1698
Application of 4D-PACK and 4D-S-PACK in the internal carotid artery occlusion: initial experience1Radiology, Renji hospital, Shanghai, China, 2Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Vessels, Blood vessels
We recruited 4 patients with internal carotid artery occlusive diseases and assessed whether 4D-MR angiography can be used as a noninvasive alternative to intraarterial DSA. All patients were imaged with TOF-MRA, 4D-PACK, 4D-S-PACK, and DSA. 4D-PACK demonstrated a sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of 100%, 100%, and 100% respectively, as same as TOF-MRA, for diagnosing ICAO in reference to DSA. Moreover, 4D-PACK along with 4D-S-PACK could provide additional dynamic information on compensatory circulation after ICAO. Our results showed that non-contrast 4D-MR angiography has the potential to become an alternative imaging approach in diagnosing ICAO and initially assessing its blood supply pattern.Introduction
Imaging of blood supply patterns is of high interest to improve diagnostics in the internal carotid artery occlusion (ICAO). Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) remains the clinical standard for diagnosing ICAO and assessing the compensatory circulation. However, this imaging approach is known to have certain limitations, including invasiveness and an association with ionizing radiation exposure. 4D-MR angiography techniques have been developed to visualize both luminal stenosis and collateral circulation. This study aimed to evaluate the usefulness of a non-contrast and non-invasive 4D-MR angiography based on super selective pseudo-continuous ASL combined with keyhole and view-sharing (4D-PACK and 4D-S-PACK) for vessel-selective visualization and to examine the ability of this technique to visualize ICAO and initially assess its blood supply pattern[1, 2].Methods
Patients diagnosed as having ICAO by ultrasound and who were scheduled for intraarterial DSA were recruited. All patients underwent multi-contrast MR imaging (extra-and-intracranial TOF-MRA, 4D-PACK, 4D-S-PACK) and DSA within 1 week. The MR angiography was performed using a 3.0-T scanner (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare). The labeling focus of 4D-PACK was placed in the upper cervical segment of the ICA, regardless of occlusion. For the labeling of ICAs, the gradient moment was set at 0.75 mT/m/ms in both the right-to-left and anterior-to-posterior directions, to create a circular labeling spot with a diameter of approximately 2 cm. Images were obtained by changing the label duration between 100, 200, 500, 800, 1200, 1600, and 2000 ms. 4D-S-PACK was used to scan the contralateral ICA and/or vertebral artery rather than the occlusive ICA[3, 4]. The selection criteria of the contralateral ICA and/or vertebral artery depended on the openness of the anterior and posterior communicating arteries and blood compensatory circulation observed on the 4D-PACK. The acquisition time for each artery was 5 min 0 s.Results
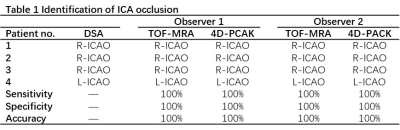
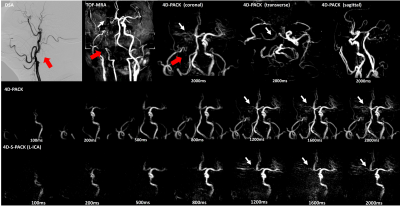
In the recruited four patients, three were right ICAOs while the remaining one was left ICAO. In reference to DSA, 4D-PACK demonstrated a sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of 100%, 100%, and 100% respectively for diagnosing ICAO by both two observers, as same as TOF-MRA (Table 1). Moreover, 4D-PACK along with 4D-S-PACK could provide additional dynamic information of compensatory circulation after ICAO, which was unable to be identified by TOF-MRA. Two patients had the blood supply of the distal MCA beyond ICAO through the anterior communicating artery, and the other 2 through the posterior communicating artery. One typical case was shown in Figure 1. The right ICAO was observed from DSA, TOF-MRA and 4D-PACK. No posterior communicating artery was observed in the coronal and transverse images of 4D-PACK. 4D-PACK and 4D-S-PACK showed the pale right MCA developed from the left ICA through anterior communicating artery.Discussion
Few studies have used non-selective ASL-based 4D-MR angiography for visualizing ICAO. The accuracy and inter-reader reproducibility were excellent for diagnosing ICAO by 4D-PACK in the recruited 4 subjects. 4D-PACK along with 4D-S-PACK could provide additional dynamic information on compensatory circulation after ICAO, which was an advantage of DSA and unable to be identified by TOF-MRA. Compared with the contralateral ICA and MCA, the CNRs of the patients’ distal MCA beyond ICAO were significantly lower when 4D-PACK and 4D-S-PACK were used. This finding could be due to the smaller amount of blood labeled by the super-selective labeling[5]. From the C3 segment to the C6 segment of ICA, the CNRs of these tortuous vessels were lower than the relatively straight vessels. The signal reduction in 4D-PACK and 4D-S-PACK sometimes wrongly showed narrow and stenosis from the actual normal vessel. We found that the super-selective labeling put in the relatively vertical vessel and as close to the imaging area as possible could improve the CNRs in the processing of scanning. More cases are needed to further validate the stability and accuracy of the technique.Conclusion
4D-PACK diagnosed ICAO reliably in the recruited 4 patients. Moreover, 4D-PACK along with 4D-S-PACK could provide additional dynamic information on compensatory circulation after ICAO. Non-contrast and non-invasive 4D-MR angiography has the potential to become an alternative imaging approach in diagnosing ICAO and initially assessing its blood supply pattern.Acknowledgements
None.References
1. Obara M., O. Togao, G.M. Beck, et al., Non-contrast enhanced 4D intracranial MR angiography based on pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling with the keyhole and view-sharing technique. Magn Reson Med, 2018. 80(2): p. 719-725.
2. Togao O., A. Hiwatashi, M. Obara, et al., 4D ASL-based MR angiography for visualization of distal arteries and leptomeningeal collateral vessels in moyamoya disease: a comparison of techniques. Eur Radiol, 2018. 28(11): p. 4871-4881.
3. Obara M., O. Togao, M. Helle, et al., Improved selective visualization of internal and external carotid artery in 4D-MR angiography based on super-selective pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling combined with CENTRA-keyhole and view-sharing (4D-S-PACK). Magn Reson Imaging, 2020. 73: p. 15-22.
4. Togao O., M. Obara, M. Helle, et al., Vessel-selective 4D-MR angiography using super-selective pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling may be a useful tool for assessing brain AVM hemodynamics. European Radiology, 2020. 30(12): p. 6452-6463.
5. Togao O., M. Obara, K. Kikuchi, et al., Vessel-Selective 4D-MRA Using Superselective Pseudocontinuous Arterial Spin-Labeling with Keyhole and View-Sharing for Visualizing Intracranial Dural AVFs. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2022. 43(3): p. 368-375.
Figures