1968
The Value of Multi-parametric MRI-Based Radiomics Model in Predicting the IDH1 Mutation in Glioma1Clinical medicine school of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, China, 2Department of Radiology ,the First Hospital Affiliated to Hainan Medical College, Haikou, China, 3GE Healthcare, Beijing, China, 4Department of Radiology, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Tumors, Radiomics
This study aims to explore the value of multi-parametric MRI-based radiomics model for non-invasively predicting IDH1 mutation in glioma. It was shown that among various single-sequence radiomics models, the contrast-enhanced T1-weighted image radiomics model should be considered as an optimal model in predicting IDH1 mutation, while the combined model based on three sequences could further improve the predicting performance.Summary of Main Findings
Multi-parametric MRI-based radiomics model could non-invasively predict IDH1 mutation in glioma.Synopsis
This study aims to explore the value of multi-parametric MRI-based radiomics model for non-invasively predicting IDH1 mutation in glioma. It was shown that among various single-sequence radiomics models, the contrast-enhanced T1-weighted image radiomics model should be considered as an optimal model in predicting IDH1 mutation, while the combined model based on three sequences could further improve the predicting performance.Introduction
Gliomas are the most common primary malignant tumor in brain, and its various molecular characteristics can lead to extensive biological characteristics and clinical heterogeneity1-3. The importance of tumor molecular characteristics was emphasized on the 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system4, which revealed that the isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutation type patients had a better prognosis than the IDH wild type5, 6. At present, the most commonly used method to assess IDH mutation status is molecular assay after biopsy or surgical resection. However, the biopsy has bias in the tissue taken, which may lead to the deviation of results, and the quality of the tissue may be too poor to complete the molecular detection7. Radiomics is a powerful tool in exploiting more tumor features that cannot be recognized by the image reviewing, which can reflect the heterogeneity of tumor more comprehensive and repeatable1,8. The purpose of the study was to explore the value of Multi-parametric MRI-based radiomics model in predicting IDH1 mutation in glioma non-invasively.Material and Methods
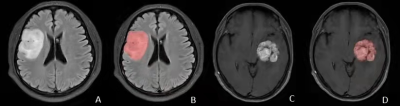
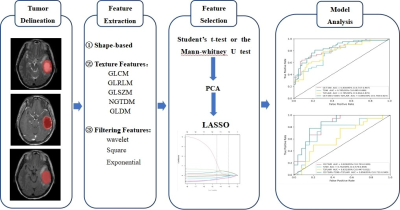
A total of 144 patients with gliomas confirmed by pathology from January 2016 to July 2022 in our hospital were retrospectively included. All patients underwent MR exams on a 3.0T scanner (SIGNATM Excite, GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA) with an 8-channel head coil before surgery. The scan sequences included routine axial T2-weighted imaging (T2WI), T2-weighted fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (T2-FLAIR) and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging (CE-T1WI). The parameters were as follows: FOV = 24 × 24 cm2, slice thickness/gap = 6/1mm, T2WI, TR/TE = 4600/107ms; T2-FLAIR, TR/TE = 7800/140ms; CE-T1WI, TR/TE = 2300/13ms; A total volume of 0.1 mmol/kg of Gd-DTPA was injected intravenously before CE-T1WI scanning. Clinical and MRI imaging features were also collected (Table 1). All patients were randomly divided into training (n=101) and testing (n=43) sets at a 7:3 ratio. ITK-SNAP software was used to delineate the region of interest (ROI) and the radiomics features were extracted by the "Pyradiomics" package in Python3.7 software. ROIs were drawn to cover the core of tumor excluded peritumoral oedema in high-grade glioma and the whole tumor in low-grade glioma (Figure1). For the statistical analysis, firstly the independent Student’s t-test or the Mann-Whitney U test was used to initially screen out the features with statistically significant differences (P < 0.05), then the Pearson correlation analysis and the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) were used to select the optimal feature which is highly correlated with IDH1 mutation status to construct radiomics labels and calculate the radiomic score (RADSCORE). Finally, we used the logistic regression algorithm to construct three models from the T2WI, T2-FLAIR, and CE-T1WI sequences respectively as well as a combined model using them all. The diagnostic performance was evaluated using area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves (AUC), the workflow of this study was in Figure 2.Results
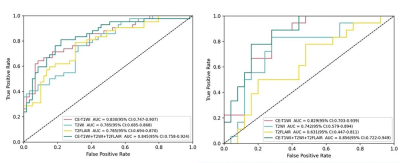
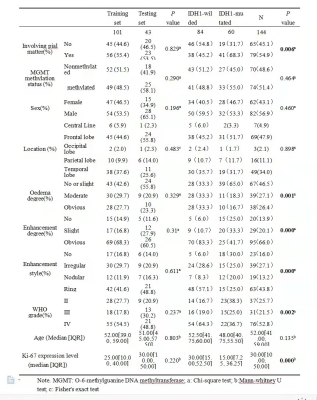
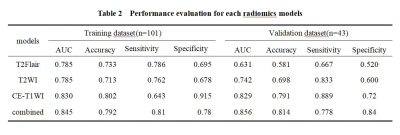
No statistically significant difference was found in the baseline characteristics between the training and testing groups (P > 0.05). There were statistically differences in enhancement degree, oedema degree, enhancement style, Ki-67 expression level and WHO-grade between IDH-mutated and IDH-wild groups (as shown in Table 1). At last, each sequence can extract 1037 radiomic features included first-order statistical features, shape features, gray level co-occurrence matrix, gray level dependence matrix, gray level run length matrix, gray level size zone matrix, neighboring gray tone dependence matrix and filtering features. After feature screening, there are 9, 10, 14, 12 features for T2WI, T2-FLAIR, CE-T1WI, T2WI+T2Flair+CE-T1WI models, respectively. Among single-sequence radiomics models, the diagnostic efficacy of CE-T1WI and T2WI models were better than that of T2-FLAIR model, and the CE-T1WI model had the best prediction performance. Its AUC values in the training and testing groups were 0.824 and 0.822. The diagnostic efficiency of the combined model based on three sequences was better than all the single sequence radiomics models, its AUC values in the training and testing groups were 0.844 and 0.853 (Table 2, Figure 3).Discussion and Conclusion
Our study demonstrated that the CE-T1WI model had the best prediction performance. As the preferred MRI sequence for the diagnosis of brain tumors, CE-T1WI can clearly show the solid and necrosis of tumors. Our study also found that multi-sequence had a better performance than one with single sequence. He et al9 reported that multi sequence model can better predict glioma biomarker status preoperatively, this result was in accordance with us. The reason may be that complementary information among Multi-parametric MRI could provide a more comprehensive understanding of tumor heterogeneity10. To conclusion, multi-parametric MRI-based radiomics model could non-invasively predict IDH1 mutation in glioma, however, the performance of different sequences is different, multiple-sequence based radiomics model could improve the prediction efficiency.Acknowledgements
Thank you very much for reading my contribution in your busy schedule. I wish you good health and all the best.References
1.Brancato V, Cerrone M, Lavitrano M, et al. A systematic review of the current status and quality of radiomics for glioma differential diagnosis. Cancers2022;14(11):2731.
2.Miller KD, Ostrom QT, Kruchko C, et al. Brain and other central nervous system tumor statistics. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians2021;71(5):381-406.
3.Wu Y, Guo Y, Ma J, et al. Research progress of gliomas in machine learning. Cells2021;10(11):3169. 4.Gritsch S, Batchelor TT, Gonzalez Castro LN. Diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic implications of the 2021 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system. Cancer2022;128(1):47-58.
5.Yu J, Shi Z, Lian Y, et al. Non-invasive IDH1 mutation estimation based on a quantitative radiomics approach for grade II glioma. European Radiology2017;27(8):3509-3522.
6.Ding H, Huang Y, Li Z, et al. Prediction of IDH status through MRI features and enlightened reflection on the delineation of target volume in low-grade gliomas. Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment2019; 18:1180675708.
7.Yogananda CGB, Shah BR, Yu FF, et al. A novel fully automated MRI-based deep learning method for classification of IDH mutation status in brain gliomas. Neuro-Oncology2019;22(3):402-411. 8.Fatania K, Mohamud F, Clark A, et al. Intensity standardization of MRI prior to radiomic feature extraction for artificial intelligence research in glioma—a systematic review. European Radiology2022;32(10):7014-7025.
9.He J, Ren J, Niu G, et al. Multi-parametric MR radiomics in brain glioma: models comparation to predict biomarker status. BMC Medical Imaging2022;22(1):137.
10.Deng D, Liao Y, Zhou J, et al. Non-invasive prediction of survival time of midline glioma patients using machine learning on Multi-parametric MRI radiomics features. Frontiers in Neurology2022;13:866274.
Figures