1709
Diagnostic value of combined DTI and DKI imaging for diffuse axonal injury of brain1Zhangjiakou First Hospital, Zhangjiakou Hebei, China, 2GE Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Traumatic brain injury, Brain
The values of fractional anisotropy (FA) in diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and the mean kurtosis (MK) and mean diffusivity(MD) values in diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) were used to analyze diffuse axonal injury of brain Injury (DAI). We explored the diagnostic value of these three parameters in DAI and found that MK was superior to FA and MD. DTI and DKI could quantitatively analyze the severity of DAI patients and reduce the misdiagnosis rate of DAI.
Purpose
Diffuse axonal injury of brain Injury(DAI) can find the distribution, signal and morphological characteristics of lesions in conventional MRI sequences, but it cannot objectively evaluate the severity of brain tissue damage by specific numerical values. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI)techniques can be used as a complement to conventional MRI sequences. Quantitative analysis of the characteristics of lesions and evaluation of their severity through the parameters of fractional anisotropy (FA) , mean diffusivity(MD) and mean kurtosis (MK) in DTI and DKI are conducive to the accurate diagnosis and clinical treatment of lesions, especially for patients with atypical MRI routine sequence, and early detection of damaged brain tissue.Methods
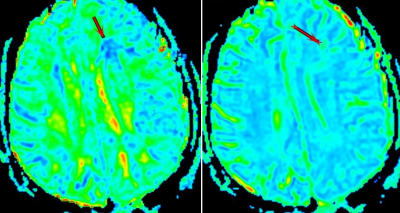
The study cohort comprised 68 male patients who underwent MRI, DTI and DKI sequences scans between July 1,2015, and February 1,2017. 40 were clinically confirmed DAI patients (DAI group) with a mean age of 48±1.2 years and 40 were healthy volunteers (control group) with a mean age of 53±3.1 years.All MRI examinations were conducted on GE signa HDxt1.5T superconducting magnetic resonance scanner. ADW4.6 workstation was used to process the data of the original image. Firstly, routine sequence MRI findings of abnormal brain parenchyma in DAI patients were observed on T1WI, T2WI, FLAIR and DWI images. Then, the Functool software package in the workstation was used to calibrate the DTI and DKI images, and the pseudo-color images of FA,MD and MK values were further reconstructed, as shown in Figure 1A-B. The lesion area of the DAI group and the corresponding layer area of the control group were selected as the region of interest (ROI), and the FA, MD and MK values of the layer were measured. Each ROI was measured three times, and we used the average value. The mean kurtosis (MK), mean diffusivity (MD) and fractional anisotropy (FA) values of the two groups were measured. Two independent sample T tests were used to analyze the MK, MD and FA values of the two groups. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of each parameter were analyzed to evaluate the diagnostic efficiency of DAI.
Results and Conclusions
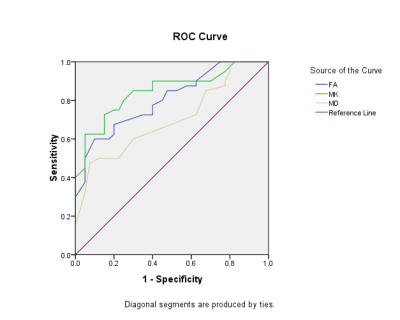
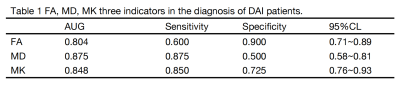
There were significant differences in FA ,MD and MK between the two groups (P <0.01). The ROC curve comparison analysis was displayed in Table 1. The area under ROC curve (AUC) of MK value was 0.848, and the sensitivity and specificity were 72.5% and 85.0%, respectively. The AUC curve of FA value was 0.804, and the sensitivity and specificity were 60.0% and 90.0%, respectively. The AUC of MD was 0.702, and the sensitivity and specificity were 50.0% and 87.5%, respectively(Tabe1, Figure 2).In the diagnosis of DAI patients in the three parameters, MK was superior to FA and MD, and the sensitivity and specificity is ideal in the diagnosis of DAI has a high diagnostic value. The results showed that MK values in DKI is suitable for DAI checks. DTI and DKI, as complementary sequences of conventional MRI sequence, could be measured to obtain specific values of different parameters, quantitatively analyze the severity of DAI patients, reduce the misdiagnosis rate of DAI, and facilitate clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Acknowledgements
no acknowledgementsReferences
[1] Abu Hamdeh Sami,Marklund Niklas,et al。Extended Anatomical Grading in Diffuse Axonal Injury Using MRI: Hemorrhagic Lesions in the Substantia Nigra and Mesencephalic Tegmentum Indicate Poor Long-Term Outcome.[J].Journal of Neurotrauma 2017,34(2):341-352。
[2] Takeda M , Iwai K , Yamada S , et al. Delayed onset of severe diffuse axonal injury: a case report[J]. Nihon Kyukyu Igakukai Zasshi, 2009, 20(7):383-389.
[3] Dai,WATANABE,Kohei,et al. Injury Analysis of a Head Subjected to the Lateral Rotational Impact Related to the Mechanism of Diffuse Axonal InjuryUsing the VOXEL Head Model[J]. Transactions of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2009.75(752):529-53