1873
A clinical validation study of synthetic high b-value reduced filed-of-view diffusion weighted imaging on prostate1Department of Radiology,Taihe Hospital,Hubei University of Medicine, Hubei, China, 2GE Healthcare, MR Research, Beijing, China, 3Department of Biomedical Engineering,Hubei University of Medicine, Hubei, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Prostate, Cancer
High b-value diffusion weighted imaging is clinically challenging due to its inherently low SNR and prone to presence of severe eddy current distortion due to utility of large diffusion sensitization gradient, not to mentioned high-resolution prostate DWI .In our study, 5b-protocol rFOV-syDWIswith pros of short scan time provided better lesion clarity and higher image quality.Moreover, synthetic ADCs offered reliable and satisfactory diagnostic value as scanned 13b-protocol DWIs despite significant difference of mean and median were found between syADCb=1500 and sADCb=1500 in PCa but not in hyperplasia, indicating diagnosis withrFOV-syADCs should be careful when referring to rFOV-sADCs.Background or Purpose
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the second most common cancer in men and the leading cause of cancer-related death in elderly men [1]. The latest edition of 2019 Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS 2.1) defines DWI as the primary evaluation sequence for peripheral zone cancer, especially the diagnostic value of high-b-value DW images[2]. However, high b-value images are challenging to be acquired and measured due to its inherently low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and prone to presence of severe eddy current distortion due to utility of large diffusion sensitization gradient [3].Synthetic DWI is a resultant of mathematical calculation and generates via DWI data with at least two different b-values. The calculated high b-value images of prostate can increase the significance of lesions and improve the image quality [4]. Although the improvement of synthetic image quality is generally recognized, no one has studied the influence of different b-value scanning numbers on the synthetic image quality up to now. Therefore, this study usedtwo protocolsof different b-value scanning numbers to synthesize the same high b-value DWI images, and further exploredthe quality and diagnostic efficiency of synthesized DW images by both protocols.Methods
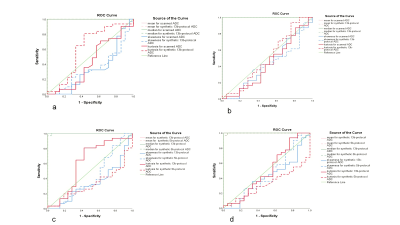
We retrospectively evaluated the data of 52 patients with prostate cancer (PCa) and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) who visited our hospital from July to December 2021. All patients underwent rFOV-DWI scans, including a 13b-protocol: b =0, 25, 50, 75, 100, 150, 200, 400, 600, 1000, 1000, 1200 and 1500 s/mm2 and a 5b-protocol: b =0, 100, 400, 800,1500 s/mm2. Synthetic reduced filed-of-view diffusion weighted images(rFOV-syDWIs) with b values of 1000 (rFOV-syDWIb=1000) and 1500 (rFOV-syDWIb=1500) were generated from two different multiple-b-value image data sets using a mono-exponential fitting algorithm. According to homoscedasticity and normality assessed by Levene test and Shapiro–Wilk test, the inter-modality differences of quantitative measurements were respectively examined by Wilcoxon signed rank test or paired t test and the inter-group differences of ADC values were examined by independent t test or Mann-Whitney U test. In addition, comparisons of the performance efficacy of ADCs in differentiation of patients with prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia were examined using ROC curves. Measurements were obtained as follows: (1) average signal intensity of a lesion (Stumor); (2) average signal intensity of Internal obturator muscle (Slesion); The following formula is used to calculate the contrast ratio (CR) for DWI images: CR= (Stumor - Slesion)/( Stumor + Slesion)Results
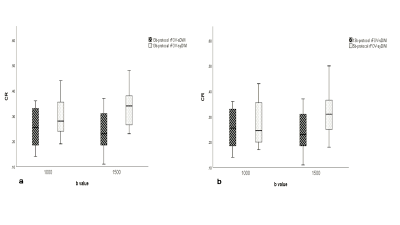
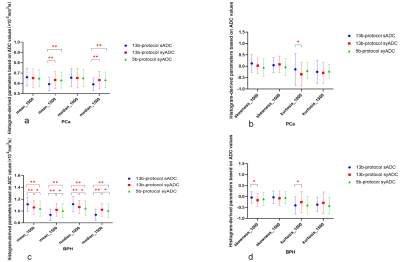
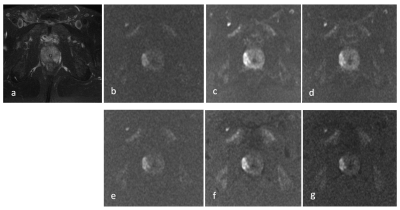
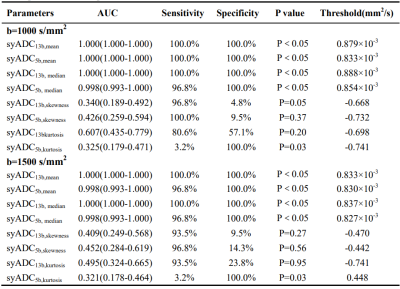
Image quality scores of rFOV-syDWIb=1000/1500 computed based on 5b- and 13b- protocols were evaluated by two radiologists (Table 1).For both multiple-b-value protocols, there were statistically higher inter-reader agreements on synthetic reduced filed-of-view DWIs than scanned reduced filed-of-view DWIs (rFOV-sDWI)(P < 0.001) and statistically higher scores (U1-U4) of synthetic DWIs than scanned ones(P < 0.05).CRs of 13b-protocol and 5b-protocol rFOV-syDWIb=1000/1500 were significantly higher than 13b-protocol rFOV-sDWIb=1000/1500 (Fig.1).Comparisons of syADC computed by 5b- and 13b-protocol DWIs were shown (Fig.2). The meanand median of 5b-protocol syADC showed approximately equivalent to those of 13b-protocol syADC (Fig.3; Table 2). An illustration of the scanned and synthetic rFOV-DWI images of a patient with PCa was shown in Fig.4.Discussion
5b-protocol synthetic DWI can be useful in clinical work with the pros of short scan time, high-b-value DWI with good image quality and satisfactory diagnosis performance despite significant difference of mean and median were found betweensyADCb=1500 and sADCb=1500in PCa but not in hyperplasia in our study.This can be explained that signal attenuates more in normal tissues and hyperplasia than tumor cells when high b value is used [5].Accordingly, BPH attenuated to the noise level first on rFOV-DWIb=1000 while both PCa and BPH attenuated to the noise level on rFOV-DWIb=1500in our study. Since synthetic ADC maps were computed with scanned b value of 0 s/mm2 and synthetic b value of 1000 or 1500 s/mm2, less noise contributed to high-b-value DW images and also different between scanned and synthetic ADC maps. Thus, we reasonably discovered that syADCmean,b=1000 was significantly lower than sADCmean, b=1000in hyperplasia instead of cancer, but syADCmean, b=1500was statistically higher than sADCmean, b=1500in both cancer and hyperplasia. Moreover, the restrictions of complex biological structures, such as organelles, cell membranes and intercellular space, make water diffusion signal attenuation a mono-exponential form when b value is less than 1000 s/mm2 but deviate from the Gaussian distribution (in a non-Gaussian displacement) when b value is greater than 1000 s/mm2[6]. Thus, mean and median of synthetic DWIs-computed ADC values might be closer to thescannedDWI-computed ADC values generated from low-b-valueimages, that is, less diffusion kurtosis effect.Histogram-derived ADC values—mean and median ofboth actually scanned andsynthetic ADC values reached perfect diagnosis efficacy with AUC of almost close and equal to 1.000 in our study, implying mean and median possess good diagnosis efficacy in detection of prostate cancer and its invasiveness [7]. There was no difference of 5b-protocol and 13b-protocol mean and median of syADCb=1000, 1500 in tumor tissues and also both diagnosis efficacy.
Conclusions
rFOV-syDWIs provided better lesion clarity and higher image quality than rFOV-sDWIs. Thus, 5b-protocol synthetic DWI is useful in clinical work with the pros of short scan time, high-b-value DWI with good image quality and satisfactory diagnosis performance.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1]Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
[2]Turkbey B, Rosenkrantz AB, Haider MA, et al. Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2.1: 2019 Update of Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2. EurUrol 2019;76(3):340–351.
[3]Blackledge MD, Leach MO, Collins DJ, Koh DM. Computed diffusion-weighted MR imaging may improve tumor detection. Radiology 2011; 261: 5 7 3–581.
[4]Ueno Y , Takahashi S, Kitajima K, Kimura T, Aoki I, Kawakami F , et al. Computed diffusion- weighted imaging using 3- T magnetic resonance imaging for prostate cancer diagnosis. EurRadiol 2013; 23: 3509–16. doi: https:// doi. org/ 10. 1007/ s00330- 013- 2958-z
[5]Vural M, Ertaş G, Onay A, et al. Conspicuity of peripheral zone prostate cancer on computed diffusion-weighted imaging: comparison of cDWI1500, cDWI2000, and cDWI3000. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:768291. doi:10.1155/2014/768291
[6]Jensen JH, Helpern JA, Ramani A, Lu H, Kaczynski K. Diffusional kurtosis imaging: the quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. MagnReson Med. 2005;53(6):1432-1440. doi:10.1002/mrm.20508
[7]Zhang YD, Wang Q, Wu CJ, et al. The histogram analysis of diffusion-weighted intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging for differentiating the gleason grade of prostate cancer. EurRadiol. 2015;25(4):994-1004. doi:10.1007/s00330-014-3511-4
Figures