Rong Xu1, Wei Huang2, Lini Liu1, Xiaoyong zhang3, and Yingkun Guo1
1West China Second University Hospital, Chengdu, China, 2West China Second Universityy Hospital, Chengdu, China, 3Clinical Science, Philips Healthcare, Chengdu, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Cardiomyopathy, Cancer
The
stage of chemotherapy in children with ALL is a long process, and the
myocardial damage caused by chemotherapy is still unknown. The different chemotherapy
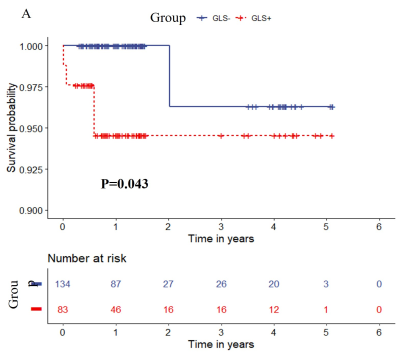
stages may have different degrees of myocardial damage. In this study, cardiac
magnetic resonance was used to evaluate myocardial strain in ALL patients at
different stages of treatment, and it was found that myocardial strain reduction was more
pronounced in the early stages of treatment, and that global strain was a risk
factor for adverse clinical outcomes.
Acknowledgements
NAReferences
[1] Steliarova-Foucher E, Colombet M, Ries LAG, et al.
International incidence of childhood cancer, 2001-10: a population-based
registry study. Lancet Oncol, 2017,18(6):719-31.
[2] Mehta
LS, Watson KE, Barac A, et al. Cardiovascular disease and breast cancer: where
these entities intersect: A scientific statement from the American heart
association. Circulation, 2018, 137(8): e30-e66.
[3]Søndergaard
MMA, Nordsmark M, Nielsen KM, Poulsen SH. Cardiovascular burden and adverse
events in patients with esophageal cancer treated with chemoradiation for
curative intent. JACC CardioOncol, 2021, 3(5):711-721.
[4]Henriksen
PA. Anthracycline cardiotoxicity: an update on mechanisms, monitoring and
prevention. Heart, 2018, 104(12): 971-77.