1752
The application of high-resolution isotropic EPI DWI by CS with different acceleration factor in brain tumor
Mengting Duan1, Yi Zhu2, Qi Wang1, and Hui Liu1
1The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Hebei, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
1The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Hebei, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Tumors, Cancer, EPI-DWI, Compressed SENSE
It has been shown before that C-SENSE can improved the ss-EPI DWI image quality in higher spatial resolution. The aim of this paper is to achieve a high-resolution isotropic EPI DWI by CS and to investigate the impact of different acceleration factor(AF) on the diagnostic quality of brain metastases in comparison with SENSE EPI DWI.Introduction
Brain metastases are a common complication of cancer and the most common type of brain tumor. [1] Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain is a state-of-the-art technique for the visualization of a wide variety of neurological and oncological diseases. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is a powerful tool for examining the microstructural and physiological features of in vivo biological tissues. It is widely used for diseases of the central nervous system and various tumor detection. DWI is a form of MR imaging based on measuring the random Brownian motion of water molecules within a voxel of tissue, which can be quantified the water diffusion by calculating the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values.[2] Currently, single-shot EPI (ssEPI) DWI is extensively used in practice as it offers the advantage of rapid image acquisition. However, most SS-DW-EPI is two-dimensional (2D) imaging which has a few millimeters of slice thickness and slice gap. Multislice imaging by an isotropic voxel with high resolution is difficult because of the low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in high-b value images and the long scan time. Sensitivity encoding (SENSE) helps to reduce the voxel size without increasing image distortion, but it often suffers from increased noise-like artifacts in the center of the images due to the high geometry factor. Recently, Compressed SENSE (CS), which combines SENSE (sensitivity encoding) and compressed sensing to accelerate the acquisition time without increasing image artifacts, has been reported to have some clinical usefulness in brain EPI DWI[3]. The aim of this paper is to achieve a high-resolution isotropic EPI DWI by CS and to investigate the impact of different acceleration factors (AF) on the diagnostic quality of brain metastases in comparison with SENSE EPI DWI.Method
The institutional review committee approved this prospective study. A total of 31 patients with intracranial tumors were enrolled. All patients were receiving an optimized a high-resolution isotropic EPI DWI sequence with different AF (3,4,5) and reconstruction by CS and SENSE on 3.0 T MR system (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, Best, Netherlands). The DWI images is based on single-shot DW-EPI acquisition with a regular sampling pattern and only reconstruction by the iterative L1-minimization optimization in wavelet transform Scan parameters were as follows: TR / TE = 7855/ 89 ms, field-of-view = 23.0 × 23.0 cm2, acquisition matrix = 154 × 154 (reconstruction matrix = 512 × 512), voxel size = 1.5 × 1. 5 × 1. 5 mm, the number of slices = 60, NSA = 2, EPI factor = 55, acceleration factor or SENSE/C-SENSE =3, 4,5, b-values = 0 and 1000 sec/mm2, Acquisition time = 2min45s for AF3, 2min29s for AF4 and 2min17s for AF5. Two typical slices were selected for each patient both on b1000 images and ADC maps and outlined the ROI on the intracranial tumor to calculate the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and the mean ADC values to objectively analyze the images. For qualitative image quality assessment, all sequence images were independently reviewed by 2 radiologists with more than 2 years of experience. The radiologists who were blinded to any clinical information evaluated overall image quality by a 5-point Likert scale. Friedman test and Dunn test were used for multiple comparisons to detect the significant differences in quantitative and qualitative image features among all sequences. P values< 0.05 were considered significant.Result and Discussion
Fig 1 and Fig2 show a presentative high b value DWI image using CS and SENSE in different AF by axial source image and sagittal reformats. CS DWI can clearly reduce the noise in the SENSE images. As can be seen in Fig2, in each AF, the EPI DWI accelerated with CS was significantly superior to SENSE both in the SNR and the overall image quality (p < 0.05). Most importantly, there were no significant differences between ADC values of CS and those of CS both in each AF. It indicated that DWI with accelerated by CS can provide accurate ADC values and not affect clinical diagnosis. The acceleration factor 4 is more suitable for clinical application according to the image quality and saved scan time.Conclusion
The newly developed Compressed SENSE reconstruction algorithm of the EPI DWI can improve the image quality of whole-brain high-resolution isotropic DWI and will not affect the clinical diagnosisAcknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Pérez-Larraya J G, Hildebrand J. Brain metastases[J]. Handbook of clinical neurology, 2014, 121: 1143-1157.
[2] Squillaci E, Manenti G, Cova M, et al. Correlation of diffusion-weighted MR imaging with cellularity of renal tumours[J]. Anticancer research, 2004, 24(6): 4175-4180.
[3] Pseudo-3D whole-brain ultra-thin-slice diffusion-weighted imaging of the brain utilizing deep learning constrained Compressed SENSE, ISMRM 2021
Figures
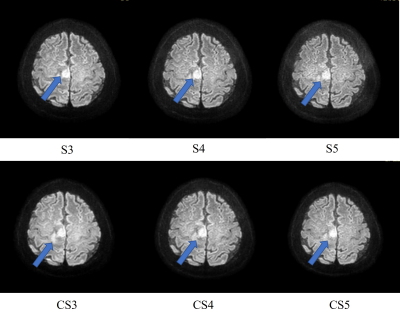
Representative high-b value DWI accelerated with SENSE and CS in different AF. Arrows indicate cancer areas.
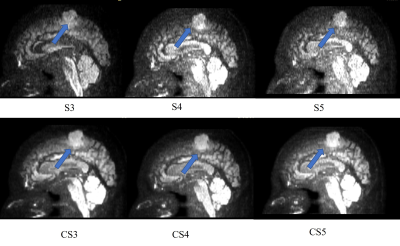
Representative high-b value DWI accelerated with SENSE and CS in different AF(sagittal reformat). Arrows indicate cancer areas.
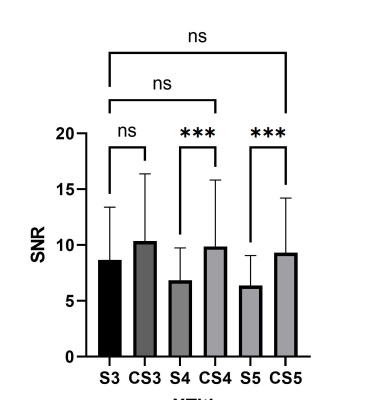
Bar plots of the SNRs in SENSE and CS with different AF
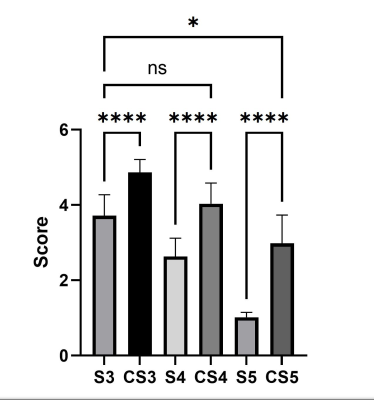
Bar plots of the Subjective scoring in SENSE and CS with different AF
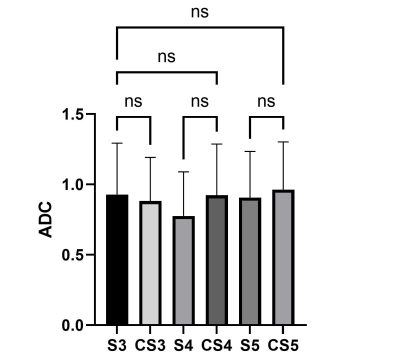
Bar plots of the ADC values in SENSE and CS with different AF
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/1752