2065
The value of the combination of Intravoxel incoherent motion and TAF11 in predicting positive margins of radical prostatectomy1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Prostate, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques
Positive surgical margins (PSMs) mean incomplete tumor excision which related with prostate cancer-specific mortality and may lead to additional treatments. As a new technique, Intravoxel incoherent motion can simultaneously demonstrate information about diffusion and perfusion. The result of this study indicate the combination of ADC, D, PPC and TAF11 can be used as a potential method in PSMs of radical prostatectomy.Introduction
Prostate cancer (PCa) is one of the most common cancer in male, which is account for 27% of all incident cancer cases in men in 2022 and the proportion of prostate cancers diagnosed at a distance increased from 3.9 % to 8.2 % over the past decade1. Treatment of PCa has changed over time and now radical prostatectomy (RP) become an important method. Nevertheless, one of the challenges remains the occurrence of positive surgical margins (PSMs), which is considered as one of the most significant indexes for biochemical recurrence (BCR) and low prostate cancer-specific survival rates2,3. Recently, mul-tiparametric resonance imaging (mpMRI) of the prostate has been developed4. Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) is a diffusion medal which simultaneously estimate the pure molecular water diffusion and microcirculation of blood in capillaries5. TATA-binding protein associated factor 11 (TAF11) is a key subunit of Transcription factor IID (TFⅡD) which plays an important role in RNA polymerase II transcription initiation6. In this study, we investigated the value of combination of IVIM and TAF11 in predicting PSMs of RP and hope to find an available and convenient method.Methods
Forty-three PCa patients from January 2016 to December 2021 who accordant with all research conditions and recruited IVIM sequences that received 3.0T MR scans and RP were included in our study. IVIM with b values of 0, 20, 50, 100, 150, 200, 400, 800, 1200, 2000, and 3000 s/mm2 was performed with a single-shot echo planar (SS-EPI) sequence. The scanning parameters were as follows: TR, 2800 milliseconds; TE, 90 milliseconds; FOV, 35×31 cm2; Voxel, 1.4×1.4 mm2; Matrix, 40×32; Slice/thickness, 7.0/1.0 mm. The scan duration is 2 minutes and 31 seconds. The following parameters were obtained using GE Functool post-processing software: ADC, D, D*, f. ImageJ 1.52V was used to test positive area of protein immunized reaction product. The interclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was used to evaluate consistency between two measurements for each parameter. Mann-Whitney U test and independent sample T test were used to analyze the differences between the two groups. The efficiency of diagnosing PSMs was analyzed by receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Significance level of all ROC analyses was tested by DeLong test. The correlation between parameters in IVIM and TAF11 was analyzed by Spearman correlation test.Results
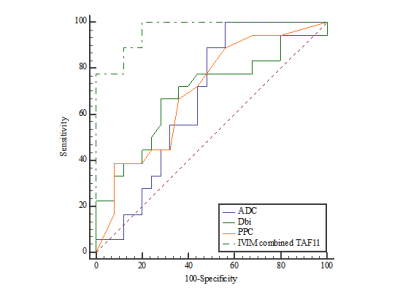
Age in patients (18 patients with PSMs and 25 patients with NSMs) ranged from 56 to 81 years, mean age for PSMs group was 72±7 years, and for NSMs group was 72±6 year, which were similar to previous research with the average age that was 67.6±6.6 years in PSMs group and 67.3±5.9 in NSMs group7. Measurement consistency between two measurements for each parameter in PSMs group and NSMs group was excellent (ICC>0.75, Table 1). The ADC and D of PSMs group were significantly lower than those of NSMs group (P≤0.05,Table 2), PPC and TAF11 were significantly higher than those of NSMs group (P≤0.05,Table 2). The ROC curve were showed in Figure 1. According to Delong test, the combination of ADC, D, PPC and TAF11 with the area under the curves (AUC) of 0.964 was statistically different than other parameters in diagnosing PSMs (P≤0.05). The Spearman correlation test shows that ADC and D had a negative correlation with TAF11 separately (P<0.05,Table 3).Discussion
In our study, we analyzed the value of IVIM for predicting PSMs. We found some remarkable points form the results. Firstly, ADC and D of PSMs group were lower than those of NSMs group. The possible reason for this phenomenon is that IVIM can reflect random micro motion of intracellular and extracellular water molecules and blood circulation8. As the diffusion coefficient, ADC and D were associated with state of extracellular space and cell membrane intact9. Secondly, TAF11 can be used as a risk factor to predict PSMs and it has higher expression in PSMs group. That may because that TAF11 has a close connection with the DNA binding surface of TATA-binding protein (TBP) and it is also essential for Super-enhancers (SEs) which play a key role in tumorigenesis and development10,11. Finally, the combination of IVIM and TAF11 has higher diagnosis efficiency in diagnosing PSMs. The ideal is that IVIM can provide molecular motion information of the lesion while TAF11 can provide information at the gene level. Joint diagnosis was a comprehensive integration of these messages. Furthermore, a negative correlation existed between IVIM and TAF11 which illustrated that IVIM may can reflect the expression variation of TAF11 but the result was needed to be verified in further research. As described, the combination of IVIM and TAF11 can be a hopeful method to predict PSMs.Conclusion
IVIM and TAF11 had the potentiality to predict PSMs after RP and the combined diagnosis was more meaningful in it.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022 Jan;72(1):7-33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21708. Epub 2022 Jan 12. PMID: 35020204.
2. Zhang B, Zhou J, Wu S, Guo M, Zhang Y, Liu R. The impact of surgical margin status on prostate cancer-specific mortality after radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Transl Oncol. 2020 Nov;22(11):2087-2096. doi: 10.1007/s12094-020-02358-y. Epub 2020 May 14. PMID: 32410119.
3. Celik S, Eker A, Bozkurt İH, Bolat D, Basmacı İ, Şefik E, Değirmenci T, Günlüsoy B. Factors affecting biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy in patients with positive and negative surgical margin. Prostate Int. 2020 Dec;8(4):178-184. doi: 10.1016/j.prnil.2020.08.003. Epub 2020 Sep 17. PMID: 33425796; PMCID: PMC7767941.
4. Nyk Ł, Tayara O, Ząbkowski T, Kryst P, Andrychowicz A, Malewski W. The role of mpMRI in qualification of patients with ISUP 1 prostate cancer on biopsy to radical prostatectomy. BMC Urol. 2021 May 18;21(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12894-021-00850-3. PMID: 34006281; PMCID: PMC8130114.
5. Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin ML, Vignaud J, Laval-Jeantet M. Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology. 1988 Aug;168(2):497-505.
6. Göös H, Kinnunen M, Salokas K, Tan Z, Liu X, Yadav L, Zhang Q, Wei GH, Varjosalo M. Human transcription factor protein interaction networks. Nat Commun. 2022 Feb 9;13(1):766. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28341-5. PMID: 35140242; PMCID: PMC8828895.
7. Li YT, Cercueil JP, Yuan J, Chen W, Loffroy R, Wáng YX. Liver intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) magnetic resonance imaging: a comprehensive review of published data on normal values and applications for fibrosis and tumor evaluation. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2017 Feb;7(1):59-78. doi: 10.21037/qims.2017.02.03. PMID: 28275560; PMCID: PMC5337188.
8. Li YT, Cercueil JP, Yuan J, Chen W, Loffroy R, Wáng YX. Liver intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) magnetic resonance imaging: a comprehensive review of published data on normal values and applications for fibrosis and tumor evaluation. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2017 Feb;7(1):59-78. doi: 10.21037/qims.2017.02.03. PMID: 28275560; PMCID: PMC5337188.
9. Bao J, Wang X, Hu C, Hou J, Dong F, Guo L. Differentiation of prostate cancer lesions in the Transition Zone by diffusion-weighted MRI. Eur J Radiol Open. 2017 Sep 29;4:123-128. doi: 10.1016/j.ejro.2017.08.003. PMID: 29034282; PMCID: PMC5633348.
10. Gupta K, Watson AA, Baptista T, Scheer E, Chambers AL, Koehler C, Zou J, Obong-Ebong I, Kandiah E, Temblador A, Round A, Forest E, Man P, Bieniossek C, Laue ED, Lemke EA, Rappsilber J, Robinson CV, Devys D, Tora L, Berger I. Architecture of TAF11/TAF13/TBP complex suggests novel regulation properties of general transcription factor TFIID. Elife. 2017 Nov 7;6:e30395. doi: 10.7554/eLife.30395. PMID: 29111974; PMCID: PMC5690282.
11. Wang C, Jiang S, Zhang L, Li D, Liang J, Narita Y, Hou I, Zhong Q, Gewurz BE, Teng M, Zhao B. TAF Family Proteins and MEF2C Are Essential for Epstein-Barr Virus Super-Enhancer Activity. J Virol. 2019 Jul 30;93(16):e00513-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00513-19. PMID: 31167905; PMCID: PMC6675876.
Figures