1950
Therapeutic Efficacy of Extracellular Vesicles from 3D Aggregated Adult Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Ischemic Stroke Assessed by MRI at 21.1 T1National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL, United States, 2Chemical & Biomedical Engineering, FAMU-FSU College of Engineering, Tallahassee, FL, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Stroke, Non-Proton, sodium, MCAO
This study evaluates the therapeutic efficacy of transplanted extracellular vesicles (EV) secreted from 3D aggregated human mesenchymal stem cells to treat transient ischemic stroke in a female rat model. The objective is to verify the presence of EV at the lesion and monitor tissue recovery using T2- and diffusion-weighted MRI at 21.1 T.Introduction
Stroke is the third leading cause of death in women, with 20% of women over the age of 55 at risk compare to the ~15% in men1. Hormones such as estrogen and progesterone, which cease after menopause, have been shown to have neuroprotective effects against ischemic stroke. Human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSC) have shown promise as a biotherapeutic for ischemic stroke due to reparative mechanisms that induce an anti-inflammatory response, angiogenesis and neurogenesis via endogenous recruitment2 . As an alternative to direct hMSC injection, extracellular vesicles (EV) derived from hMSC have been shown to have therapeutic potential. EV are membrane enclosed, cell-derived vesicles that cannot independently replicate. In order to increase the therapeutic potential of the EV, the EV are derived from hMSC that have been aggregated as 3D spheroids3. EV generated from aggregates are smaller in size, with higher miRNA expression and upregulation of cytokines and anti-inflammatory factors. Ultra-high field MRI at 21.1 T is able to track the labeled EV using T2*-weighted imaging and provide increased sensitivity to assess lesion recovery using T2- and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI). Previous studies have shown evidence of the establishment of restoration of sodium homeostasis and reduced sodium lesion volume over a period of 7 d4. 3D sodium (23Na) chemical shift imaging (CSI) and relaxation enhanced MR spectroscopy are examined to track re-establishment of sodium homeostasis.Methods
EV Isolation: hMSC are aggregated at passage 4 in ultra-low attachment using a WAVE Bioreactor4. The EV are harvested from aggregates, labeled with 1 mg/mL of ultra-small iron-oxide nanoparticles, and purified for injection using ultracentrifugation.Animal Model: A transient middle cerebral artery occlusion model5 was instituted in female Sprague-Dawley rats for 1 h. Immediately following the occlusion, the animals received the treatment (EV or saline control (n=3)) via intraarterial injection.
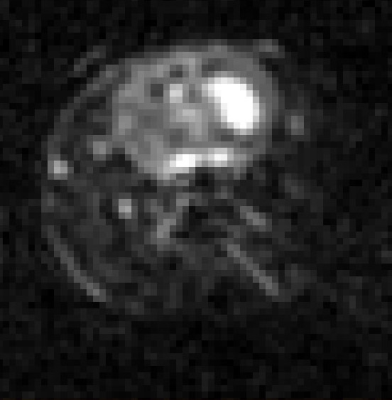
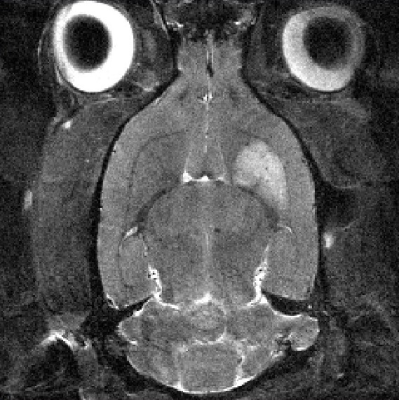
MR Imaging: Data were acquired using the 21.1-T (900-MHz) vertical bore magnet at the NHMFL. In vivo assessment utilized a linear birdcage double-tuned 23Na/1H radio frequency coil on 0, 1, 3, 9 and 21-d post-ischemia to assess tissue recovery and treatment efficacy. Cell administration was confirmed with gradient recalled echo images (50x50-µm in-plane resolution). Lesion volume was evaluated using T2W RARE at a 100x100-µm resolution. Changes in the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) were evaluated using spin-echo EPI DWI acquired at 200x200-µm resolution. 3D 23Na CSI was acquired at 1-mm isotropic resolution. T2W images enabled anatomical reference to the ischemic lesion and contralateral alignment.
Analysis: The 3D 23Na CSI data were reconstructed in MATLAB to a xero-filled 0.5-mm isotropic resolution. The volumetric and signal analysis for the 3D 23Na CSI, T2W and DWI were performed in Amira 3D Visualization Software. A signal threshold generated from the contralateral hemisphere was used to define the ischemic lesion.
Results & Discussion
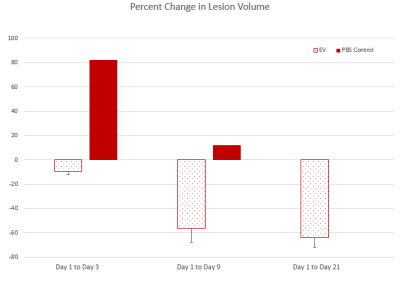
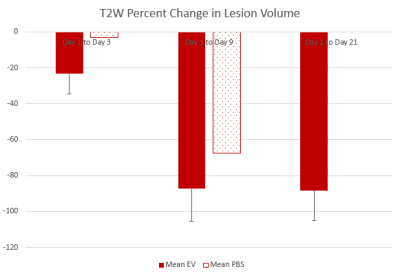
The 3D 23Na CSI data show that lesion volume of the group that received the EV treatment decrease from day 1 to 3, whereas the group that received the saline control treatment had an increase in lesion volume. By day 9, both groups begin to exhibit a decrease in the lesion volume (Figure 1). Similar results can be seen in the T2W group. DWI data shows an increase in the ADC for all groups from day 1 to 3. This would indicate that there is edema or cellular swelling. By day 9, a decrease in ADC is observed.Conclusions
The preliminary results of this study would indicate that the EV treatment could offer significant improvement in ischemic stroke recovery. Further studies are undergoing including relaxation enhanced MR spectroscopy and behavioral studies over a period of 21 days.Acknowledgements
All work has been conducted in accordance with the Florida State University Animal Care and Use Committee. This work was supported by the NIH (RO1-NS102395 awarded to SCG). The National High Magnetic Field Laboratory is funded by the NSF (DMR-1644779) and the State of Florida.References
1. Rexrode KM, Kathryn M. Rexrode Correspondence to: Kathryn M. Rexrode, Madsen TE, et al (2022) The impact of sex and gender on stroke. In: Circulation Research. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.319915. Accessed 9 Nov 2022
2. Zhang Y, Dong N, Hong H, Qi J, Zhang S, Wang J. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Therapeutic Mechanisms for Stroke. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 25;23(5):2550. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052550. PMID: 35269692; PMCID: PMC8910569.
3. Yuan X, Sun L, Jeske R, Nkosi D, York SB, Liu Y, Grant SC, Meckes DG Jr, Li Y. Engineering extracellular vesicles by three-dimensional dynamic culture of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022 Jun;11(6):e12235. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12235. PMID: 35716062; PMCID: PMC9206229.
4. Xuegang Yuan, Jens T. Rosenberg, Yijun Liu, Samuel C. Grant, Teng Ma, Aggregation of human mesenchymal stem cells enhances survival and efficacy in stroke treatment, Cytotherapy, Volume 21, Issue 10, 2019, Pages 1033-1048, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcyt.2019.04.055
5. Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989 Jan;20(1):84-91. doi: 10.1161/01.str.20.1.84. PMID: 2643202.
Figures