1677
To Compare the Application Value of Reduced Field-of-View IRIS-DWI Sequence and TSE-DWI Sequence in Rectal Cancer
Jianwei Zeng1, Haini Zhang1, Yankai Meng1, Lu Han2, Peng Wu2, and Kai Xu1
1Department of Radiology, the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xu zhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China
1Department of Radiology, the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xu zhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Cancer, High-Field MRI
The rFOV IRIS-DWI and rFOV TSE-DWI sequences are newer techniques in rectal magnetic resonance. In this study, we compared the image quality between reduced field-of-view (rFOV) diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) sequence based on image reconstruction using image-space sampling functions (IRIS) and rFOV turbo spin echo-diffusion weighted imaging (TSE-DWI) sequence. Through subjective and objective image quality analysis, we found different application values of rFOV IRIS-DWI and rFOVTSE-DWI sequences in rectal cancer.Objective
To compare the image quality between reduced field-of-view (rFOV) diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) sequence based on image reconstruction using image-space sampling functions (IRIS) and rFOV turbo spin echo-diffusion weighted imaging (TSE-DWI) sequence.
Methods
All rectal cancer patients underwent rectal MRI in our institution between May 2022 and October 2022 were retrospective analysis. All patients were scanned on a 3.0T MR scanner (Elition, PHILIPS, The Netherlands) with a 32-channel body array coil. All enrolled patients were randomly scanned rFOV IRIS-DWI, rFOV TSE-DWI sequence (Table 1). All DWI images were uploaded to the Philips IntelligenceSpace Portal (ISP) workstation (Version 10.1) and were analized by a senior radiologist with more than 20 years of experience in MRI rectal cancer. The image evaluation included subjective and objective image quality analysis. Subjective image quality assessment included image distortion, image artifact, lesion visibility, image anatomy according to the evaluation criteria of 5 points scales reference. Then, the overall image quality was calculated. Objective image quality included image signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), comparative signal-to-noise ratio (CNR), tumor ADC value, tumor maximum level area, the average tumor maximum area and tumor volume.
Results
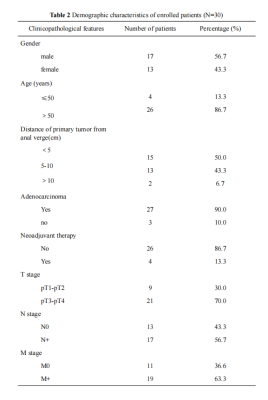
In this study, there were 17 male (56.7%) and 13 female (43.3%). The median age of all patients were 60 years ranged from 35 to 81 years (Table 2). The image distortion and artifact of rFOV TSE-DWI sequence were superior to the rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). The lesion visibility and the rectal intestinal wall anatomy in the rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence were superior to that of the rFOV TSE-DWI sequence (P < 0.05) (Table 3, Figure 1). The ADC value of the rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence was significantly lower than the rFOV TSE-DWI sequence (0.86×10-3 mm2/s vs. 1.07×10-3mm2/s, respectively, P < 0.001) (Table 4, Figure 2). The SNR of the rFOV TSE-DWI sequence was significantly higher than the rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence (P = 0.002). However, the CNR of the rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence was 0.85, and the rFOV TSE-DWI sequence was 0.52, respectively. The difference was significant (P < 0.05) (Figure 3).
Conclusion
For the image distortion and artifacts of rectal cancer, the rFOV TSE-DWI sequence were superior to the rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence. Howerver, the tumor conspicuity and anatomy structure in the rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence were better than the rFOV TSE-DWI sequence.
To compare the image quality between reduced field-of-view (rFOV) diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) sequence based on image reconstruction using image-space sampling functions (IRIS) and rFOV turbo spin echo-diffusion weighted imaging (TSE-DWI) sequence.
Methods
All rectal cancer patients underwent rectal MRI in our institution between May 2022 and October 2022 were retrospective analysis. All patients were scanned on a 3.0T MR scanner (Elition, PHILIPS, The Netherlands) with a 32-channel body array coil. All enrolled patients were randomly scanned rFOV IRIS-DWI, rFOV TSE-DWI sequence (Table 1). All DWI images were uploaded to the Philips IntelligenceSpace Portal (ISP) workstation (Version 10.1) and were analized by a senior radiologist with more than 20 years of experience in MRI rectal cancer. The image evaluation included subjective and objective image quality analysis. Subjective image quality assessment included image distortion, image artifact, lesion visibility, image anatomy according to the evaluation criteria of 5 points scales reference. Then, the overall image quality was calculated. Objective image quality included image signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), comparative signal-to-noise ratio (CNR), tumor ADC value, tumor maximum level area, the average tumor maximum area and tumor volume.
Results
In this study, there were 17 male (56.7%) and 13 female (43.3%). The median age of all patients were 60 years ranged from 35 to 81 years (Table 2). The image distortion and artifact of rFOV TSE-DWI sequence were superior to the rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). The lesion visibility and the rectal intestinal wall anatomy in the rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence were superior to that of the rFOV TSE-DWI sequence (P < 0.05) (Table 3, Figure 1). The ADC value of the rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence was significantly lower than the rFOV TSE-DWI sequence (0.86×10-3 mm2/s vs. 1.07×10-3mm2/s, respectively, P < 0.001) (Table 4, Figure 2). The SNR of the rFOV TSE-DWI sequence was significantly higher than the rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence (P = 0.002). However, the CNR of the rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence was 0.85, and the rFOV TSE-DWI sequence was 0.52, respectively. The difference was significant (P < 0.05) (Figure 3).
Conclusion
For the image distortion and artifacts of rectal cancer, the rFOV TSE-DWI sequence were superior to the rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence. Howerver, the tumor conspicuity and anatomy structure in the rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence were better than the rFOV TSE-DWI sequence.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021,71(3):209-249.
[2] Xu Z, Huang F, Wu Z, et al. Technical Note: Clustering-based motion compensation scheme for multishot diffusion tensor imaging[J]. Med Phys, 2018,45(12):5515-5524.
[3] Xia C, Liu X, Peng W, et al. Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging improves the image quality of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in rectal cancer: Comparison with single-shot echo-planar diffusion-weighted sequences[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2016,85(10):1818-1823.
Figures
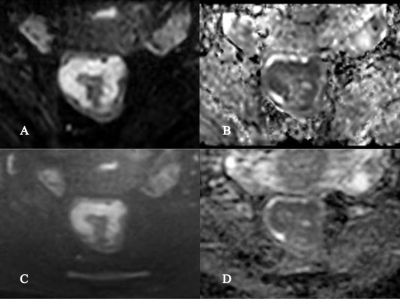
Figure 1 A 53 years-old-female patient demonstrated with rectal adenocarcinoma. rFOV IRIS-DWI b=800 s/mm2 image (A), rFOV IRIS-DWI ADC image (B), rFOV TSE-DWI b=800 s/mm2 image (C), and rFOV TSE-DWI ADC image (D). The subjective score rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence image distortion, artifacts, visibility, and anatomy were all 5 points, and the overall image quality score was 20 points. The deformation, artifacts, visibility, and anatomy of the rFOV TSE-DWI sequence image were scored 5, 5, 5, and 4, respectively, and the overall image quality score was 19 points.
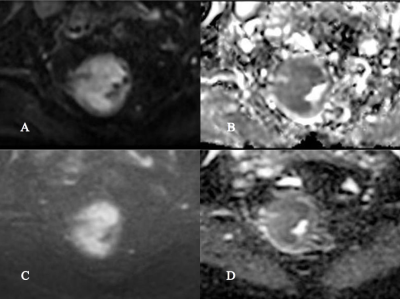
Figure 2 A 57 years-old female patient with rectal adenocarcinoma. rFOV IRIS-DWI b=800 s/mm2 image (A), rFOV IRIS-DWI ADC image (B), rFOV TSE-DWI b=800 s/mm2 image (C) and rFOV TSE-DWI ADC image (D). The rFOV IRIS-DWI sequences SNR, CNR, and ADC are 42.53, 0.9, and 1.04, respectively. The rFOV TSE-DWI sequences SNR, CNR, and ADC are 62.43, 0.53, and 1.25, respectively.
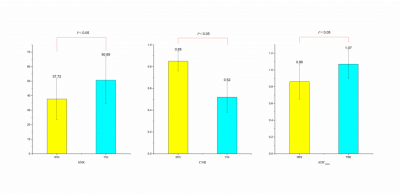
Figure 3 The comparison of objective image quality between rFOV IRIS-DWI and rFOVTSE-DWI sequence
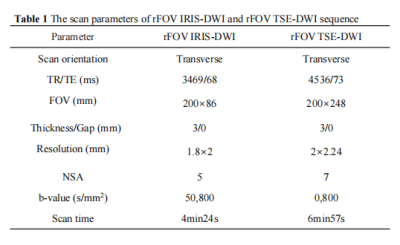
Note: TR, repetition time; TE, echo time; FOV, field of view; NSA, number of signal averaged.
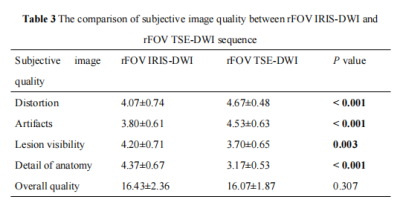
Note: rFOV, reduced field of view; IRIS-DWI, image reconstruction using image-space sampling functions diffusion weighted imaging; TSE-DWI, turbo spin echo diffusion weighted imaging; Bold indicates that the difference is statistically significant.
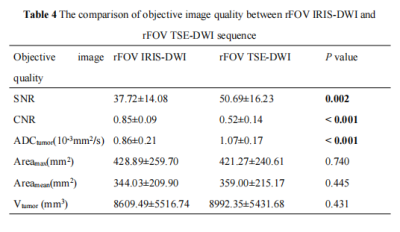
Note: rFOV, reduced field of view; IRIS-DWI, image reconstruction using image-space sampling functions diffusion weighted imaging; TSE-DWI, turbo spin echo diffusion weighted imaging; SNR, signal noise ratio; CNR, contrast to noise ratio; ADCtumor, apparent diffusion coefficient; Areamax, Tumor maximum layer area; Areamean, the average of the maximum layer of the lesion and the sum of the areas above and below it; Vtumor, tumor volume; Bold indicates that the difference is statistically significant.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/1677