1737
Predicting brain age using partition modeling strategy and Atlas-based attentional enhancement in Chinese population
Yang Yang1, Bingsheng Huang2, Yingqian Chen3, Yingtong Wu2, Chuxuan Lin2, Zhiyun Yang3, and Xia Liu4
1Department of Radiology, Suining Central Hospital, Suining, China, 2Medical AI Lab, School of Biomedical Engineering, Health Science Center, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China, 3Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China, 4Department of Radiology, Shenzhen Kangning Hospital, Shenzhen, China
1Department of Radiology, Suining Central Hospital, Suining, China, 2Medical AI Lab, School of Biomedical Engineering, Health Science Center, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China, 3Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China, 4Department of Radiology, Shenzhen Kangning Hospital, Shenzhen, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Neurodegeneration, Neurodegeneration, Brain age, Partition modeling
This study aimed to develop and construct a MRI-based full-age-range brain age prediction model that can be applied in the Chinese health care system. We proposed a brain age prediction method based on transfer learning and partition modeling , which was using Atlas attention enhancement. The performance of models with different image masks were compared and the model constructed based on top60% image mask achieved the best prediction performance. The brain age prediction method proposed in this study can provide objective brain age for assessing brain health status in Chinese population.Objectives
Brain age prediction based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been widely used to estimate the health status of the brain. However, few studies of brain age prediction based on Chinese population have been reported. We aimed to develop and construct a MRI-based full-age-range brain age prediction model that can be applied in the Chinese health care system.Methods
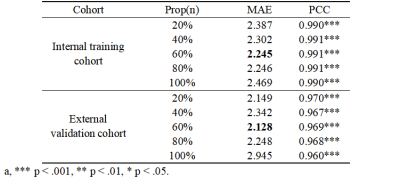
Domestic healthy subjects (n = 424; aged 6-85 years) were recruited from four hospitals. The training cohort (n = 354) was composed of T1-weighted images of healthy subjects from center 1, center 2 and center 3, while the test cohort (n = 70) from center 4. We firstly used the strategy of partitioned modeling separating all samples into four age groups. We used transfer learning to obtain pre-training weights from a large set of MRI scans (n = 1481; aged 50-85 years) from internationally available datasets, and the weights were provided to train deep learning-based models on our recruited dataset for each age group. Furthermore, attention maps generated by deep learning Grad-CAM technology found critical brain regions during modeling, which showed higher intensity in attention maps. Atlas attention enhancement method was used to improve the performance of brain age prediction model, which used Atlas masks to enhance the attention of critical brain regions. We made top20%, top40%, top60%, top80% and top100% image masks based on Anatomical Automatic Labeling (AAL) Atlas, respectively. The top20%, top40%, top60%, top80% and top100% image masks were respectively defined as accumulating from the brain region with the highest attention score until the sum of the first n brain regions accounts for 20%, 40%, 60%, 80% and 100% of the sum (Figure 1). The performance of models constructed with different image masks were compared. The performance of brain age prediction was evaluated by using mean absolute error (MAE) and Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC).Results
Deep transfer partitioned model with Atlas attention-enhancement constructed based on top60% image mask achieved the best prediction performance (Table 1). The prediction performance with a MAE of 2.245 years and a PCC of 0.991 (p<0.001) was achieved in the training cohort. Predictive performance with a MAE of 2.128 years and a PCC of 0.969 (p<0.001) was achieved in the test cohort. In each age group, most of the critical brain regions in top60% image mask were brain regions with significant changes in the brain during the developmental and aging stages, which strongly explained the effectiveness of the model.Conclusions
We successfully constructed a full-age-range brain age prediction model suitable for the Chinese population, and further improved the performance of prediction model using Atlas attention enhancement method.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
No reference found.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/1737