1949
The value of multimodal MR imaging in patients with acute cerebral infarction1The fourth hospital of Harbin, Harbin, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Blood vessels, Brain
Cerebrovascular diseases are one of the main causes of death and disability in the adult population. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) could provide quantitative parameters to evaluate the process of diseases, including Diffusion-weighted imaging(DWI), three-dimensional arterial spin labeling (3D ASL), and 4D-TRANCE. Results showed the maximum area size of 3D-ASL and 4D-TRANCE had predictive significance when evaluating patients with acute ischemic cerebral infarction by National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score, which could provide objective and useful parameters in further diagnosis.Introduction
The causes and pathophysiological processes of ischemic cerebrovascular diseases are complex, acute ischemic stroke is the highest disability rate of single disease. Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is considered as the golden standard technology for evaluating vascular morphology and characteristics, while with the advantage of invasive and risk of danger. National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score is a quantitative indicator of disease severity, which is commonly used as surrogate endpoints in clinical studies to stratify patients according to the NIHSS score to guide clinical decision-making. However, there may be some differences from different assessors.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) could overcome these characteristics, which has been widely used in clinical practice. In particular, DWI, 3D-ASL and could provide diffusion and perfusion information in neuro system. Furthermore, Time-resolved three-dimensional arterial spin labeling magnetic resonance angiography (4D-TRANCE) can obtain higher spatial resolution of arteries and blood vessels 1. 4D-TRANCE is an alternative non-invasive sequence, which captures morphological and blood flow data of the cerebrovascular system6.However, the studies on DWI, 3D-ASL and 4D-TRANCE sequences for acute cerebral infarction based on NIHSS score were limited. Therefore, the aim of this study is to comprehensively evaluate the cerebral blood flow perfusion of patients with ischemic cerebral infarction according to clinical NIHSS score by using multimodal magnetic resonance imaging.Methods
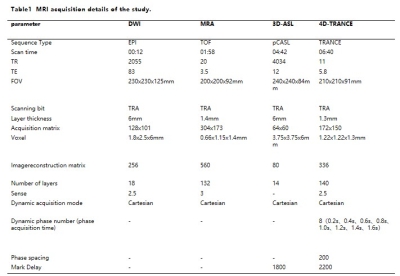
Patients with clinically confirmed acute ischemic cerebrovascular disease were prospectively collected. All participants were performed by a 3.0T MR platform (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, the Netherlands). Parameters of DWI, MRA, 3D-ASL, and 4D-TRANCE sequence parameters were listed in Table 1.Image data were transmitted to ISP workstation (Intellispace Portal; Version 10.1; Philips Healthcare, Best, the Netherlands) for post-processing by a 5-year experienced radiologist. Statistical analyzed by SPSS 26 . ANOVA and post-hoc of Tukey test were used to explored the differences among different groups. Spearman method was used for investigate the correlation between groups. Logistic regression analysis were chosen to identify significant independent predictive parameters. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) were calculated for assessing diagnosis ability.Results
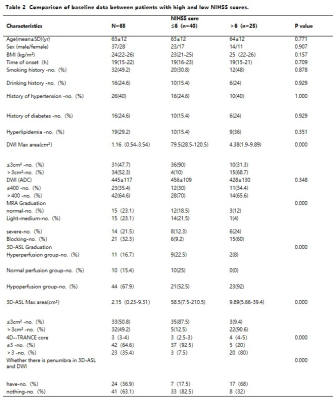
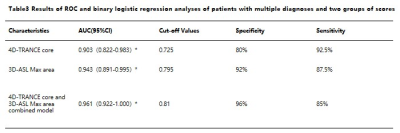
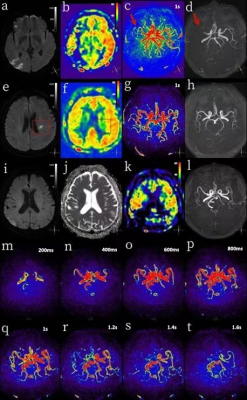
65 patients with acute cerebral infarction were divided into two groups, 25 patients with score>6 as mild-group and 40patients with score ≤ 6 as severe. There were significant differences in 3D-ASL maximum area and 4D-TRANCE score in Table 2(p<0.05).Patients with different sequences were shown in Figure 1. The diagnostic performance showed that AUC of 3D-ASL, 4D-TRANCE score of these two groups was 0.903 and 0.943, the corresponding sensitivity was 80%, 92% and specificity was 92.5% and 87.5%, respectively (Table 3) .The combined model achieved the highest prediction ability (AUC: 0.961, sensitivity: 96%, specificity: 85%. (Figure 2)Discussion
DWI, 3D-ASL and 4D-TRANCE technology were performed to evaluate patients with acute cerebral infarction based on NIHSS score in this study. Results showed that the maximum area of 3D-ASL and 4D-TRANCE score were significantly different, and the combined model had the highest prediction ability. 3D-ASL can reflect the cerebral blood flow perfusion under physiological conditions, while DWI can only identify acute cerebral infarction. Abundant collateral circulation can attenuate the ischemic core progression and reduce the final infarct area, so that the clinical symptoms of patients are less severe than those shown by DWI, which was consistent with the researches4.5. For the assessment of 4D-TRANCE, 61% of the patients with acute ischemic stroke showed that inconsistent blood flow velocity of bilateral vessels. This maybe illustrated that the stenosis degree of the diseased side artery was discrepant, leading to the increase or decrease of blood flow velocity, which would affect the blood supply of the infarcted area. Moreover, 33% of patients had a global out flow delay, the labeled blood flow in this part still did not flow out completely after 1.6s of the labeling delay, which indicated that the overall blood flow speed slowed down and the perfusion delayed. Arteriosclerosis, high blood lipid concentration or fibrin content in the blood, even abnormal development of blood vessels and low heart function could be the reasons that brain blood supply slow, leading to ischemic symptoms. 3D-ASL perfusion could not fully reflect the cerebral parenchyma perfusion, while 4D-TRANCE technology can be used for comprehensive evaluation on observing cerebral parenchyma perfusion with multiple PLD time for identifying hemodynamics of blood vessels. Therefore, this study indicated that the combination of DWI, 3D-ASL and 4D-TRANCE examination can better explain the cause of clinical ischemic symptoms.Conclusion
The combined application of DWI, 4D-TRANCE and 3D-ASL in patients with acute ischemic stroke can evaluate the cerebral perfusion, hemodynamics and collateral circulation which can predict the clinical situation of patients based on NIHSS score.Summary of main findings
The combined assessment of multimodal of 3D-ASL and 4D-TRANCE could assess patients with acute cerebral based on clinical NIHSS scores.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1.Phellan R, Lindner T, Helle M, et al. A methodology for generating four-dimensional arterial spin labeling MR angiography virtual phantoms. Med Image Anal, 2019, 56(3): 184-192.
2. van Osch MJ, Teeuwisse WM, Chen Z, et al. Advances in arterial spin labelling MRI methods for measuring perfusion and collateral flow. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2018, 38(9): 1461-1480.
3. Müller SJ, Khadhraoui E, Kube JMV, et al. Diagnostic value of diffusion-weighted STEAM-MRI in ischemic stroke. Eur J Radiol. 2021;139:109677.
4.Lou X, Yu S, Scalzo F, Starkman S, Ali LK, Kim D, et al. Multi-delay ASL can identify leptomeningeal collateral perfusion in endovascular therapy of ischemic stroke. Oncotarget. 2017, 8(2):2437–2443.
5.Okazaki S, Griebe M, Gregori J, Günther M, Sauter-Servaes J, Wolf ME, et al. Prediction of early reperfusion from repeated arterial spin labeling perfusion magnetic resonance imaging during intravenous thrombolysis. Stroke. 2016;47:247–250.
6.Phellan R,Lindner T,Helle M,et al. Phellan R, Lindner T, Helle M, et al. Segmentation-Based Blood Flow Parameter Refinement in Cerebrovascular Structures Using 4-D Arterial Spin Labeling MRA. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2020;67(7):1936-1946.
Figures