1807
Apparent diffusion coefficient of the lumbar intervertebral disc as a quantitative indicator of disease severity and treatment effectiveness1Laboratory for Biomarker Imaging Science, Hokkaido University Graduate School of Biomedical Science and Engineering, Hokkaido, Japan, 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hokkaido University Faculty of Medicine, Hokkaido, Japan, 3Grobal Center for Biomedical Science and Engineering, Hokkaido University Faculty of Medicine, Hokkaido, Japan
Synopsis
Keywords: Quantitative Imaging, Degenerative, Intervertebral disc degeneration, ADC, T1rho, T2*, Lumbar
This prospective study aimed to evaluate the role of T1ρ, T2*, and ADC – the quantitative MRI indices, in determining the severity of intervertebral disc degeneration and treatment effectiveness. All three indices decreased with increasing Pfirmman grade, which determines the severity, suggestive of their potential as indicators of disease severity. The mean ADC of the degenerated disc increased significantly after surgery, suggesting its potential as a treatment effectiveness indicator.Introduction
Lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD) is a major cause of back pain and disability. It often requires surgical treatment, such as the injection of gelatinous alginate into the degenerated nucleus pulposus2. Pfirrmann grading system, a visual assessment using T2-weighted images obtained from MRI, is widely used to evaluate the severity of IVDD. However, this method is subjective1; the results may vary among observers. Therefore, a quantitative evaluation method for the degree of IVDD is desired. In the disease course, IVDD progresses with a decrease in water content along with that of proteoglycans in the nucleus pulposus. From these changes, several quantitative indices, such as T1ρ, T2*, ADC, are expected to be used for the quantitative evaluation of IVDD. This prospective study aimed to evaluate the role of these quantitative indices in determining the severity of IVDD and treatment effectiveness.Materials and methods
Thirty serial patients admitted for the surgical treatment of lumbar IVDD {mean age (standard deviation) = 36.4 (7.65) years; male: female = 20: 10} were enrolled. Sagittal T2-weighted images (TR/TE = 4000/90 ms, ETL = 25), T2*-weighted images (TR/TE = 5.8/0, 12, 25, 51 ms), T1ρ-weighted images (TR/TE = 5.8/1 ms, TSL= 0, 20, 40, 80 ms), and diffusion-weighted imaging (TR/TE = 3109/54 ms, b = 1000 s/mm2) were performed before and 24 weeks after surgery, using a 3T scanner (Achieva TX or Ingenia Elition, Philips, Best, the Netherlands). T2-weighted images were used to determine Pfirrmann grade. To limit observer bias, the grading was done by consensus reading among a radiologist and two orthopedic surgeons. T1ρ, T2*, and ADC of the intervertebral discs were calculated voxel-by-voxel. Using mid-sagittal images used to calculate these indices, artifact-free regions of interest (ROIs) were placed semi-automatically over each entire intervertebral disc, using Jim8 software (Xinapse system, UK). The ROIs were then allowed to overlay on the respective index maps, and the mean values were derived. To evaluate the role of these quantitative indices in determining the severity of IVDD, the mean values measured at the pre-treatment state were tested for correlation with Pfirrmann grade, using Spearman's correlation analysis. To evaluate the role of these quantitative indices in determining treatment effectiveness, the normalized mean values (i.e., normalized between the treated intervertebral disc and L2/3 intervertebral disc) were compared between the two time points using Wilcoxon rank-sum tests. A comparison of the mean value of the surgically treated intervertebral disc to that of the L2/3 intervertebral disc was also performed. In any condition, P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.Results
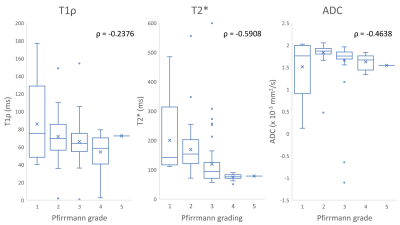
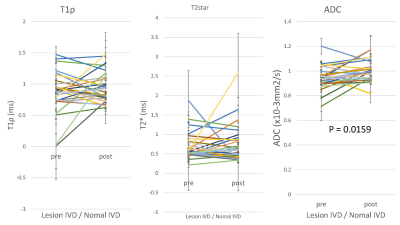
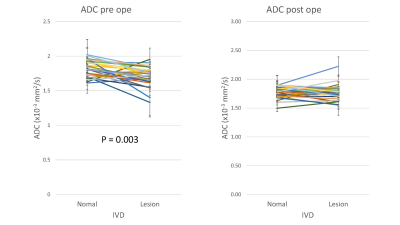
Before surgery, 5, 43, 55, 16, and 1 IVDs were considered Pfirrmann grades I, II, III, IV, and IV, respectively. T2* (ρ= -0.5908, p < 0.0001) and ADC (ρ= -0.4638, p < 0.0001) showed moderate negative correlation with Pfirrmann grade, whereas T1ρ(ρ= -0.2376, p = 0.009) showed a weak negative correlation with it (Fig. 1). All surgically treated intervertebral discs were either L4/5 or L5/S1. Comparison of the mean values before and after surgery showed no significant difference in T1ρ (pre-surgery = 0.9167 ± 0.3052; c.f. post-surgery = 0.9461 ± 0.2319, p = 0.9031) and T2* (pre-surgery = 0.7029 ± 0.3791; c.f. post-surgery = 0.7190 ± 0.3667, p = 0.8392). However, the normalized mean ADC of the intervertebral disc increased significantly after surgery (pre-surgery = 0.6344 ± 1.4128; c.f. post-surgery = 0.9987 ± 0.0864, p = 0.0159) (Fig.2). At the pre-operative state, T2* (disc to be treated = 100.95 ± 53.89 ; c.f. L2/3 intervertebral disc = 163.83 ± 89.99, p<0.0001) and ADC (disc to be treated = 1.5827 ± 0.5444; c.f. L2/3 intervertebral disc = 1.7102 ± 0.3885, p=0.003) of the discs to-be treated were significantly lower than those of L2/3 intervertebral disc. However, only T2* remained significantly different after surgery (P= 0.0014) (Fig. 3).Discussion
The significant association of T1ρ, T2*, and ADC of the intervertebral disc with Pfirmann grade suggests that these indices can be used to evaluate IVDD unbiasedly. The weaker degree of correlation of T1ρ may imply that the other two indices are more suited for the evaluation. Theoretically, T1ρis expected to reflect proteoglycan degeneration in the early stages of IVDD. Failure to observe a strong correlation with IVDD severity may be due to an increase in TypeⅠcollagen in the nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus increases3. From the degree of correlation with IVDD severity and a difference between pre- and post-surgery are thought to suggest that ADC suits best as a quantifier of intervertebral discs.Conclusion
Quantitative evaluation of IVDD is possible. ADC can become a helpful index in determining the severity of IVIDD or treatment effectiveness.Acknowledgements
Part of the analysis environment used in this study was provided by Philips Japan.References
1. James F. Griffith, Yi-Xiang J. Wang, Gregory E. Antonio, Kai Chow Choi, Alfred Yu, Anil T. Ahuja, Ping Chung Leung. Modified Pfirrmann Grading System for Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. SPINE. 2007, E708–E712
2. Risbud, Makarand V. Albert, Todd J. Guttapalli, Asha. Vresilovic, Edward J. Hillibrand, Alan S. Vaccaro, Alexander R. Shapiro, Irving M. Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Towards a Nucleus Pulposus-like Phenotype In Vitro: Implications for Cell-Based Transplantation Therapy. SPINE. 2004. P2627-2632.
3. Huaizhen Liang, Rongjin Luo, Gaocai Li, Weifeng Zhang, Yu Song, Cao Yang. The Proteolysis of ECM in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022, 23, 1715
Figures