1572
The value of an apparent diffusion coefficient histogram model in predicting meningioma recurrence1Lanzhou University Second Hospital, LanZhou, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Tumors, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques
This study evaluated the feasibility of the model combining conventional MRI features and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) histogram parameters for predicting recurrent meningioma. The results showed that tumor shape and ADCp1 were independent risk factors for predicting meningioma recurrence after removing confounding factors by single and multiple logistic regression analysis. The logistic regression model nomogram constructed based on the above two risk factors for predicting meningioma recurrence, which had a higher predictive effect than a single risk factor. In conclusion, logistic regression model nomogram have important value in predicting meningioma recurrence and helping patients achieve the greatest survival benefit.Introduction
Introduction: Meningiomas arise from arachnoid cap cells and account for more than one-third of all primary central nervous system tumors1. More than 80% of meningiomas are low-grade and, although generally considered benign, some of these cases may be more aggressive, behaving similarly to high-grade lesions, with recurrence rates of 7–25%2. WHO grade II meningiomas exhibit intermediate biological behavior between those of benign and malignant meningiomas, with higher recurrence rates than those of low-grade meningiomas, at 29–52%3. WHO grade III meningiomas are the most malignant meningiomas, accounting for 1–3% of all meningiomas and showing a very high tendency to invade and recur, with a recurrence rate of about 50–94% after surgical resection4. Previous study5 have suggested that recurrent atypical meningiomas are intractable tumors with very high recurrence and mortality rates and may predict poor outcomes. Therefore, thorough analysis and understanding of the factors influencing meningioma recurrence are important for patient management and achieving individualized treatment. Histogram analysis is a mathematical method that comprehensively assesses the biological characteristics of tumors and reflects tumor heterogeneity by automatically generating multiple quantitative parameters from delineated regions of interest (ROIs)6. Kurokawa et al.7 have demonstrated that apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) histogram analysis is effective in predicting recurrence in glioblastoma patients. These studies suggest that ADC histogram analysis may also be utilized as a quantitative method to predict meningioma recurrence. A further previous study8 has shown that factors such as age, tumor location, histopathological grade, degree of resection, Ki-67 proliferation index, and maximum tumor diameter are closely related to recurrence in patients with meningioma. Given the limited precision and validity of a single factor for predicting recurrence, a comprehensive evaluation system containing multiple factors may be more suitable.The purpose of study to investigate the predictive value of a model combining conventional MRI features and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) histogram parameters for recurrent meningioma.Method
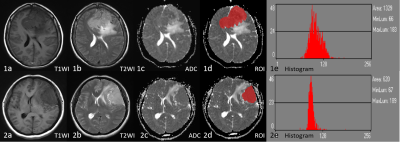
Methods: Seventy-two patients with meningioma confirmed by surgical and pathological findings in our hospital (January 2017 – June 2020) were retrospectively assigned to either the recurrence or non-recurrence group, based on whether they developed recurrence before June 2022. MaZda software was used to delineate the region of interest at the largest tumor level and generate histogram parameters which, in combination with conventional MRI features, informed a logistic regression model nomogram for predicting recurrence. The predictive efficacy and diagnostic of this model were assessed by calibration and decision curves, and receiver operating characteristic curve, respectively.Results
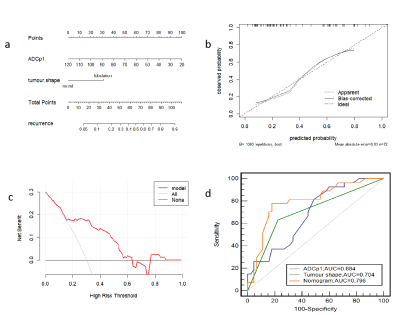
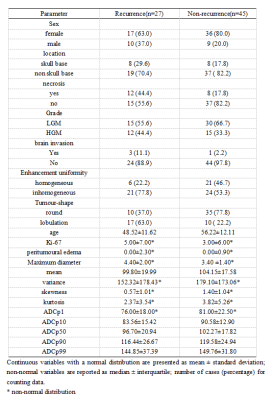
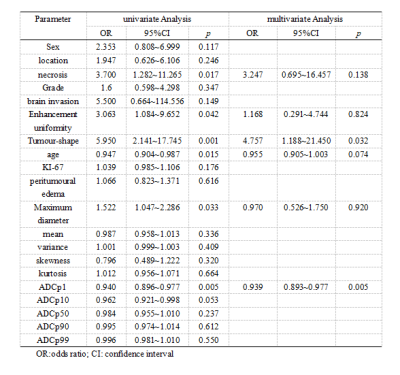
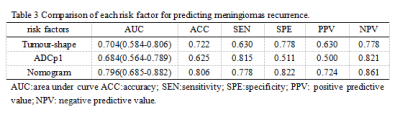
Results: Age, maximum diameter, necrosis, enhancement uniformity, tumor shape, and ADC first percentile (ADCp1) were significantly different histogram parameters between the two groups (p < 0.05), with the latter two being independent risk factors for recurrence. The model constructed using these two factors had the best predictive efficacy, and its area under the curve, accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value were 0.796 (0.685–0.882), 80.6%, 77.8%, 88.2%, 72.4%, and 86.1%, respectively. The calibration curve showed good agreement between the model-predicted and actual probabilities of recurrence. The decision curve indicated good clinical availability of the model.Discussion
Dicussion: This study constructed a model based on conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) features and ADC histogram parameters to comprehensively and intuitively predict recurrence in meningioma patients and help achieve accurate management and treatment. To our knowledge, this is also the first study to use ADC histograms to predict meningioma recurrence. Accurate prediction of meningioma recurrence is helpful for postoperative management of patients with meningioma, as well as for achieving individualized treatment. The results of this study showed that ADCp1 and tumor shape were two independent risk factors for predicting meningioma recurrence, and the logistic regression model nomogram constructed by fusing the two had the best efficacy in predicting meningioma recurrence. Our study showed that mean, ADCp1, ADCp10, ADCp50, ADCp90, and ADCp99 in the recurrence group were less than those in the non-recurrence group, and ADCp1 was significantly different between the two groups. Contrary to the expected results, variance, skewness, and kurtosis were lower in the recurrence group than in the non-recurrence group. We believe that the most likely explanation for this difference is that delineation of ROIs in this study avoided macroscopic necrosis and hemorrhage, thus affecting the spatial distribution of ADC histograms. It may also be associated with the insufficient sample size in this study. The logistic regression model nomogram constructed based on the above two risk factors for predicting meningioma recurrence, which had a higher predictive effect than a single risk factor. The predicted probability of the calibration curve of this model is in good agreement with the actual probability, which indicates the reliability and reproducibility of the nomogram. Preoperative predicting meningioma recurrence is instructive for clinical development of appropriate surgical plans to help patients achieve the greatest survival benefit.Conclusion
Conclusion: This model based on conventional MRI features and ADC histogram parameters can directly and reliably predict meningioma recurrence, providing a guiding basis for selecting treatment options and individualized treatment.Acknowledgements
We are greatly indebted to all patients, doctors, and statistical consultants who were involved in our study.References
1. Ogasawara C, Philbrick BD, Adamson DC. Meningioma: A Review of Epidemiology, Pathology, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Future Directions[J]. Biomedicines. 2021;9(3).
2. Youngblood MW, Miyagishima DF, Jin L, et al. Associations of meningioma molecular subgroup and tumor recurrence[J]. Neuro-oncology. 2021;23(5):783-94.
3. Garzon-Muvdi T, Maxwell R, Luksik A, et al. Scalp Invasion by Atypical or Anaplastic Meningioma Is a Risk Factor for Development of Systemic Metastasis[J]. World neurosurgery. 2020;142:e133-e9.
4. Zhang GS, Zhang YY, He F, et al. Primary intracranial papillary meningioma: Analysis of factors of prognosis and systematic review[J]. Journal of clinical neuroscience : official journal of the Neurosurgical Society of Australasia. 2021;91:118-24.
5. Cao X, Hao S, Wu Z, et al. Treatment Response and Prognosis After Recurrence of Atypical Meningiomas[J]. World neurosurgery. 2015;84(4):1014-9.
6. Ozturk M, Polat AV, Selcuk MB. Whole-lesion ADC histogram analysis versus single-slice ADC measurement for the differentiation of benign and malignant soft tissue tumors[J]. European journal of radiology. 2021;143:109934.
7. Kurokawa R, Baba A, Kurokawa M, et al. Pretreatment ADC Histogram Analysis as a Prognostic Imaging Biomarker for Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma Treated with Bevacizumab: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis[J]. AJNR American journal of neuroradiology. 2022;43(2):202-6.
8. Hortobágyi T, Bencze J, Varkoly G, Kouhsari MC, Klekner Á. Meningioma recurrence[J]. Open medicine (Warsaw, Poland). 2016;11(1):168-73.
Figures