1676
Multiparametric MRI Evaluation of Vesical Imaging‑Reporting and Data System (VI‑RADS) for bladder cancer after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Xinxin Zhang1, Yichen Wang1, Sicong Wang2, Jianzhong Shou1, Yan Chen1, and Xinming Zhao1
1National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100021, China, Beijing, China, 2GE Healthcare, MR Research China, Beijing, Beijing, China
1National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100021, China, Beijing, China, 2GE Healthcare, MR Research China, Beijing, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Cancer, Bladder
Local tumor restaging after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) treatment is urgently needed. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate whether VI-RADS could accurately detect muscle invasion in BC patients after NAC treatment. VI-RADS scores of bladder cancer after NAC were independently assessed by two radiologists. With an optimal cut-off value ≥4, the AUC values for the VI-RADS scores for predicting muscle invasion were 0.91, and 0.94 for reader 1 and reader 2 respectively. VI-RADS could potentially be a restaging tool for patients who underwent NAC.Objective
Vesical Imaging-Reporting and Data System (VI-RADS) has been shown to be effective in predicting muscle invasion for bladder cancer (BC) without treatment. At present, local tumor restaging after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) treatment is urgently needed. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate whether VI-RADS could accurately detect muscle invasion in BC patients after NAC treatment.Methods
In this retrospective study, patients with MIBC who underwent MRI after neoadjuvant chemotherapy were enrolled from September 2015 to May 2022. VI-RADS scores were independently assessed by two radiologists. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was used to evaluate the diagnostic performance of the VI-RADS scores in the prediction of muscle invasion. Sensitivity, specificity, and area under the curve (AUC) were calculated. Weighted kappa statistic was used to assess the interobserver agreement.Results
A total of 53 patients (median age, 62 years; age range, 29–78 years; 47 men) were included in the final analysis. A total of 28 patients of 53 patients (53%) had MIBC (T2 or higher) and 25 of 53(47%) had NMIBC. With an optimal cut-off value ≥ 4, the AUC values for the VI-RADS scores for predicting muscle invasion were 0.91, and 0.94, for reader 1 and reader 2 respectively. Excellent inter-reader agreement in VI-RADS scoring (k range, 0.88–0.92) was observed.Conclusion
VI-RADS could accurately assess muscle invasion in BC patients after NAC treatment. VI-RADS could potentially be an excellent restaging tool for patients who underwent NAC.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
No reference found.Figures
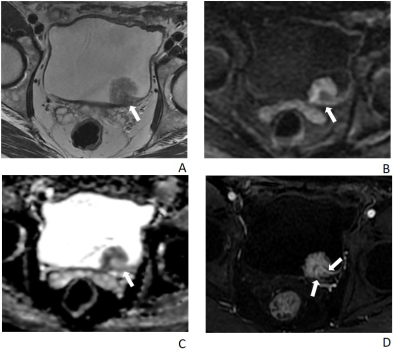
Figure.
1 A 69-year-old man underwent 3 cycles of NAC followed by partial cystectomy.
Histopathology confirmed a non-MIBC. The
score of VI-RADS were all 2.
A,
T2W imaging shows an exophytic tumor with slightly low SI stalk (arrow) on the left
posterior side of bladder.
B
and C, DWI (b = 1000) and ADC map, respectively, show an exophytic lesion with
restricted diffusion, with low SI stalk connecting to left posterior side of
bladder wall on DWI.
D,
Axial DCE T1-weighted image shows tumor at left posterior wall with continuous
submucosal linear enhancement (arrows).
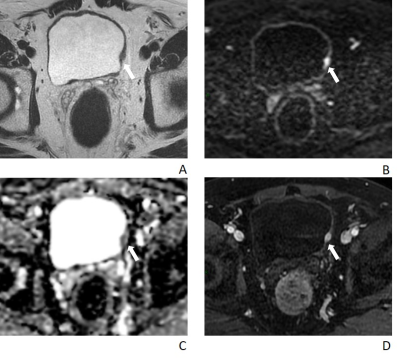
Figure.
2 A 73-year-old man with hematuria underwent 3 cycles of NAC followed by transurethral resection of
the bladder tumor. Histopathology confirmed a MIBC. The score of VI-RADS were all 5.
A,
T2W imaging shows an endophytic tumor extending to extravesical fat on the left
side of bladder,.
B
and C, DWI (b = 1000) and ADC map, respectively, show high SI tumor on DWI and
low SI tumor
on
ADC extending to the entire bladder wall and extravesical fat.
D,
Axial DCE T1W imaging shows tumor early enhancement extends to the entire
bladder wall and to extravesical fat on the left side of bladder.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/1676