2074
Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging: an alternative method to differentiate the prostate diseases1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Clinical and Technical Support, Philips Healthcare, Shenzhen, China, 3Clinical and Technical Support, Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Prostate, Prostate
Differentiation of prostate hyperplasia, prostatitis and prostate cancerremains challenge using conventional MR techniques, especially for prostatitis and prostate cancer. This study evaluates the value of Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging to differentiate these diseases. Results of this study indicate that ADC value has no significant difference, but Fraction of Fast ADC-Mono and Fraction of Fast ADC-Bi shows significant difference between prostate hyperplasia vs prostate cancer. Slow ADC-Bi values shows difference between prostatitis vs prostate cancer. In summary, IVIM combined with different fitting scheme is potentially a promising and valuable method for differentiation of prostate hyperplasia, prostatitis and prostate cancer.Synopsis
Differentiation of prostate hyperplasia, prostatitis and prostate cancerremains challenge using conventional MR techniques, especially for prostatitis and prostate cancer. This study evaluates the value of Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging to differentiate these diseases. Results of this study indicate that ADC value has no significant difference, but Fraction of Fast ADC-Mono and Fraction of Fast ADC-Bi shows significant difference between prostate hyperplasia vs prostate cancer. Slow ADC-Bi values shows difference between prostatitis vs prostate cancer. In summary, IVIM combined with different fitting scheme is potentially a promising and valuable method for differentiation of prostate hyperplasia, prostatitis and prostate cancer.Summary of main findings
We investigated value of IVIM parameters from different scheme in differentiating prostate diseases, it showed that IVIM with the combination of different fitting scheme could be used for better differentiate and diagnose prostate hyperplasia, prostatitis and prostate cancer.Introduction
Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging techniquewas first introducedby Le Bihan et al. in 1986[1]. It can be used to separatewater molecule diffusion (D) component by the microscopic movement of molecules in voxels, including the diffusion of water molecules inside and outside the cell and microvascular perfusion or pseudo‐diffusion (D*) by the microcirculation perfusion of blood. IVIM has been investigated in diseases of many system[2-3], including the application of prostate diseases [4-5]. However, it remains challenge for the differentiation of prostate hyperplasia, prostatitis and prostate cancer using conventional MR techniques, even using IVIM, especially for prostatitis and prostate cancer occurred in the peripheral zone. This study is to investigate the value of different IVIM fitting schemes using Mono-exponential, Bi-exponential and Tri-exponential in the differentiation of benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostatitis and prostate cancer.Materials and Methods
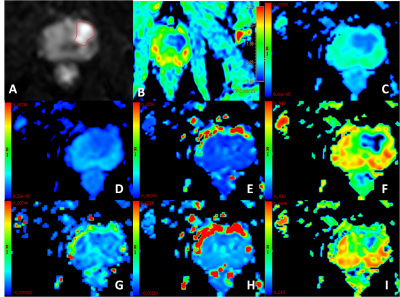
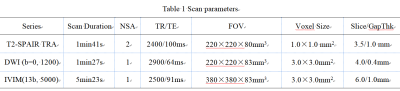
This study has been approved by the local IRB.87 patients with 30prostatic hyperplasia (Group A), 15prostatitis(Group B), 42prostate cancer (Group C)from April 2019 to August were included for retrospective analysis. MRI was performed using an 3.0T MR scanner (IngeniaCX, Philips Healthcare, the Netherlands), using 16-channel body coils. The protocols contain the routine T2WI SPAIR, diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) (b values = 0, 20, 50, 100, 150, 200, 400, 800, 1200, 2000, 3000, 4000, 5000). Detailed parameters were listed in Table 1.Results and Discussion
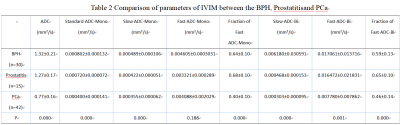
The consistency of the data obtained by the two observers was good.ADC value is statistical difference between prostate hyperplasia vs prostate cancer and prostatitis vs prostate cancer. As Table2 showed, Standard ADC-Mono, Slow ADC-Mono, Fraction of Fast ADC-Mono, Standard ADC-Bi, Slow ADC-Bi and Fraction of Fast ADC-Bi have statistical difference (P<0.05).Standard ADC-Mono and Slow ADC-Mono has statistical difference when compared these 3 groups one to one(P<0.05). Fraction of Fast ADC-Mono and Fraction of Fast ADC-Bihave statistical difference between group A vs group B and group B vs group C(P<0.05).Slow ADC-Bi has statistical difference between group B and group C(P<0.05).Fast ADC-Bi has statistical difference between group A and group C (P<0.05). The values of Standard ADC-Mono and Slow ADC-Mono show a decreasing trend in prostate hyperplasia, prostatitis, and prostate cancer. This may be due to the extracellular space is reduced because of cell edema in prostatitis, the diffusion of water molecules is limited. For prostate cancer, cancer cells proliferate significantly, they are tightly arranged, and the diffusion of water molecules is also limited. The parameters of the microcirculation perfusion (Fraction of Fast ADC-Mono, Fraction of Fast ADC-Bi) are lower in prostate cancer than in benign prostate lesions (prostatic hyperplasia and prostatitis). This may be caused by increasing of permeability for blood vessels along with the progression of prostate cancer, and the interstitial hydraulic pressure increases beyond the critical value. IVIM using different fitting algorithm is potentially a promising and valuable method for better differentiation of prostate hyperplasia, prostatitis and prostate cancer.Conclusion
This study evaluates the value of Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging to differentiate these diseases. Results of this study indicate that ADC value has no significant difference, but Fraction of Fast ADC-Mono and Fraction of Fast ADC-Bi shows significant differencebetween prostate hyperplasia vs prostate cancer. Slow ADC-Bi values showsdifferencebetween prostatitis vs prostate cancer. In Summary, IVIM combined with different fitting scheme has better performance than DWI in the diagnosis of prostate diseases.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, et al. MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology, 1986, 161(2): 401-407.
2.GuangmingZhu, Jeremy JHeit, Blake WMartin, et al. Optimized Combination of b-values for IVIM Perfusion Imaging in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients. Clinical neuroradiology, 2020, 30(3):535-544.
3. Andreas JulianRiexinger, JanMartin, SusanneRauh, et al. On the Field Strength Dependence of Bi- and Triexponential Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) Parameters in the Liver. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging: JMRI, 2019, 50(6):1883-1892.
4. YingLiu, XuanWang, YadongCui, et al. Comparative Study of Monoexponential, Intravoxel Incoherent Motion, Kurtosis, and IVIM-Kurtosis Models for the Diagnosis and Aggressiveness Assessment of Prostate Cancer.[J]. Frontiers in oncology, 2020, 10:1763.
5. MuratBeyhan, RecepSade, ErdemKoc, et al. The evaluation of prostate lesions with IVIM DWI and MR perfusion parameters at 3T MRI. La Radiologia medica, 2019, 124(2):87-93.
Figures