1646
MR-based Radiomics Models for Predicting Pathological Complete Response in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer: A Two-Centre, Multi-Vendor Study1Radiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Guangzhou, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Cancer, Radiomics
The response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) is especially important for prognostic and management decisions. In this study, we used cross-vendor data from two centers to validate the generalization ability of radiomics model based on multiparametric-MRI (MP-MRI) for predicting pCR and to compare the discriminatory performance of different classifiers. Our results demonstrated that radiomics can be used to predict pCR. The clinical-radiomics model had superior performance compared to the radiomics model and clinical model. Furthermore, the RF classifier outperformed the other classifiers in prediction.Introduction
Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) has been proven effective in the downstaging of locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC), and it leads to pathologic complete response (pCR) in about 20% of patients[1-4]. The patient’s response to nCRT is particularly important for prognosis and management decisions[5]. At present, therapy response is determined by histopathologic assessment after surgery[5]. However, predicting pCR prior to resection may aid in treatment planning. Accordingly, development of a noninvasive response evaluation model could aid in the identification of patients with good response who are likely to benefit from local resection, as well as those achieving pCR who might benefit from a watch-and-wait or nonsurgical strategy. Radiomics enables extracting high-dimensional, mineable data from medical images and providing quantitative features that may aid in diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment response, etc.[6] . Moreover, it is important to choose a suitable machine learning method for a radiomics model. Different machine learning methods may show different performance when applied in different organs [7-9]. Therefore, This study aims to use radiomics analysis based on multiparametric MRI(MP-MRI) to predict the pCR of LARC. In addition, different classifiers were compared to determine an optimal machine learning method.Methods
In this study, 151 patients (center I: n=100; center II: n=51; in total 4 vendors) were retrospectively analyzed. The data from center Ⅰ were divided into training set and internal validation set according to the ratio of 8:2, and the data from center Ⅱ were used as external validation set. Radiomic features were extracted from multiparametric MRI, including T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) and diffusion-weighted images (DWI) before and after nCRT. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) was used to filter radiomics features and clinical features. Six classification methods, including logistic regression (LR), support vector machine (SVM), K-nearest neighbor (KNN), naive Bayesian (NB), eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), and random forest (RF) were used to construct prediction models (clinical model, radiomics model, and clinical- radiomics combined models). Performance was compared by AUC, sensitivity, accuracy, precision, and specificity. Histological results were used as the reference standard.Results
Eleven radiomics feature and four clinical features were chosen as pCR- related signatures (Figure 1). In the clinical model, the RF classifier showed the best prediction performance in the external validation set with an AUC of 0.687 and an accuracy of 68.7% (Table 1). In the radiomics model, the RF algorithm achieved 74.0% accuracy (an AUC of 0.863) and 84.4% (an AUC of 0.829) in the internal and external validation sets (Table 2). In clinical-radiomics model, RF algorithm exhibited high and stable predictive performance in the internal and external validation datasets with an AUC of 0.906 (87.3% sensitivity, 73.7 % specificity, 76.0% accuracy) and 0.872 (77.3% sensitivity, 88.2% specificity, 86.3% accuracy), respectively (Table 3). RF showed a better predictive performance than the other classifiers in the external validation datasets of three models.Discussion
In this study, we developed and validated multi-machine learning models (clinical, radiomics, and clinical- radiomics model) to predict the pCR of LARC, and compared the performance of different classification algorithms. The radiomics-clinical model showed improved performance in predicting pCR except for NB classifier. RF exhibited higher AUC and accuracy than other classifiers in the external validation cohorts of three models. Furthermore, the clinical-radiomics model combined with the RF algorithm achieved the high and stable predictive capability in both validation and testing cohorts. Studies demonstrated that an ML approach can achieve satisfactory overall diagnostic accuracy when predicting good response, down-staging, or pCR[10, 11]. Compared to previous studies that were primarily focused on MR-based radiomics acquired before nCRT[11, 12], we added T2WI and DWI MR information after nCRT to the analysis of radiomics.As pre-treatment MRIs are associated with response to chemoradiotherapy, radiomics information obtained after nCRT is closer to the surgical pathology, which can improve the model's reliability in detecting pCR. Additionally, MRI radiomics after nCRT provides values that determine a decision on organ preservation before treatment. Our results partially agree with those of Bulens et al and Liu et al, who demonstrated the importance of post-chemoradiation therapy MR data in the evaluation of tumour response[13, 14].Conclusion
In this study we developed and validated MP-MRI-based radiomics models for predicting pCR, which proved to be accurate and generalizable.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgment was found.References
1. Benson AB, Venook AP, Al-Hawary MM, et al. Rectal Cancer, Version 2.2018, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network : JNCCN 2018; 16:874-901
2. van der Valk MJM, Hilling DE, Bastiaannet E, et al. Long-term outcomes of clinical complete responders after neoadjuvant treatment for rectal cancer in the International Watch & Wait Database (IWWD): an international multicentre registry study. Lancet (London, England) 2018; 391:2537-2545
3. Maas M, Nelemans PJ, Valentini V, et al. Long-term outcome in patients with a pathological complete response after chemoradiation for rectal cancer: a pooled analysis of individual patient data. The Lancet Oncology 2010; 11:835-844
4. Al-Sukhni E, Attwood K, Mattson DM, Gabriel E, Nurkin SJ. Predictors of Pathologic Complete Response Following Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy for Rectal Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2016; 23:1177-1186
5. Patel UB, Taylor F, Blomqvist L, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging-detected tumor response for locally advanced rectal cancer predicts survival outcomes: MERCURY experience. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29:3753-3760
6. Bi WL, Hosny A, Schabath MB, et al. Artificial intelligence in cancer imaging: Clinical challenges and applications. CA Cancer J Clin 2019; 69:127-157
7. Yin P, Mao N, Zhao C, et al. Comparison of radiomics machine-learning classifiers and feature selection for differentiation of sacral chordoma and sacral giant cell tumour based on 3D computed tomography features. Eur Radiol 2019; 29:1841-1847
8. Maniruzzaman M, Jahanur Rahman M, Ahammed B, et al. Statistical characterization and classification of colon microarray gene expression data using multiple machine learning paradigms. Computer methods and programs in biomedicine 2019; 176:173-193
9. Zhang Y, Cheng C, Liu Z, et al. Radiomics analysis for the differentiation of autoimmune pancreatitis and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in (18) F-FDG PET/CT. Med Phys 2019; 46:4520-4530
10. Shi L, Zhang Y, Nie K, et al. Machine learning for prediction of chemoradiation therapy response in rectal cancer using pre-treatment and mid-radiation multi-parametric MRI. Magn Reson Imaging 2019; 61:33-40
11. Antunes JT, Ofshteyn A, Bera K, et al. Radiomic Features of Primary Rectal Cancers on Baseline T(2) -Weighted MRI Are Associated With Pathologic Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation: A Multisite Study. J Magn Reson Imaging 2020; 52:1531-1541
12. Petresc B, Lebovici A, Caraiani C, Feier DS, Graur F, Buruian MM. Pre-Treatment T2-WI Based Radiomics Features for Prediction of Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer Non-Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy: A Preliminary Study. Cancers 2020; 12
13. Liu Z, Zhang XY, Shi YJ, et al. Radiomics Analysis for Evaluation of Pathological Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2017; 23:7253-7262
14. Bulens P, Couwenberg A, Intven M, et al. Predicting the tumor response to chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer: Model development and external validation using MRI radiomics. Radiother Oncol 2020; 142:246-252
15. Da-Ano R, Visvikis D, Hatt M. Harmonization strategies for multicenter radiomics investigations. Phys Med Biol 2020; 65:24tr02
16. Orlhac F, Lecler A, Savatovski J, et al. How can we combat multicenter variability in MR radiomics? Validation of a correction procedure. Eur Radiol 2021; 31:2272-2280
Figures
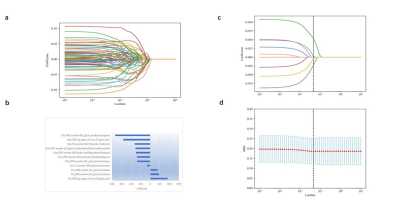
Figure 1: The radiomics and clinical features were selected using the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression model. (a) LASSO regression coefficients of radiomics features. (b) After multiple comparisons correction, a total of 11 radiomics features were selected. (c) When performing feature selection of clinical features, we use MSE to calculate the loss and determine the optimal value of λ at the minimum MSE (indicated by the dotted line in the figure). (d) The four optimal clinical features with nonzero coefficients are indicated in the plot.
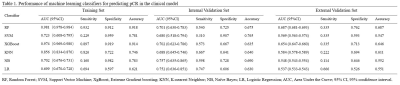
Table 1. Performance of machine learning classifiers for predicting pCR in the clinical model
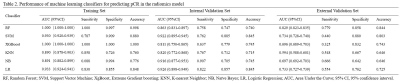
Table 2. Performance of machine learning classifiers for predicting pCR in the radiomics model
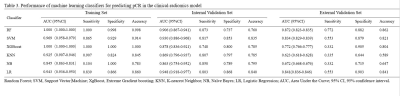
Table 3. Performance of machine learning classifiers for predicting pCR in the clinical-radiomics model