2MR Collaboration,Central Research Institute, United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 3MR Collaboration,Central Research Institute, United Imaging Healthcare, shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Stroke, Ischemia, T2 Star
Multiple parametric (MTP) is a novel quantitative MRI technique that allows the generation of quantitative maps as well as synthetic weightings from a single acquisition. Preliminary results show that MTP synthetic sequence can effectively distinguish infarcted brain from normal tissue with a good diagnostic performance. MTP imaging offers the potential to create a standardized brain imaging protocol providing multiple types of quantitative tissue property information and qualitative information in just a few minutes. The aim of this study is to evaluate the potential of MTP in the mapping-based identification of acute ischemic stroke.Introduction
Acute ischemic stroke is the most common serious manifestation of cerebrovascular disease and a major cause of severe disability1. A patient presenting with acute onset of a focal neurologic deficit should undergo a rapid, focused history and examination. However, fast imaging or high-resolution achievement often lead to great noise artifacts in reconstructed magnetic resonance images, which interfere with subsequent clinical diagnosis. Additionally, conventional MR imaging does not include quantitative assessment for the prohibitively long acquisition time in most cases. MTP synthetic sequence allows rapid simultaneous quantification of multiple tissue characteristics, including T1, T2 Star, R2 star, proton density (PD), and quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) with one acquisition2. This study was conducted to investigate the value of MTP in the diagnosis of acute cerebral infarction.Methods
Twenty patients with acute or subacute cerebral MCA infarction were scanned by conventional MR imaging as well as MTP. The clinical base data of all patients were recorded including National Institute of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score on admission. To quantify MTP-derived T1, PD, R2 Star, T2 Star and QSM values in ischemic lesion, ROIs were manually drawn to outline the lesions on the infarct core (IC) and mirror area. The ratio of the quantitative parameters between the lesion and the contralateral normal tissue were calculated. Statistical analysis of the obtained T1, PD, R2 Star, T2 Star and QSM values between lesions and contralateral side were compared by the independent sample t-test or Mann-Whitney U test. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, wherein areas under the curves (AUCs) and 95% confidence intervals were calculated to compare the discriminatory power of quantitative parameters of MTP for predicting infarction. Spearman correlation analysis were separately used to analyze the relationships between the NIHSS score and the ratio of MTP quantitative parameters.Results
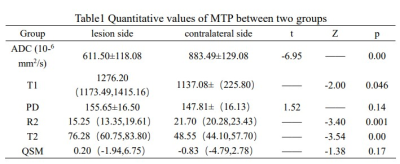
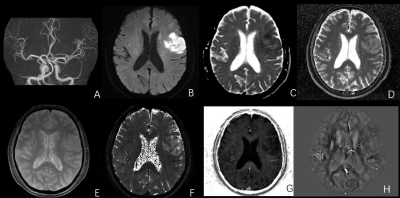
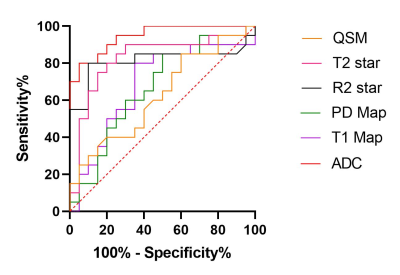
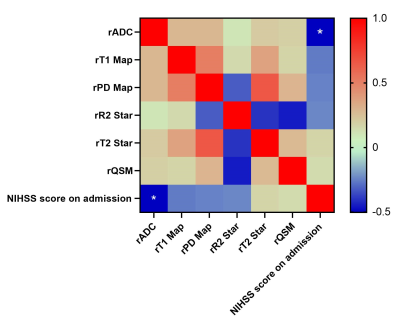
A total of 20 patients (age 68.60±13.96, 70% men) were analyzed and divided into lesion group and contralateral group. The value of ADC and R2 Star of ischemic lesion area were significantly lower than those of the mirror area of the opposite healthy side, while the value of T1 Map and T2 Star was higher in lesion group (p<0.05). There were no differences in the value of PD Map and QSM between lesion group and contralateral group (Table 1, Figure 1). The AUC of the MTP-derived ADC, T1 Map, PD Map, R2 Star, T2 Star to predict acute ischemic stroke was 0.95, 0.69, 0.67, 0.81, 0.83, respectively (p < 0.05, Figure 2). Among these parameters, ADC and T2 Star have produced best performances, while the difference of QSM values did not reach statistical significance (p >0.05). NIHSS score on admission was negatively correlated with the rADC (R=0.-0.50, p=0.02, Figure 3), but other quantitative ratios have no correlation with NIHSS score (p >0.05).Discussion
One major thrust in radiology today is image standardization with a focus on rapidly acquired quantitative multi-contrast information. This is critical for multi-center trials, for the collection of big data and for the use of artificial intelligence in evaluating the data3. MTP offers multiple sets of qualitative images and parametric maps with high SNR, quantitative accuracy, and acquisition/reconstruction efficiency. SWI and QSM have great application value in the diagnosis of cerebral micro hemorrhage4, however, these approaches are relatively time-consuming. T2 Map has been assessed in acute stroke in a previous study focused on ischemic lesion with a known time of symptom onset5. This study also confirmed that T2 Map can effectively distinguish infarction areas and is very sensitive to brain edema. MTP is capable of achieving a better balanced performance on imaging efficiency, resolution and SNR, these advantages are very useful for patients with acute cerebral infarction.Conclusion
The application of MTP synthetic sequence can shorten the examination time of patients and obtain routine and quantitative MRI images. MTP synthetic sequence can effectively distinguish infarcted brain tissue from normal tissue with a good diagnostic performance.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Feske SK. Ischemic Stroke. Am J Med. 2021 Dec;134(12):1457-1464. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2021.07.027. Epub 2021 Aug 27. PMID: 34454905.
2. Ye Y, Lyu J, Hu Y, et al. MULTI-parametric MR imaging with fLEXible design (MULTIPLEX). Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2021
3. Yongsheng, Chen, Saifeng, et al. STrategically Acquired Gradient Echo (STAGE) imaging, part I: Creating enhanced T1 contrast and standardized susceptibility weighted imaging and quantitative susceptibility mapping[J]. Magnetic resonance imaging: An International journal of basic research and clinical applications, 2018, 46:130-139.
4. Wicaksono KP, Fushimi Y, Nakajima S, Yokota Y, Oshima S, Otani S, Sakurama A, Shima A, Sawamoto N, Okada T, Nakamoto Y. Two-Minute Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping From Three-Dimensional Echo-Planar Imaging: Accuracy, Reliability, and Detection Performance in Patients With Cerebral Microbleeds. Invest Radiol. 2021 Feb 1;56(2):69-77.
5. Siemonsen S, Mouridsen K, Holst B et al (2009) Quantitative t2 values predict time from symptom onset in acute stroke patients. Stroke 40:1612–1616
Figures