1564
Application of Water-Fat Imaging in Spinal Diseases: comparison with conventional T1-weighted and T2-weighted STIR Images
Nan Wang1, Guobin Li2, Shuheng Zhang2, Dan Yu3, Yongming Dai3, and Qingwei Song1
1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare Co., Ltd, Shanghai, China, 3MR Collaboration, Central Research Institute, United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China
1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare Co., Ltd, Shanghai, China, 3MR Collaboration, Central Research Institute, United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Cancer, Whole Body
Water-Fat Imaging (WFI) based on chemical shifts can provide excellent separation of water and fat in tissue. This work investigated the application of WFI to spinal diseases. The diagnosis performances were compared with the T1-weighted (T1W) and T2-weighted short-TI-inversion-recovery (T2W STIR) sequence. For hyperosteogeny, spinal metastasis, and disc herniation, the WFI showed comparable performance as the combination of T1W and T2W STIR imaging within a much shorter acquisition time.Summary of Main Findings
For common spinal diseases, WFI FSE T2 weighted can replace T1-weighted and T2-weighted STIR while reducing the total scanning time.Introduction
There exist different types of fat-suppression techniques, including chemical shift selective fat saturation (CHESS), short inversion time inversion recovery (STIR), and the water-fat imaging technique (WFI). The WFI is a chemical shift-based water-fat separation technique that exploits the chemical shift between protons of water and fat to decompose the signal from these two tissues in the same voxel, producing four image sets: in-phase (IP, equivalent to standard non-fat suppressed images), out-of-phase (OP), water-only, and fat-only images. Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (WB-MRI) has become increasingly popular during the past decades[1,2]. The absence of radiation exposure and contrast-agent administration provides advantages in addition to high sensitivity to depiction of bone, soft tissue, and visceral structures. Whole-spine scanning is essential for whole-body magnetic resonance imaging, which was limited by scanning time. Applying WFI and AI-assisted Compressed Sensing (ACS) technology can significantly shorten the scanning time and provide a variety of images simultaneously. The purpose of this study was to compare the diagnostic performance of WFI Fast-Spin-Echo T2-weighted imaging (FSE T2WI) with conventional T1-weighted (T1W) and T2-weighted (T2W) STIR imaging in spinal disease detection.Materials and methods
Between September 2022 and October 2022, 12 patients who had undergone whole-spine MRI performed on a 3T MR system ((uMR Omega, United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China)) were enrolled. Three diseases were assessed, including hyperosteogeny, spinal metastasis, and disc herniation. The following sagittal imaging sequences were evaluated: T1W, T2W-STIR, and WFI FSE T2W. The whole spine scan was divided into three sections. The total scanning time of WFI FSE T2W sequence was 5min03s. The total scanning time of T1W and T2W STIR sequences was 7min21s. Detailed protocols are shown in Table 1. Two radiologists independently evaluated each image set for lesions. The Kappa test was used to analyze the intra-observer and inter-observer consistency of bone lesion assessment and to evaluate the performance of WFI FSE T2WI on spine diseases.Results
The intra- and inter-obsevers reliabilities were excellent.. The consistency of the evaluation of vertebral hyperosteogeny, spinal metastasis, and disc herniation by T1WI, T2W STIR images, and WFI FSE T2WI for observer 1 was 0.936, 0.932, and 0.931, respectively. The consistency of the evaluation of vertebral hyperosteogeny, spinal metastasis, and disc herniation by T1WI, T2W STIR, and WFI FSE T2WI for observer 2 was 0.926, 0.946, and 0.909, respectively. The consistency of vertebral hyperosteogeny, spinal metastasis, and disc herniation by WFI FSE T2WI between observers 1 and 2 were 0.974, 0.871, and 0.945, respectively.Discussion and Conclusions
WFI FSE T2-weighted images could provide a variety of comparisons(IP, OP, Water and Fat). The WFI sequence provides a variety of contrast images through one scan, which is beneficial to detect lesions. The diagnostic performance of WFI FSE T2 weighted imaging was comparable to that of conventional T1WI and T2WI-STIR in detecting spinal diseases.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1]. Na Kim J, Jin Park H, Yeon Won S, et al. Whole-body MRI for preventive health screening in a general population: Prevalence of incidental findings around the hip[J]. Eur J Radiol. 2022, 150:110239.
[2]. Van Nieuwenhove S, Van Damme J, Padhani AR, et al. Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging for prostate cancer assessment: Current status and future directions[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022, 55(3):653-680.
Figures
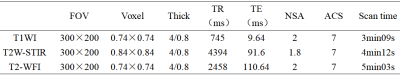
Table 1: Full spine scanning parameters
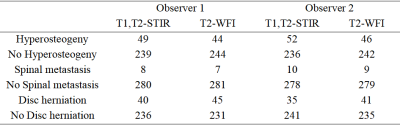
Table 2: Two observers evaluated the count of spinal lesions
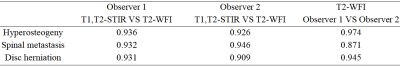
Table 3: Evaluation of lesion consistency
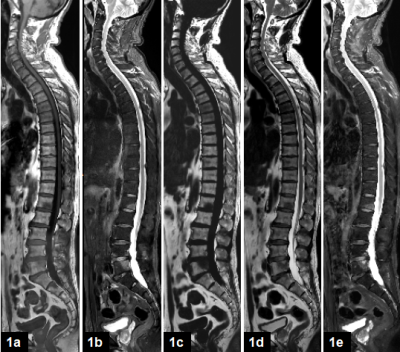
Fig1. 1a-1e are full spine image of 65-year-old male lung cancer patient, T1WI, T2-STIR, T2-WFI(Fat), T2-WFI(IP), T2-WFI(Water). Either conventional T1WI, T2-STIR or T2-WFI sequence can clearly show vertebral metastasis of lumbar1 and lumbar5.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/1564