1505
Study on the influence of different scanning directions of whole-body MRI on the detection of lesions1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare Co., Ltd, Shanghai, China, 3MR Collaboration, Central Research Institute, United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Cancer, Whole Body
Whole-body MRI (WB-MRI) is proposed as a potential modality to evaluate the entire body with excellent spatial resolution and high sensitivity. However, the long scanning time of WB-MRI has still limited the clinical application. This study compared the time cost and lesion display effect of WB-MRI in different scan directions. This study demonstrated that using coronal scanning in WB-MRI is an effective method to reduce the scan time and achieve good performance in detecting lesions in clinical applications.Summary of Main Findings
On the premise of ensuring the accuracy of diagnosis and the detection of lesions, the coronal scanning of whole-body magnetic resonance can save scanning time.Introduction
Whole-body MRI (WB-MRI) is a powerful imaging modality for the detection and characterization of pathologies in multiple organs[1.2]. Compared to computed tomography (CT) and other imaging modality, WB-MRI can provide a wide anatomical coverage without exposing subjects to ionizing radiation. Improvements in scanner performance and optimization of pulse sequences have effectively reduced acquisition times and paved the way for the adoption of WB-MRI in several clinical contexts[3.4]. However, the long scanning time of WB-MRI has still limited the clinical application. Different scanning directions have different scanning times for lesion display, therefore choosing the reliable scanning direction can reduce the scanning time and obtain higher image quality for lesion detection. The purpose of our study was to compare the time cost and lesion display effect of coronal and transverse WB-MRI scans.Materials and methods
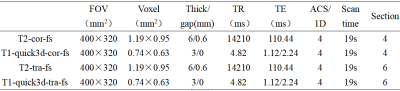
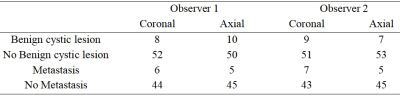
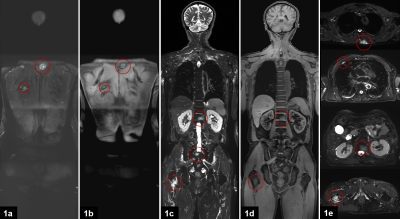
Between September 2022 and October 2022, 10 patients who had undergone the coronal and axial position of whole-body MRI (WB-MRI) were enrolled in a 3T MR system (uMR Omega, United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China). Among them, two diseases including benign cystic lesion and metastasis were analyzed. The following image sets were evaluated: T2-cor-fs, T1-quick3d-cor-fs, T2-tra-fs, T1-quick3d-tra-fs. The coronal WB-MRI scanning was divided into four parts. The axial WB-MRI scanning was divided into six parts. The total scanning time of coronal WB-MRI was 152s. The total scanning time of axial WB-MRI was 228s. Table 1 showed detailed scanning parameters. Two observers independently evaluated each image for lesions (Table 2). The Kappa test was used to analyze the inter-observer consistency of lesion assessment, and to evaluate the performance of coronal WB-MRI on diseases.Results
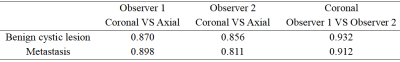
Compared with axial scanning, coronal scanning saves about 33% time in whole-body magnetic resonance (Table 1). The two observers have a high degree of consistency in the identification of lesions using coronal WB-MRI. In the evaluation of both benign cystic lesion and metastasis, the consistency between coronal and axial were 0.870, and 0.898 for observer 1 and 0.856, and 0.811 for observer 2, respectively (Table 3). The consistency of benign cystic lesion and metastasis by coronal WB-MRI between observers 1 and 2 were 0.932 and 0.912 respectively (Table 3).Discussion and Conclusions
Whole-body MRI is proposed as a potential modality to evaluate the entire body with excellent spatial resolution and high sensitivity. This study compared the time cost and lesion display effect of WB-MRI in different scan directions. Results showed that WB-MRI with coronal scanning could save about 33% scanning times while maintaining equal diagnostic confidence compared to transverse WB-MRI scans. In clinical applications, the shorter acquisition time could reduce the appearance of motion artifacts and enhance the patient experience of WB-MRI scanning. In addition, accurately detecting lesions is crucial in clinical detection, the good consistency between coronal and axial may indicate that using coronal scanning in WB-MRI is an effective method to reduce the scan time and achieve good performance in detecting lesions. In conclusion, this study showed that in disease detection, segmented coronal scanning can save time compared with segmented axial scanning, and has the same disease detection effect.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1]. Lee SY, Park HJ, Kim MS, et al. An initial experience with the use of whole body MRI for cancer screening and regular health checks[J]. PLoS One. 2018, 13(11):e0206681.
[2]. Na Kim J, Jin Park H, Yeon Won S, er al. Whole-body MRI for preventive health screening in a general population: Prevalence of incidental findings around the hip[J]. Eur J Radiol. 2022, 150:110239.
[3]. Tarnoki DL, Tarnoki AD, Richter A, et al. Clinical value of whole-body magnetic resonance imaging in health screening of general adult population[J]. Radiol Oncol. 2015, 49(1):10-6.
[4]. Zugni F, Padhani AR, Koh DM, et al. Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (WB-MRI) for cancer screening in asymptomatic subjects of the general population: review and recommendations[J]. Cancer Imaging. 2020, 20(1):34.