1473
Deep Learning Reconstruction to Pelvis Multi-Shot DWI Improved Image Quality with Less Image Distortion: A Preliminary Study
Elaine Yuen Phin Lee1, Chia-Wei Li2, Patricia Lan3, Xinzeng Wang4, Arnaud Guidon5, and Chien-Yuan Lin2
1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Queen Mary Hospital, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China, 2GE Healthcare, Taipei, Taiwan, 3GE Healthcare, Menlo Park, CA, United States, 4GE Healthcare, Houston, TX, United States, 5GE Healthcare, Boston, MA, United States
1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Queen Mary Hospital, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China, 2GE Healthcare, Taipei, Taiwan, 3GE Healthcare, Menlo Park, CA, United States, 4GE Healthcare, Houston, TX, United States, 5GE Healthcare, Boston, MA, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Pelvis, Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Deep learning reconstruction, Multi-shot DWI
This study introduced the deep learning reconstruction (DLRecon) to multi-shot DWI (MUSE-DWI) in the pelvis and aimed to investigate the changes in SNR and image quality with MUSE-DWI DLRecon. Compared with the MUSE-DWI non-DLRecon, the MUSE-DWI DLRecon showed higher SNR with stable ADC quantification. With that, DLRecon could reduce image distortion using higher shots MUSE-DWI with comparable SNR and scan time to clinically used 2-shot MUSE-DWI. This preliminary result showed the potential power of DLRecon in the pelvis allowing higher shots MUSE-DWI to be integrated in clinical practice to reduce image distortion.INTRODUCTION
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) provides functional and microstructural information on biological tissues without the use of contrast medium [1]. Multiplexed Sensitivity Encoding (MUSE) technique with the multi-shot capacity has proven to be useful in achieving higher spatial resolution and fidelity for DWI images [2]. However, applying higher shots MUSE-DWI to accomplish high fidelity data comes with constraint in long scan time and making its clinical integration challenging. In this preliminary study, we introduced the deep learning-based reconstruction with noise reduction strategy (DLRecon) [3] to pelvis multi-shot MUSE-DWI with two aims: first, to investigate the improvement of SNR and the variation of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) derived from MUSE-DWI DLRecon; second, to evaluate the image quality and acquisition time for higher shots MUSE-DWI DLRecon.METHODS
We acquired 2 sets of data to investigate the feasibility of applying DLRecon in MUSE-DWI and its image quality. In dataset 1, pelvis images were acquired from 3 female participants, and the parameters were listed as follows: TR, 4804 ms; TE, 70 ms; FOV, 40 x 40 cm2; matrix size, 128 x 128; slice thickness: 7 mm; numbers of b-value, 3 (0, 400, and 800); NEX, 2. The SNR was calculated by 3 ROIs (background, cervix, and pelvic muscles; Figure 1). The ADC values with DLRecon and non-DLRecon methods were compared. In dataset 2, we acquired MUSE-DWI with 2-, 3-, and 4-shot in one male participant to investigate the feasibility of higher shots MUSE-DWI DLRecon (parameters listed in Table 1). Contouring of the prostate was manually selected and the Hausdorff distance between prostate contours on SSFSE images and MUSE-DWI images (b800) was used to evaluate the image distortion. All images were acquired on 3T SIGNA Premier MRI.RESULTS and DISCUSSION
MUSE-DWI DLRecon reduced background noise compared with MUSE non-DLRecon (Figure 2). In the quantitative analysis, the MUSE-DWI DLRecon improved SNR from 16% to 116% on b0, 23% to 232% on b400, and 29% to 75% on b800 images (Table 2). The difference of ADC between MUSE-DWI DLRecon and non-DLRecon ranged from -3.06% to +1.37%. In Figure 3, there was less distortion on the 3- and 4-shot MUSE-DWI images than the 2-shot MUSE-DWI images with Hausdorff distances of 6.8, 6.0, and 5.8 mm on the 2-, 3-, and 4-shot MUSE-DWI images (Table 3), respectively. The SNR and scan time of 3- and 4-shot MUSE-DWI DLRecon were comparable to the 2-shot MUSE-DWI non-DLRecon (Table1, Figure 4).CONCLUSION
Our results showed SNR improvement in MUSE-DWI DLRecon with no significant change in quantitative ADC values. Moreover, higher shots MUSE-DWI DLRecon demonstrated less-distortion with comparable SNR and scan time to 2-shot MUSE-DWI non-DLRecon. Our preliminary finding suggested that MUSE-DWI DLRecon could be beneficial in region susceptible to image distortion or where high-density diffusion directions are needed in complex diffusion modelling.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Duarte AL, Dias JL, Cunha TM. Pitfalls of diffusion-weighted imaging of the female pelvis. Radiol Bras. 2018 Jan-Feb;51(1):37-44.
2. Chen NK, Guidon A, Chang HC, Song AW. A robust multi-shot scan strategy for high-resolution diffusion weighted MRI enabled by multiplexed sensitivity-encoding (MUSE). Neuroimage. 2013 May 15;72:41-7.
3. Matthew J. Middione, Alimohammad S. Moalem, Cheng William Hong, Arnaud Guidon, Daniel B. Ennis, and Ryan L. Brunsing (2022). Multishot EPI and a Deep Learning-Based Noise Reduction Strategy for High Resolution Pancreatic DWI. International Symposium of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 2022 Conference.
Figures
Figure 1. The ROIs selection.
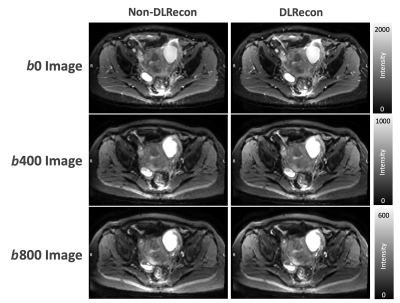
Figure 2. The MUSE images with DLRecon and non-DLRecon. MUSE DL shows reduced background noise compared with MUSE non-DLRecon.
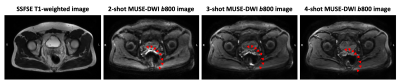
Figure 3. The susceptibility artifact of MUSE images with three various shots setting. Red arrows indicate the distortion resulted from the susceptibility.
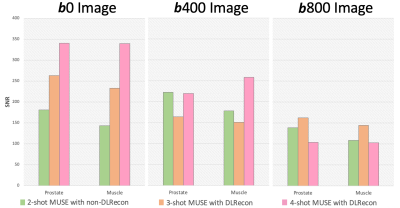
Figure 4. The SNR comparison between the MUSE images with various shots settings.
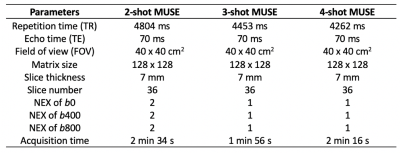
Table 1. The parameters of the 2-, 3-, and 4-shot MUSE in the dataset 2.
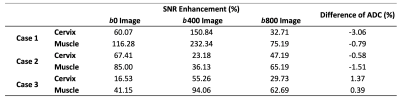
Table 2. The SNR comparison between DLRecon and non-DLRecon.
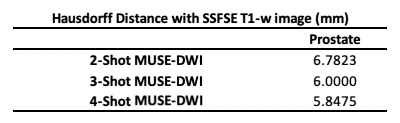
Table 3. The Hausdorff distance between the prostate contours on the SSFSE images and the MUSE images with various shots settings.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/1473