2070
Distinguishing prostate cancer from prostate hyperplasia nodules using histograms based on amide proton transfer MRI and DWI
You Yun1, Zhiwei Shen2, and Xuejun Chen1
1The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University & Henan Cancer Hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
1The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University & Henan Cancer Hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Prostate, CEST & MT
The diagnostic value of histograms based on 3D APT MRI and ADC in the central glandular region for the differentiation of prostate cancer and prostate hyperplastic nodules was evaluated in this study. The results showed that the 3D APT MRI and ADC histograms had better diagnostic efficacy in the central glandular region for the differentiation of prostate cancer and prostate hyperplastic nodules, but the diagnostic efficacy of the 3D APT.Introduction
Prostate cancer is the most frequent type of cancer in males [1]. Despite the fact that the recent release of PI-RADS version 2.1 has increased the sensitivity of prostate cancer detection, diagnostic consistency is low for inexperienced young physicians [2, 3]. Prostate cancer in the central glandular area, in particular, is difficult to distinguish from hyperplastic nodules with mainly mesenchymal hyperplasia.Diffusion-weighted imaging has been widely employed in the identification, localisation, and invasiveness of prostate cancer with major therapeutic implications. However, ADC levels for stromal hyperplasia and central zone prostate cancer have been shown to overlap significantly, making differentiated diagnosis challenging.
Amide proton transfer weighted (APTw) MRI is a type of chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging that evaluates the chemical transfer properties of amide protons with a chemical shift of 3.5 ppm, which reflects the concentration of mobile macromolecules. Previous research has demonstrated that APTw can assess tumor histological grade.
Previous research utilized the average and median to define the biological characteristics of tumors, which were inaccurate. For the differential detection of prostate cancer, whole-tumor histograms outperforms ROI-based approaches. As a result, the histogram approach was utilized in this study to assess the efficiency of amide proton transfer weighted MRI and diffusion weighted imaging in discriminating prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia nodules in the prostate's core glandular area.
Method
This research included sixteen patients with central glandular prostate cancer and six patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. All patients were pathologically confirmed and previously untreated, had lesions bigger than 5 mm in diameter, and had multiparametric MRI, including APTw MRI and DWI, within 2 weeks after puncture.All patients had conventional MRIs and 3D APT prostate scans in a 3.0T MR scanner (Ingenia CX, Philips healthcare) with a 32-channel body phased coil. Sagittal T2WI and axial T1WI, T2WI, frequency inversion recovery fat suppression T2WI, and DWI included the routine scan sequences. For DWI sequence, b = 0, 1000 s/mm2, TR = 3500ms, TE = 55ms, matrix = 104x125, layer thickness = 3mm. TR 6294ms TE 5.9 ms matrix 116x177, layer thickness 6 mm, scan length 5 min40s were employed in 3D DIXON-TSE APT sequence.
Image post-processing and histogram parameter computation were performed in MATLAB program. Two imaging physicians (each with four and ten years of diagnostic experience) interpreted the conventional MRI precisely according to PI-RADS version 2.1, identified the highest PI-RADS score lesion inside the puncture region as the target lesion, and delineated it layer by layer. The ROI was drawn on T2WI and then aligned to the 3D APT and ADC images to make the ROI range similar for both 3D APT and ADC. Post-processing provided the 5% bit, 25% bit, 50% bit, 75% bit, 95% bit, kurtosis, skewness, mean, maximum, and lowest values of 3D APT and ADC images, respectively. The inter-group variations in the aboved parameters in prostate cancer and BPH nodules in the central glandular area were analyzed. The diagnostic effectiveness of each parameter of 3D APT and ADC images was evaluated using the ROC curve.
Results
The 5th (p = 0.017), 25th (p = 0.001), 50th (p = 0.020), 75th (p 0.017), kurtosis (p 0.023), skewness (p 0.008), and mean (p 0.001) of prostate cancer in the central gland area were significantly greater than those of benign prostatic hyperplasia nodules in the 3D APT histogram parameters. The 5th (p = 0.018), 25th (p = 0.021), mean value (P = 0.038), and minimum value (p = 0.008) of prostate cancer in the central gland area were smaller than those of benign prostatic hyperplasia nodules in the ADC histogram parameters, but there was significant overlap between them, as shown in Table 1.Among the 3D APT histogram metrics, 5th, 25th, 50th, skewness, and mean have the best diagnostic effectiveness. AUCs were 0.958, 0.958, 0.917, 0.875, and 0.922, in that order. 75 percentile and kurtosis AUCs were 0.792 and 0.667, respectively. The diagnostic power of the 5th and 25th percentiles was greater than kurtosis (p = 0.022).The AUC of 5th, 25th, mean, and minimum of the ADC histogram were 0. 833, 0.875, 0.792, and 0. 875, respectively, and there was no difference in the diagnostic performance of other parameter. The diagnostic efficiency of 5th, 25th, and mean ADC histogram is slightly higher than that of 3D APT histogram, but there is no significant difference.
Conclusion
The histograms based on 3D APT MRI and ADC are useful in differentiating prostate cancer and prostatic hyperplasia nodules in the central gland region, with 3D APT MRI having slightly greater diagnostic effectiveness.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A: Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 2021, 71(1):7-33.
2. Beetz NL, Haas M, Baur A, Konietschke F, Roy A, Hamm CA, Rudolph MM, Shnayien S, Hamm B, Cash H et al: Inter-Reader Variability Using PI-RADS v2 Versus PI-RADS v2.1: Most New Disagreement Stems from Scores 1 and 2. Rofo 2022, 194(8):852-861.
3. Lee CH, Vellayappan B, Tan CH: Comparison of diagnostic performance and inter-reader agreement between PI-RADS v2.1 and PI-RADS v2: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Radiol 2022, 95(1131):20210509.
Figures
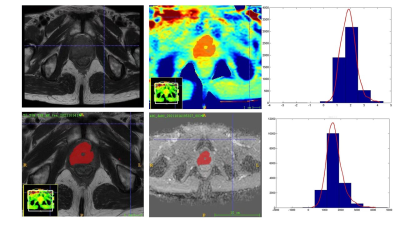
Figure 1: Male patient, 71 years old; T2WI picture showing a tumor in the central glandular area of the prostate, PI-RADS score of 5, APT and ADC histograms, and puncture pathology confirming prostate cancer.
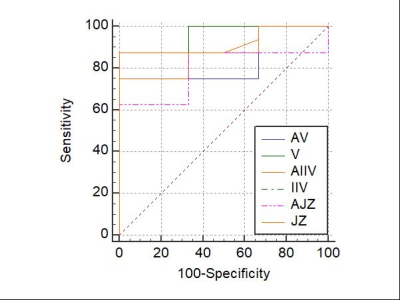
Comparison of the area under the histograms of the 3D APT quantitative parameters at 5th (V), 25th (IIV), and mean (JZ) with ADC quantitative parameters at 5th (AV), 25th (AIIV), and mean (JZ) (AJZ)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/2070