1762
Widened-bandwidth RF volume coil using crossed elliptical winding for Halbach-array-based portable MRI knee scanner1Engineering Product Developement, Singapore University of Technology and Design, Singapore, Singapore
Synopsis
Keywords: Low-Field MRI, Low-Field MRI, RF coil
A widened-bandwidth RF volume coil using crossed elliptical winding pattern (symmetric in azimuthal direction) is proposed for Halbach-array-based portable MRI knee scanner. The fractional bandwidth (FBW) is 0.51% centered at 2.84 MHz (B0 = 67mT) with a high B1 field strength (57µT) and a high homogeneity (94%) within a cylindrical volume of diameter and length of both 95mm. Compared to solenoid coils of comparable dimensions, it is an increase of 18% in FBW, an improvement in homogeneity by 6.1%, and only a compromise of 1.9% in the field strength, which is the best combination.
INTRODUCTION
The portable Halbach-array-based MRI knee scanner with less homogeneous B0 field1 has built-in gradient which reduces the hardware complexity by reducing the number of gradient coils and amplifiers. However, the system requires to have RF coils with wider bandwidth to work with the B0 inhomogeneity, and high sensitivity to compensate a low B0 field strength. Solenoid coils with cylindrical profile2 or tapered profile3,4 were designed to achieve high B1 sensitivity and improved homogeneity. However, traditional solenoid RF coils are narrow band in nature which necessitates the use of resistor in the tuning / matching circuit to increase the bandwidth although additional loss is introduced3. There is a need to explore RF coil designs with widened bandwidth without much compromise in sensitivity and homogeneity.In the literature, single-turn crossed elliptical RF coil was proposed to provide better access for lower neck imaging5. However, multi-turn crossed ellipses and its potential to increase the bandwidth have not been explored earlier since such need has only emerged with the recent developments in portable MRI. Hence, in this work, we propose a crossed-elliptical RF volume coil with a winding pattern consisting of multiple crossed elliptical turns symmetrically distributed in the azimuthal direction, to achieve an increased bandwidth with improved B1 homogeneity and without much compromise of field intensity within a cylindrical volume of a diameter and a length of both 95mm and being suitable to be used in the portable MRI knee scanners. It can be scaled to other body-part dedicated scanners.
METHODS
The proposed coil has N crossed elliptical loops that are symmetrically distributed in the azimuthal direction with an angular pitch (pϕ) as shown in Fig.1. The working frequency is 2.84MHz for the Halbach array that has an average field of 67mT1. The ratio of the coil length (L) and the diameter (D) was set to unity to maintain symmetry in the structure, L=D=105mm to fit in the Halbach array, and for a cylindrical field of view (FoV) with a diameter and a length of both 95mm, $$$\varnothing$$$95L95mm. In this design, N=4, and thus pϕ is 45o. The diameter of the wire is 1mm. The proposed RF volume coil was simulated using frequency domain solver in CST microwave design studio (2021) and Sim4Life6. For comparison, solenoid coils with a comparable fractional bandwidth (FBW) (N=6), or a comparable B1avg (N=7), and with the same L and D were simulated.RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The design parameters, and the simulated performances (FBW, Bandwidth(BW), Q, B1avg, inhomogeneity(IH), inductance(L) and resistance(R) ) at 2.84MHz($$$f_0$$$) are tabulated in Fig.2(a) and (b), respectively. Fig.2(c) shows the S11s of the coils under consideration. IH is obtained from root mean square deviation (σ) relative to B1avg (σ/B1avg×100) within the defined FoV. As shown in Fig.2(b), when a solenoid has a comparable BW (N=6) as that of the proposed coil, B1avg decreases and B1-IH is worsen within the considered 3D FoV. Whereas, at N=7 when the solenoid has a comparable B1avg, the BW is reduced to 0.43% (15.7% reduction compared to the proposed coil) and meanwhile the B1-IH stays high. The comparison to the solenoids with the same L and D shows that the proposed coil has widened BW while keeping the field strength high and the B1-IH low.The simulated B1 distributions of the considered coils at 2.84MHz on the xy-planes (z=0,10,20,30mm) and the xz-plane (y=0) within the FoV are shown in Fig.3. Comparing the field distribution of the proposed coil across the different xy-planes at row 1, B1avg is spread uniformly with only a difference of 1.8µT between z = 0 and 30mm whereas both solenoid coils show a reduction of about 6.0µT in B1avg between the two xy-planes. Comparing the field distribution in the xz-plane (y=0), the proposed coil shows about 5-6% improved homogeneity compared to the two solenoids.Fig. 4 shows the simulated B1 distributions at the two cutoff frequencies $$$(f_0±BW/2)$$$ of the proposed coil ($$$f_L$$$=2.833MHz, $$$f_U$$$=2.847MHz) and $$$f_0$$$, on the central xy- and xz-plane, for the three coils under comparison. As shown in Fig. 4, the proposed coil shows a reduction of about 5.7µT when moving from the center to the sides of the band and a stable IH of 6-7%. The six-turn solenoid shows a lower B1avg, and a higher B1avg reduction crossing the band while the IH is at 12% moving along the z-direction. For the seven-turn solenoid, at all frequencies, B1avg on the xy-plane is higher than those of the proposed coil; at 2.84MHz, B1avg on the xz-plane is comparable to those of the proposed coil, and becomes smaller at $$$f_L$$$ and $$$f_U$$$. Moreover, comparing these two solenoids, the seven-turn one has a higher B1avg reduction of 8.6µT at the same band span, and the IH is similarly at 12% along the z-direction as the six-turn one. Based on the observations, the proposed coil shows higher and more uniform B1 across $$$f_L$$$ and $$$f_U$$$ in the FoV compared to the two solenoids.
CONCLUSION
The proposed crossed-elliptical volume coil shows a widened BW and a good balance in B1 field strength and homogeneity in the FoV for knee scans ($$$\varnothing$$$95L95mm). It is promising for the portable MRI scanners that have less homogeneous B0.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
- Ren, Zhi Hua, et al. "A low-field portable magnetic resonance imaging system for head imaging." 2017 Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium-Fall (PIERS-FALL). IEEE, 2017.
- Blasiak, Barbara, et al. "An optimized solenoidal head radiofrequency coil for low-field magnetic resonance imaging." Magnetic resonance imaging 27.9 (2009): 1302-1308.
- Shen, Sheng, et al. "Optimization of a Close-Fitting Volume RF Coil for Brain Imaging at 6.5 mT Using Linear Programming." IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 68.4 (2020): 1106-1114.
- Rajendran, Meena, and Shaoying Huang. "Asymmetric Tapered Solenoid Designs for Halbach based Portable Magnetic Resonance Imaging." IEEE Journal of Electromagnetics, RF and Microwaves in Medicine and Biology (2022).
- Redpath, Thomas William, and R. D. Selbie. "A crossed ellipse RF coil for NMR imaging of the head and neck." Physics in Medicine & Biology 29.6 (1984): 739.
- Sim4Life (https://zmt.swiss/sim4life/)
Figures
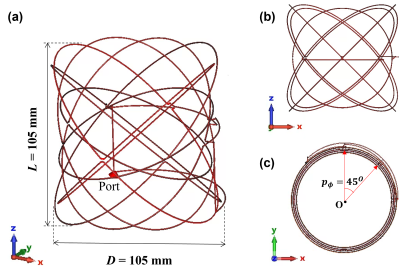
Fig. 1. Illustration of the proposed wideband RF volume coil with crossed elliptical winding pattern: (a) 3D-view, (b) side view and (c) top view. Design parameters: Length (L), Diameter (D), and azimuthal pitch (pϕ). The number of turns (N) in the coil is four.
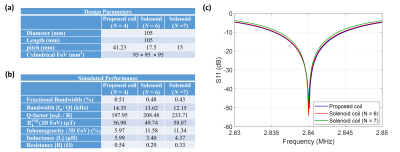
Fig.2. (a) Design parameters, (b) simulated performance, and (c) simulated S11 plot of the the proposed RF volume coil using crossed elliptical winding and reference solenoid coils with N = 6 and 7 turns.
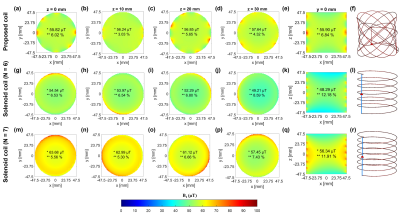
Fig. 3. Simulated B1 field distributions at 2.84 MHz on the xy−planes (z=0,10,20,30mm), and the xz−plane (y = 0) using a 1A current excitation (column 1 to 5): (a)-(e) the proposed crossed-elliptical RF volume coil, (g)-(k) solenoid coil with N = 6, and (m)-(q) solenoid coil with N = 7 from row 1 to 3, respectively. The coil profiles are shown in column 6. B1avg and IH are labelled in each sub-plot, indicated by ‘*’ and “**”, respectively.
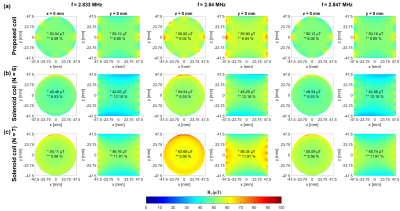
Fig. 4. Simulated B1 field distribution at the lower cutoff (fL=2.833MHz), resonant (f0= 2.84MHz) and upper cutoff (fU=2.847MHz) frequencies of the proposed coil on the xy−plane (z = 0) and the xz−plane (y = 0) for (a) the proposed crossed-elliptical RF volume coil (N = 4), b) solenoid coil with N = 6, and (c) solenoid coil with N = 7 from row 1 to 3, respectively. B1avg and IH are labelled in each sub-plot, indicated by ‘*’ and “**”, respectively.