2087
Correlation between magnetic resonance perfusion and Ki-67 expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma1Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2GE Healthcare, MR Research China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Sparse & Low-Rank Models, Cancer
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a common malignancy in Southeast Asia. In this study, we explore the correlation between the quantitative parameters derived from dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance (DCE-MRI) of NPC with Ki-67 index. Results showed that the Ktrans mean was positively correlated with Ki-67. The Ktrans mean value was significantly higher in cases with a high Ki-67 status than in those with a low Ki-67 status (AUC 0.8519), and the cutoff value, sensitivity, and specificity was 0.479, 77.78%, and 100%, respectively, suggesting the Ktrans parameter of DCE-MRI has the most utility in distinguishing between high and low Ki-67 levels.Purpose
To explore the correlation between the quantitative parameters derived from dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance (DCE-MRI) of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) with Ki-67 index.Introduction
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a common malignancy in Southeast Asia, especially in Southern China. NPC is treated primarily by intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) with or without chemotherapy. Drug resistance, local recurrence, and distant metastasis remain major problems predicting poor survival in patients with radiotherapy-insensitive NPC. The cell proliferation has an important impact on the response to radiotherapy and chemotherapy, and it is an important indicator of tumor efficacy. Nuclear Ki-67 protein is associated with cell proliferative activity, which may be an indicator of tumor aggressiveness. The high expression of Ki-67 contributes to the radio resistance of patients with locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma and is an indicator of poor prognosis. [1]Methods
Twenty-four cases with an initial diagnosis of NPC confirmed by pathology were collected in the study. All cases were assessed by immunohistochemistry with Ki-67 index and performed MRI examination on a GE Signa HDxt 3.0T MR system with an 8-channel head & neck phased array coil, while LAVA-Flex sequence was used for DCE-MRI sacnning. Two radiologists independently measured the average value of Reflux rate (Kep), volume transfer constant (Ktrans) and volume fraction of the extravascular extracellular matrix (Ve). The ROIs were drawn to cover as much parenchyma of the mass as possible. The correlation between quantitative parameters and Ki-67 index were analyzed by Pearson's rank coefficient analysis. According to the Ki-67 index, the patients were divided into two groups: high (≥50%) and low (<50%). Independent samples T test was then used to compare the differences in quantitative parameters between the high and low Ki-67 groups. [1-5]Results
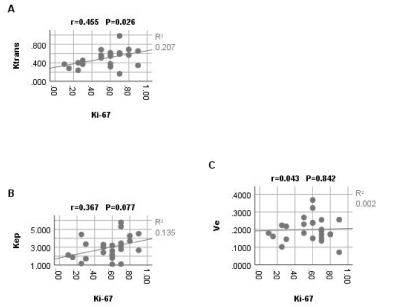
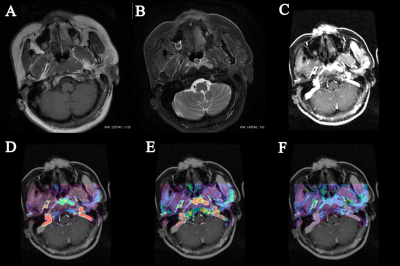
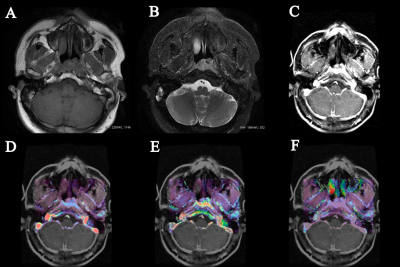
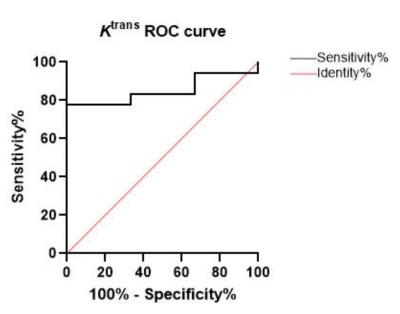
The Ki-67 values ranged from 10% to 90%, with an average of 56.04%. The Ktrans mean was positively correlated with Ki-67, and the correlation coefficients r was 0.455 (p=0.026; Figure 2A). Kep mean and Ve mean were not significantly correlated with Ki-67 (p >0.05; Figure 2B.C) (Table 1.a). Using a 50% cutoff, 18 tumors (75%) were categorized as high Ki-67, and the remaining 6 (25%) were categorized as low Ki-67. The Ktrans mean value was significantly higher in cases with a high Ki-67 status than in those with a low Ki-67 status (p=0.013) (Figures 3,4). Contrastingly, there was no significant difference in Kep and Ve between the 2 groups (Table 1.b) . The area under the curve (AUC) value of Ktrans mean is 0.8519, and the cutoff value, sensitivity, and specificity was 0.479, 77.78%, and 100%, respectively (Figure 5).Conclusion
The Ktrans parameter of DCE-MRI has the most utility in distinguishing between high and low Ki-67 levels, which can better evaluate the degree of tumor proliferation, the higher the Ktrans the faster the tumor proliferation.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1.Huang W, Zhang Q, Wu G, et al. DCE-MRI quantitative transport mapping for noninvasively detecting hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha, epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression, and Ki-67 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Radiother Oncol, 2021. 164: p. 146-154.
2.Jansen J F, Carlson D L, Lu Y, et al. Correlation of a priori DCE-MRI and (1)H-MRS data with molecular markers in neck nodal metastases: Initial analysis. Oral Oncol, 2012. 48(8): p. 717-22.
3.Surov A, Meyer H J, Gawlitza M, et al. Correlations Between DCE MRI and Histopathological Parameters in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Transl Oncol, 2017. 10(1): p. 17-21.
4.Shi S, Cao X, Gu M, et al. Upregulated Expression of SOX4 Is Associated with Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Dis Markers, 2015. 2015: p. 658141.
5.Huang Z, Xu X, Meng X, et al. Correlations between ADC values and molecular markers of Ki-67 and HIF-1alpha in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Radiol, 2015. 84(12): p. 2464-9.
Figures

Table 1.a Correlations between quantitative MR parameters (Ktrans, Kep, and Ve) and Ki-67 labeling index in NPC
Table 1.b Comparison of Ktrans, Kep, and Ve values of NPC with low and high Ki-67 statuses (mean ± SD)