1668
Prediction of visceral pleural invasion in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer by T2WI1Hebei Medical University Fourth Affiliated Hospital, Shijiazhuang, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers, Beiing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Cancer, Lung
This study investigated the clinical value of MRI T2WI for VPI in early-stage NSCLC. Four MRI signs of VPI in lung cancer were summarized by MR T2WI of patients with early-stage NSCLC suspected of VPI. Among them, category 3 signs and category 4 signs had higher positive predictive values. This indicates that T2WI is useful in the prediction of VPI in early-stage NSCLC.Introduction
Visceral pleural invasion (Visceral pleural invasion, VPI) is one of the most important poor prognostic factors for lung cancer and a crucial predictor of postoperative recurrence and lymph node metastasis [1-4].The 8th edition of TNM staging standard for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) suggests that T1 lung cancer with VPI should be upgraded to T2, and IA to IB[5]. Preoperative assessment of the presence or absence of VPI plays a significant role in formulating surgical plans and selecting postoperative adjuvant therapy. However, the accuracy of CT features for pathological VPI prediction ranged from 62.7% (432 of 689 patients) to 72.3% (498 of 689 patients),the positive predictive values ranged from 44.1% (173 of 392 patients) to 56.4% (88 of 156 patients), suggesting that approximately half of the CT-based predictions were false-positive[6]. In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) chest scanning, compared with other sequences (such as UTE), T2WI can provide great contrast and details for lung lesions. At present, there is no report on MRI signs of NSCLC VPI. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to investigate the diagnostic value of T2WI for VPI in early-stage NSCLC.Methods
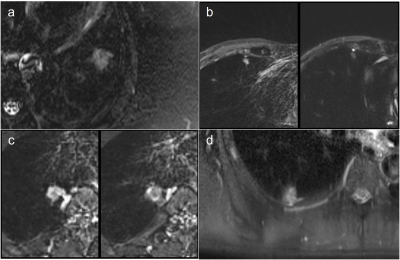
Thirty-three patients (9 males, 14 females, age ranges 32-81 years) with early-stage NSCLC suspected of VPI underwent chest scan on the 3.0 T scanner (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Germany), and all patients gave written informed consent. Among them, there were 21 lesions with VPI confirmed by postoperative pathological elastic fiber staining, and 12 lesions without VPI. T2WI adopts by short-time-inversion-recovery (STIR) sequence scanning, and the parameters are as follows: TE=79 ms, TR=2500 ms, TI=240 ms, flip angle=240°, slice thickness= 3 mm,matrix=320 *320, FOV = 380 *380mm2. The T2WI signal characteristics of all lesions in contact with the pleura were classified into 4 categories: 1, no T2WI high signal; 2, dot-like T2WI signal; 3, line-like T2WI high signal; and 4, rabbit draft sign. as shown in Fig 1. The chi-square test was used to compare the differences of these four types of signals in predicting VPI, and their sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value were calculated respectively.Results
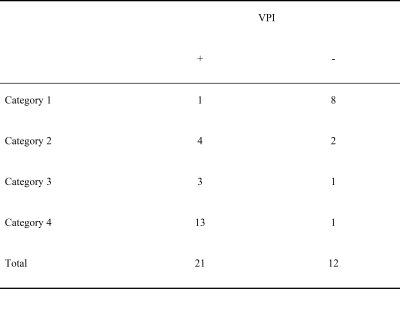
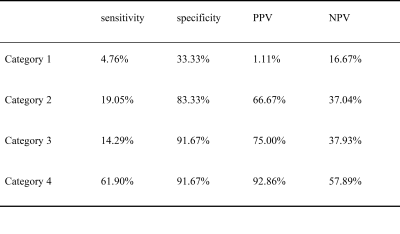
Among all confirmed lesions with VPI, there were 1 case in category 1, 4 cases in category 2, 3 cases in category 3, and 13 cases in category 4, as shown in Table 1. The sensitivity of category 1 in predicting VPI was 4.76%, specificity was 33.33%, positive predictive value was 1.11%, and negative predictive value was 16.67%. The sensitivity of category 2 in predicting VPI was 19.05%, specificity was 83.33%, positive predictive value was 66.67%, and negative predictive value was 37.04%. The sensitivity of category 3 in predicting VPI was 14.29%, specificity was 91.67%, positive predictive value was 75.00%, and negative predictive value was 37.93%.The sensitivity of category 4 in predicting VPI was 67.90%, specificity was 91.67%, positive predictive value was 92.86%, and negative predictive value was 57.89%,as shown in Table 2.Dissussion
The results showed that VPI in early-stage NSCLC had characteristic signs on T2WI. Category 3 and Category 4 signs had higher positive predictive values than CT-based predictions. This may be due to the obstruction of pleural lymphatic backflow by the VPI of lung cancer. There is a very small amount of pleural effusion on the pleural contact surface of the tumor, which can be shown on T2WI. It is a preliminary study of VPI MRI signs of early-stage NSCLC. In the future, a larger sample size and multiple centers need to validate this finding. Accurate prediction of VPI in early-stage NSCLC can improve the prognosis and avoid unnecessary extensive resection, postoperative radiotherapy and chemotherapy.Conclusion
T2WI is useful in the prediction of VPI in early-stage NSCLCKeywords
magnetic resonance imaging, VPI, non-small cell lung cancer, T2WIAcknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Jiwangga D, Cho S, Kim K, Jheon S. Recurrence Pattern of Pathologic Stage I Lung Adenocarcinoma With Visceral Pleural Invasion. Ann Thorac Surg 2017;103(4):1126-31.
[2] Neri S, Menju T, Sowa T, Yutaka Y, Nakajima D, Hamaji M, et al. Prognostic impact of microscopic vessel invasion and visceral pleural invasion and their correlations with epithelial-mesenchymal transition, cancer stemness, and treatment failure in lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2019;128:13-9.
[3] Tian D, Pei Y, Zheng Q, Zhang J, Li S, Wang X, et al. Effect of visceral pleural invasion on the prognosis of patients with lymph node negative non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer 2017;8(2):97-105.
[4] Zhang H, Lu C, Lu Y, Yu B, Lv F, Zhu Z. The predictive and prognostic values of factors associated with visceral pleural involvement in resected lung adenocarcinomas. Onco Targets Ther 2016;9:2337-48. [5] Goldstraw P, Chansky K, Crowley J, Rami-Porta R, Asamura H, Eberhardt WE, et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for Revision of the TNM Stage Groupings in the Forthcoming (Eighth) Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2016;11(1):39-51.
[6] Kim H, Goo JM, Kim YT, Park CM. CT-defined Visceral Pleural Invasion in T1 Lung Adenocarcinoma: Lack of Relationship to Disease-Free Survival. Radiology 2019;292(3):741-9.
Figures