1969
Multi-Parametric MRI-based radiomics for noninvasively predicting Tert genotype in Oligodendroglomas
Jun Zhao1, Tiejun Gan2, Xiaoai Ke1, Wanjun Hu2, Qing Zhou1, Jing Zhang2, and Junlin Zhou1
1Department of Radiology, Lanzhou University Second Hospital, Lanzhou, China, 2Department of Magnetic Resonance, Lanzhou University Second Hospital, Lanzhou, China
1Department of Radiology, Lanzhou University Second Hospital, Lanzhou, China, 2Department of Magnetic Resonance, Lanzhou University Second Hospital, Lanzhou, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Tumors, Radiomics, Multimodal,Quantitative Imaging
In this study, radiomic based predictive models using MRI can non-invasively assess Tert genotype of Oligodendrogliomas(ODs).Compared With histopathological assessment,radiomic based predictive models has its unique advantages in assessing Tert genotype of ODs. such as noninvasive, more comprehensive information about tumor heterogeneity and repeatable.Furthermore,radiomic based predictive models can clearly and directly show Tert genotype of ODs.Therefore, it is a potential alternative to invasive biopsy.Introduction
Oligodendrogliomas(ODs)are diffuse infiltrative neoplasms that generally include low- and inter mediate-grade gliomas (World Health Organization [WHO] grade 2 or 3)1.In almost all patients, despite an initial slow growth rate, the outcome is ultimately fatal.These tumors follow heterogeneous clinical outcomes-most patients in ODs relapse after treatment within months and even progress to glioblastoma (WHO grade 4), while others remain indolent for years2.Treatment planning, response monitoring, and overall prognosis assessment for ODs patients depend heavily on the genetic and epigenetic factors in each individual tumor.The accurate evaluation of the molecular alternations of ODs and their prognostic value,has always been a major clinical problem to be solved urgently.However, Histopathological assessment is invasive and has sampling errors, and its diagnostic value is limited.radiomic based predictive models can noninvasively provide more comprehensive information about tumor heterogeneity than focal tissue samples, however, such information is behind the images that beyond visual perception3.This study mainly explores the advantages of in noninvasively evaluating Tert genotype in ODs using quantitative MRI-based radiomics.Methods
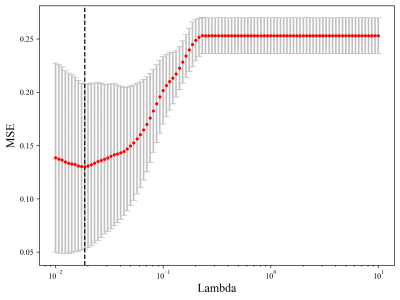
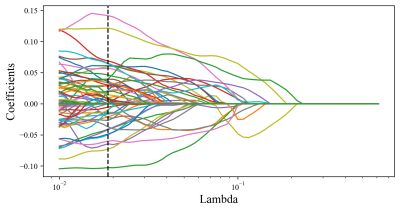
135 patients who were Pathologically diagnosed with ODs in Lanzhou University Second hospital from March 2016 to April 2022 were retrospectively enrolled.All patients underwent MRI examinations within one week prior to surgery.MR images were acquired in the routine clinical workup using one 1.5 T MR Area (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany)as well as three 3.0TMR systems, including SIGNA Premier(GE Healthcare,Milwaukee, WI,USA), Verio(Siemens Healthcare,Erlangen,Germany) and IngeniaCX(Philips Medical Systems, Best, Netherlands),equipped with 32-channel head coil.The axial imaging sequences included T1WI, cT1WI and T2WI.All the patients were randomly divided into the training and the validation cohorts by computer sampling at a ratio of 7 : 3.The registered MR images were resampled to a uniform voxel size of 1×1×1 mm across all patients for radiomics construction using Elastix Registration in 3DSlicer.The three-dimensional segmentation was conducted by an open-source software ITK-SNAP (www.itk-snap.org). The region of interest (ROI) of tumor region including contrast enhancing portion,non-enhancing central tumor component and the edema portion;The image segmentation was performed by a neuroradiologist (with 5 years of experience in neuro-radiology) and then validated by an experienced neuroradiologist (with 10 years of experience in neuro-radiology).Discrepancies between the two neuroradiologists were resolved by consensus. Neuroradiologists were blinded to the patients′clinical and genetic information. Presurgical MRIs of 135 patients with ODs extracted radiomic features were extracted by using Pyradiomics 2.0.0). Totally 1874 radiomics features were, respectively, extracted from multi-Parametric MRI sequence (T1WI, T2WI, and Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging(cT1WI)) using ensemble learning. Firstly, an optimal radiomics signature (Radscore) was established based on LASSO regression. Secondly, univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed to investigate important potential variables as predictors of Tert genotype. Besides, multiparameter models were established and evaluated. Eventually, an optimal model was visualized as radiomics nomogram for clinical evaluations.Results
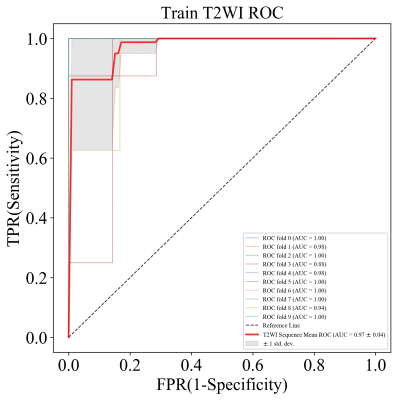
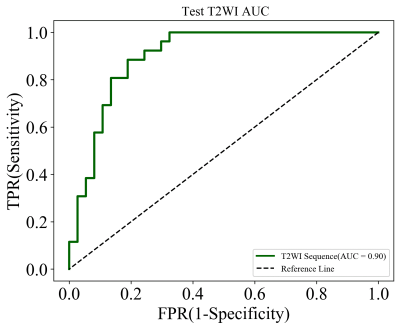
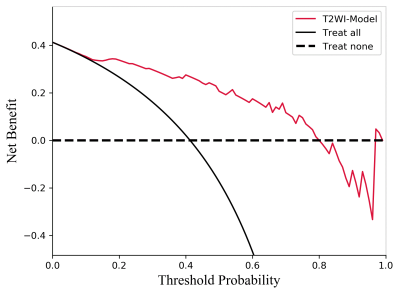
The results showed that the image model incorporating radiomic signatures from cT1WI achieved mean AUC of 0.95±0.04 in taining cohorts and 0.87 in validation cohorts for predicting TERT genotype respectively. the image model incorporating radiomic signatures from T1WI achieved mean AUC of 0.96±0.05 in taining cohorts and 0.84 in validation cohorts for predicting TERT genotype respectively.the image model incorporating radiomic signatures from T2WI achieved mean AUC of 0.97±0.04 in taining cohorts and 0.90 in validation cohorts for predicting TERT genotype respectively. T2WI-based radiomic signature yielded favorable performance in predicting TERT genotype (AUC =0.90) in validation cohorts.Discussion
Radiogenomics was a new field for studying the relationship between radiological features and genomic data, which explored the relationship between radiological features and gene phenotypes by extracting quantitative information on a large number of radiological data features. As Gillies states4, “radiomics: images are data, not just pictures,”radiomics analysis will play an increasingly important role in clinical work.In this study, we found that the multi-Parametric MRI-based radiomics method can well predict TERT genotype in ODs.T2WI-based radiomic signature yielded favorable performance.Conclusion
Multi-Parametric MRI-based radiomics may be useful for noninvasively detecting Tert genotype in ODs regardless of grades. Ensemble learning analysis of MR imaging data predicted TERT genotype with high accuracy.Acknowledgements
This research was partially supported by Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province(Grant No.21JR7RA404);
This research was partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of china(Grant No. 82071872)
References
[1]LOUIS D N, PERRY A, WESSELING P, et al. 2021. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Neuro Oncol [J], 23: 1231-1251.[2]VAN DEN BENT M J, WEFEL J S, SCHIFF D, et al. 2011. Response assessment in neuro-oncology (a report of the RANO group): assessment of outcome in trials of diffuse low-grade gliomas. Lancet Oncol [J], 12: 583-593.
[3]GORE S, CHOUGULE T, JAGTAP J, et al. 2021. A Review of Radiomics and Deep Predictive Modeling in Glioma Characterization. Acad Radiol [J], 28: 1599-1621.
[4]GILLIES R J, KINAHAN P E, HRICAK H 2016. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology [J], 278: 563-577.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/1969