1617
Joint MR T1 and T2* Parameter Mapping with Scan Specific Unsupervised Networks1Industrial Engineering and Management Systems, Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran, Iran (Islamic Republic of), 2Department of Computer Engineering, Hongik University, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 3Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, United States, 4Radiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Quantitative Imaging, Quantitative Imaging, Image Reconstruction
We introduce a new method for joint T1 and T2* MR parameter mapping in MAPLE framework which takes advantage of multi-echo multi-flip angle (MEMFA) gradient echo data. It combines joint reconstruction of MEMFA data with a joint relaxation signal model to improve parameter estimation. The proposed method estimates T1 and T2* parameters jointly with enough flexibility to incorporate different standard and state-of-the-art reconstruction methods, including zero-shot self-supervised learning (ZS-SSL) reconstruction. It improves the reconstruction performance of the methods with learnable parameters by offering a physics-based additional regularization into their optimization process and exploiting spatio-temporal correlations.Introduction
While MRI is a powerful imaging modality allowing quantitative measurements of inherent tissue parameters including T1 ,T2 and T*2 maps, the long scan time has been one of the major limitations [1]. The main approaches to existing accelerated MR parameter mapping are reconstruction-based [2]–[7], model-based [8]–[14], and deep learning methods [15]–[18]. Recently Kim et. al. [19] introduced a novel parameter mapping named MAPLE, which synergistically combined reconstruction- and model-based methods while avoiding drawbacks of large-scale networks. In this work, we introduce a new parameter estimation method that synergizes information available in a scan-specific MEMFA dataset to jointly estimate T1 , T*2 and field map parameters simultaneously. This work is an extension of MAPLE enabling joint estimation of T1 and T*2 . We also embedded zero-shot self-supervised learning (ZS-SSL) [20] as a physics-guided scan-specific unsupervised network into this framework for improved joint MR parameter estimation.Theory and Methods
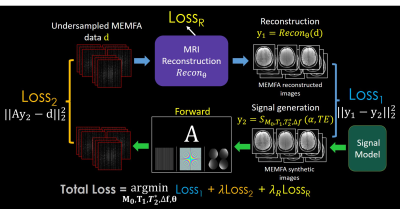
Fig. 1. shows the main steps of the proposed method based on the MAPLE framework. At first step, the reconstruction block (top left) inputs the undersampled MEMFA k-space data into an image reconstruction method to reconstruct MEMFA images. Joint reconstruction of MEMFA data has a synergic effect and improves the performance. The signal model (bottom right) block generates the synthetic MEMFA images corresponding to the joint relaxation signal model with estimated parameters M0 (proton density), T1 , T*2 , and Δf (field map). The joint formulation of the relaxation signal model processes data with diversity in echo times (TEs) and FAs. Thus, with richer structure of data, it improves the generated synthetic data as the output of the signal model block.Loss1 is computed by comparing the reconstructed and synthetic MEMFA images. The synthetic images are then transformed to their corresponding undersampled k-space data through a forward model A which incorporates coil sensitivity maps, Fourier transform, and undersampling. Matching the original undersampled k-space data and the output of the forward model forms the Loss2 function. A third loss function LossR , is used in cases where the reconstruction method includes learnable parameters "θ". A scaled summation of these three loss function creates the final loss function Loss which jointly optimizes M0, T1 , T2* and θ parameters.
The proposed joint MAPLE framework can tune the learnable parameters of the reconstruction method with the outputs of a physics-based signal model which can exploit spatio-temporal correlations in MEMFA data. ZS-SSL as a scan-specific unsupervised network has an unrolled network structure with convolutional operators which uses a small number of learnable parameters in comparison to other supervised approaches, and is further incorporated into the proposed joint MAPLE.
Dataset: We acquired a fully sampled in-vivo data with 6 echoes and 3 FAs from a Siemens scanner using a 32-channel head-coil, FOV=224mmx192mm, matrix size=224x192, TR=34ms, FAs=(4,10,14) with 6 TEs for each FA and first TE=3.6ms and ΔTE=5ms. We used joint T1 / T2* relaxation signal model as follows:
$$S_{M_{0},T_{1},T_2^*,\Delta\mathbf{f}}(\alpha,TE)[M_{0}exp(-TE/T_2^*)exp(i2\pi\Delta\mathbf{f}.TE)]sin(\alpha)\frac{1-exp(-TR/T_{1})}{1-cos(\alpha)exp(-TR/T_{1})}$$
With $$$\mathbf{M}_0\in\mathbb{C}$$$ and $$$ \mathbf{T}_1,\mathbf{T}_2^*\in\mathbb{R}$$$ and an additional phase $$$\Delta\mathbf{f}\in\mathbb{R}$$$ from magnetic field inhomogeneities. The performance of the proposed model is evaluated in the presence of different reconstruction methods of SENSE [21], SENSE with joint total variation (SENSE-JTV) [22], LORAKI [23] and ZS-SSL.
Results
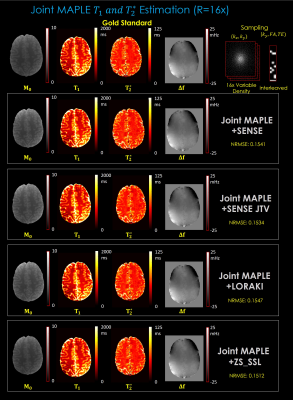
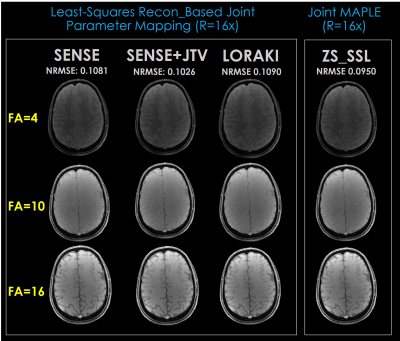
Fig. 2. shows the parameter maps estimated by the proposed joint MAPLE with 2D R=16x variable density undersampling and demonstrates the flexibility of the method synergizing with the powerful methods like ZS-SSL as well as the standard ones. Among the multiple reconstruction methods, ZS-SSL shows better performance in terms of NRMSE which was computed between the fully sampled and the synthetic data generated from the estimated parameter maps.Fig. 3. shows images of the first echo time (TE= 3.6ms) of each FA (4, 6, 10) from an MEMFA image structure generated by the proposed joint signal model after M0, T1 , T2*, Δf estimation. Images related to SENSE, SENSE+JTV and LORAKI generated with conventional least-squares fitting. ZS-SSL images are generated using joint MAPLE. The proposed method works well in two approaches at high acceleration (R=16x) and MAPLE with ZS-SSL outperforms the conventional approach.
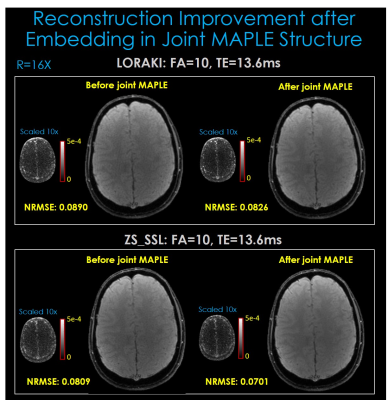
Fig. 4. indicates that joint MAPLE improves the performance of reconstruction algorithms with learnable parameters. When their parameters are tuned with physics-based new regularization which exploits spatio-temporal correlations, they can generate more precise MEMFA images. Fig. 4. also shows improvement in the error images of LORAKI and ZS-SSL which have already powerful performance after one plug and play iteration.
Discussion and Conclusion
In joint MAPLE, we extended the MR parameter mapping that can jointly estimate T1 and T2* parameters taking advantage of multi-echo multi-flip angle data and both reconstruction-based and model-based parameter mapping approaches. The proposed joint estimation model is flexible enough to work with the standard and the-state-of-the-art reconstruction algorithms. We incorporated ZS-SSL reconstruction method in the proposed method and demonstrated that it outperforms the other benchmarked methods. The proposed joint signal model is differentiable and training can be conducted automatically through deep learning toolboxes. Joint MAPLE can improve the reconstruction performance of methods with learnable parameters.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by research grants NIH R01 EB028797, U01 EB025162, P41 EB030006, U01 EB026996, R03 EB031175 and the NVidia Corporation for computing support.References
[1] L. Feng, D. Ma, and F. Liu, “Rapid MR relaxometry using deep learning: An overview of current techniques and emerging trends,” NMR Biomed., vol. 35, no. 4, p. e4416, 2022.
[2] L. Wang, M. E. Schweitzer, A. Padua, and R. R. Regatte, “Rapid 3D‐T1 mapping of cartilage with variable flip angle and parallel imaging at 3.0 T,” J. Magn. Reson. Imaging An Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med., vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 154–161, 2008.
[3] M. Doneva, P. Börnert, H. Eggers, C. Stehning, J. Sénégas, and A. Mertins, “Compressed sensing reconstruction for magnetic resonance parameter mapping,” Magn. Reson. Med., vol. 64, no. 4, pp. 1114–1120, 2010.
[4] C. Huang, C. G. Graff, E. W. Clarkson, A. Bilgin, and M. I. Altbach, “T2 mapping from highly undersampled data by reconstruction of principal component coefficient maps using compressed sensing,” Magn. Reson. Med., vol. 67, no. 5, pp. 1355–1366, 2012.
[5] J. V Velikina, A. L. Alexander, and A. Samsonov, “Accelerating MR parameter mapping using sparsity‐promoting regularization in parametric dimension,” Magn. Reson. Med., vol. 70, no. 5, pp. 1263–1273, 2013.
[6] T. Zhang and J. M. Pauly, “Levesque IRJMrim,” Accel. Param. Mapp. with a Local. low Rank constraint, vol. 73, no. 2, pp. 655–661, 2015.
[7] B. Zhao, W. Lu, T. K. Hitchens, F. Lam, C. Ho, and Z. Liang, “Accelerated MR parameter mapping with low‐rank and sparsity constraints,” Magn. Reson. Med., vol. 74, no. 2, pp. 489–498, 2015.
[8] T. J. Sumpf, M. Uecker, S. Boretius, and J. Frahm, “Model‐based nonlinear inverse reconstruction for T2 mapping using highly undersampled spin‐echo MRI,” J. Magn. Reson. Imaging, vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 420–428, 2011.
[9] T. J. Sumpf, A. Petrovic, M. Uecker, F. Knoll, and J. Frahm, “Fast T2 mapping with improved accuracy using undersampled spin-echo MRI and model-based reconstructions with a generating function,” IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, vol. 33, no. 12, pp. 2213–2222, 2014.
[10] B. Zhao, F. Lam, and Z.-P. Liang, “Model-based MR parameter mapping with sparsity constraints: parameter estimation and performance bounds,” IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, vol. 33, no. 9, pp. 1832–1844, 2014.
[11] V. Roeloffs, X. Wang, T. J. Sumpf, M. Untenberger, D. Voit, and J. Frahm, “Model‐based reconstruction for T1 mapping using single‐shot inversion‐recovery radial FLASH,” Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol., vol. 26, no. 4, pp. 254–263, 2016.
[12] X. Wang et al., “Model‐based T 1 mapping with sparsity constraints using single‐shot inversion‐recovery radial FLASH,” Magn. Reson. Med., vol. 79, no. 2, pp. 730–740, 2018.
[13] T. Hilbert et al., “Accelerated T2 mapping combining parallel MRI and model‐based reconstruction: GRAPPATINI,” J. Magn. Reson. Imaging, vol. 48, no. 2, pp. 359–368, 2018.
[14] O. Maier et al., “Rapid T1 quantification from high resolution 3D data with model‐based reconstruction,” Magn. Reson. Med., vol. 81, no. 3, pp. 2072–2089, 2019.
[15] O. Cohen, B. Zhu, and M. S. Rosen, “MR fingerprinting deep reconstruction network (DRONE),” Magn. Reson. Med., vol. 80, no. 3, pp. 885–894, 2018.
[16] F. Liu, L. Feng, and R. Kijowski, “MANTIS: Model‐Augmented Neural neTwork with Incoherent k‐space Sampling for efficient MR parameter mapping,” Magn. Reson. Med., vol. 82, no. 1, pp. 174–188, 2019.
[17] F. Liu, R. Kijowski, G. El Fakhri, and L. Feng, “Magnetic resonance parameter mapping using model‐guided self‐supervised deep learning,” Magn. Reson. Med., vol. 85, no. 6, pp. 3211–3226, 2021.
[18] Y. Jun, H. Shin, T. Eo, T. Kim, and D. Hwang, “Deep model-based magnetic resonance parameter mapping network (DOPAMINE) for fast T1 mapping using variable flip angle method,” Med. Image Anal., vol. 70, p. 102017, 2021.
[19] T. H. Kim, J. Cho, B. Zhao, B. Bilgic. Accelerated MR Parameter Mapping With Scan-Specific Unsupervised Networks. International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Annual Meeting (ISMRM), London, 2022, p. 4402.
[20] B. Yaman, S. A. H. Hosseini, and M. Akçakaya, “Zero-shot self-supervised learning for MRI reconstruction,” arXiv Prepr. arXiv2102.07737, 2021.
[21] Pruessmann, K. P., Weiger, M., Scheidegger, M. B. & Boesiger, P. SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. An Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 42, 952–962 (1999).
[22] Chen, C., Li, Y. & Huang, J. Calibrationless parallel MRI with joint total variation regularization. in International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention 106–114 (Springer, 2013).
[23] Kim, T. H., Garg, P. & Haldar, J. P. LORAKI: Autocalibrated recurrent neural networks for autoregressive MRI reconstruction in k-space. arXiv Prepr. arXiv1904.09390 (2019).
Figures