1435
Fractal Analysis in Cardiovascular MR: Prognostic Value of Biventricular Trabecular Complexity in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy1Renji Hospital affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 3Beijing Anzhen Hospital affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Cardiomyopathy, Heart
Trabecular complexity of left and right ventricles can be quantified as fractal dimension (FD), a number between 1 to 2, by fractal analysis on short axis cine images of cardiovascular magnetic resonance. We found that biventricular FDs provide significant prognostic value for sudden cardiac death and composited adverse events including rehospitalization due to heart failure in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). LV maximal apical FD and RV global FD are independent prognostic factors in HCM. In addition, they provide incremental prognostic value to the conventional predictors including European Society of Cardiology predictors and late gadolinium enhancement percentage.Introduction
Since hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) can lead to sudden cardiac death (SCD), heart failure and other adverse events, the prediction of HCM prognosis is important for early intervention and enhanced risk stratification. The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) provides a wide accepted model for predicting risk of sudden cardiac death and the need for implanting cardioverter defibrillator in HCM1. The ESC model needs update with American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology (AHA/ACC) guidelines2 and more promising markers. Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was proved to be a risk factor of poor outcome in patients with HCM in extensive studies3. Trabecular complexity can be quantified by fractal analysis based on cine images of cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR), which yields the fractal dimension index (FD) 4, a number between 1-2. FD is independent of the ventricular wall thickness, and a higher value indicates a greater degree of surface complexity5, 6. Left ventricular (LV) FD has been applied in HCM prognostic evaluation as a novel marker recently7.This study sought to investigate the prognostic value of left and right ventricular FDs in patients with HCM.Methods
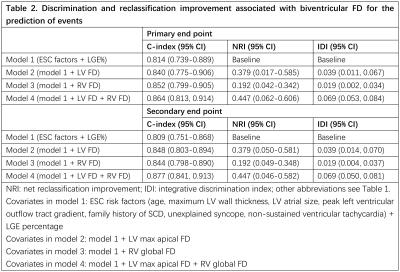
This retrospective study included 284 (192 men, median age 53 years) patients with HCM who underwent CMR, with median follow-up of 24 months. Both left and right ventricular trabeculae complexities were quantified as FDs using short-axis cine images. In our study, fractal analysis was performed by FracAnalyse using Matlab software (MathWorks, Natick, Mass) with custom-written code which was available online for free8. The core principle of FD calculation was extracting endocardial border through image segmentation and then calculating the endocardial border complexity with box-counting method9, 10. For each slice, a polygonal contour of the right ventricle and a round contour of the left ventricle were manually delineated within the mid-wall myocardium on the end-diastolic phase cine image. Then, the endocardial contour was delineated automatically and the FD value was calculated by FracAnalyse software. The average FD of each slice in the ventricle was defined as the global FD. Ventricular slices were split into basal and apical stacks by half and the highest FD value was obtained separately to assess the maximal apical and basal FDs. The primary end point included SCD, resuscitated cardiac arrest, and received adequate defibrillation from an implantable cardioverter defibrillator discharge. The secondary end point included the primary end point and rehospitalization due to heart failure. Univariate and multivariate Cox regressions were performed to find out whether biventricular FDs are independent predictors. The survival curves of high and low FD groups were established by the Kaplan-Meier method and compared with the log-rank test. The optimal cutoff value is defined by the most significant (log-rank test) split (surv_cutpoint in survminer R package) 11. Prediction models were established by adding biventricular FDs to ESC predictors (age, maximum LV wall thickness, LV atrial size, peak left ventricular outflow tract gradient, family history of SCD, unexplained syncope, non-sustained ventricular tachycardia) and LGE percentage. Concordance indexes were calculated to compare their prediction ability.Results
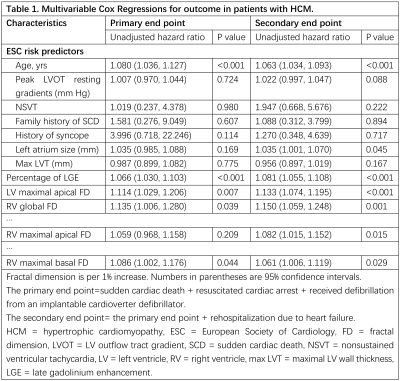
High biventricular FD groups had higher risk of both primary and secondary end than those with lower FD according to the Kaplan-Meier curves (all P<0.05). Cox analysis revealed that LV maximal apical FD (HR range 1.114-1.133; all P<0.05) and right ventricular (RV) global FD (HR range 1.135-1.150; all P<0.05) were significant prognostic factors of both end points after adjustment for the ESC predictors (age, maximum LV wall thickness, LV atrial size, peak left ventricular outflow tract gradient, family history of SCD, unexplained syncope, non-sustained ventricular tachycardia), and LGE percentage. The prediction model with addition of both ventricular FDs (c-index: 0.864-0.877) had the best performance.Conclusions
Higher biventricular FDs are associated with increased risks of SCD events and rehospitalization due to heart failure in patients with HCM. LV maximal apical FD and RV global FD were independent predictors of SCD events and rehospitalization due to heart failure in patients with HCM. The addition of biventricular FDs to the conventional prediction model contributed incremental prognosis value in HCM. The quantification of trabecular complexity may improve risk stratification of patients with HCM for early intervention.Discussion
Trabecular morphology is thought to be related with genetic, environmental, and hemodynamic factors, indicating that it may be modified and adapt to altered loading conditions and ventricle remodeling5. Studies suggest that trabecular complexity has influence on the susceptibility to cardiovascular disease12. HCM is a myocardial disease with hyper-trabeculation and diverse patterns of phenotypic expression. Previous study indicated that abnormal trabecular patterning was found in HCM and preclinical HCM13. Further histological and pathological investigations are needed to explain the underlying mechanism of the influence of ventricular trabeculae.Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the co-authors for their valuable contributions.References
1. O'Mahony C, Jichi F, Pavlou M, et al. A novel clinical risk prediction model for sudden cardiac death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM Risk-SCD). European Heart Journal. 2013;35(30):2010-2020.
2. Ommen SR, Mital S, Burke MA, et al. 2020 AHA/ACC Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients With Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. Dec 22 2020;142(25):e533-e557.
3. Chan RH, Maron BJ, Olivotto I, et al. Prognostic value of quantitative contrast-enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance for the evaluation of sudden death risk in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circulation. Aug 5 2014;130(6):484-495.
4. Captur G, Muthurangu V, Cook C, et al. Quantification of left ventricular trabeculae using fractal analysis. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. 2013/05/10 2013;15(1):36.
5. Captur G, Zemrak F, Muthurangu V, et al. Fractal Analysis of Myocardial Trabeculations in 2547 Study Participants: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Radiology. Dec 2015;277(3):707-715.
6. van Waning JI, Caliskan K, Hoedemaekers YM, et al. Genetics, Clinical Features, and Long-Term Outcome of Noncompaction Cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. Feb 20 2018;71(7):711-722.
7. Wang J, Li Y, Yang F, et al. Fractal Analysis: Prognostic Value of Left Ventricular Trabecular Complexity Cardiovascular MRI in Participants with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Radiology. 2021/01/01 2020;298(1):71-79.
8. Cai J. UK-Digital-Heart-Project/fracAnalyse: fracAnalyse v1.2. 2017. http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.837246
9. Zheng T, Ma X, Li S, et al. Value of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Fractal Analysis Combined With Myocardial Strain in Discriminating Isolated Left Ventricular Noncompaction and Dilated Cardiomyopathy. J Magn Reson Imaging. Jul 2019;50(1):153-163.
10. Krupickova S, Hatipoglu S, DiSalvo G, et al. Left ventricular noncompaction in pediatric population: could cardiovascular magnetic resonance derived fractal analysis aid diagnosis? J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. Jul 8 2021;23(1):90.
11. Budczies J, Klauschen F, Sinn BV, et al. Cutoff Finder: a comprehensive and straightforward Web application enabling rapid biomarker cutoff optimization. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51862.
12. Meyer HV, Dawes TJW, Serrani M, et al. Genetic and functional insights into the fractal structure of the heart. Nature. Aug 2020;584(7822):589-594.
13. Captur G, Lopes LR, Patel V, et al. Abnormal cardiac formation in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: fractal analysis of trabeculae and preclinical gene expression. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. Jun 2014;7(3):241-248.Figures
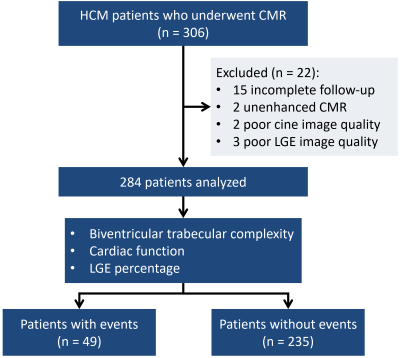
Figure 1. Flowchart shows the inclusion and exclusion criteria. HCM: hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; CMR: cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging; Late gadolinium enhancement; events: composite of primary and secondary end points (sudden cardiac death, resuscitated cardiac arrest, received adequate defibrillation from an implantable cardioverter defibrillator discharge, and rehospitalization due to heart failure).
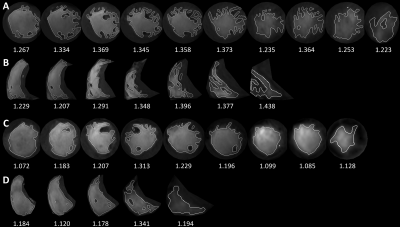
Figure 2. Fractal dimension (FD) images of two hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) patients. FracAnalyse software calculated the FD values automatically. A, B: left ventricular and right ventricular FD images of a patient who reached primary end point and with high biventricular FDs (LV max apical FD=1.374, RV global FD=1.327). C, D: biventricular FD images of a patient with no events and with low biventricular FDs (LV max apical FD=1.196, RV global FD=1.203).
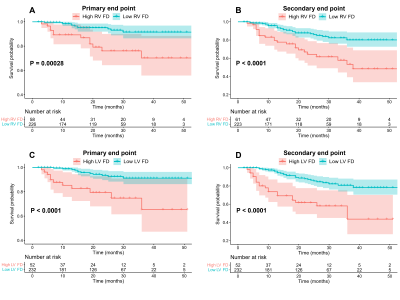
Figure 4. Survival curves of high and low FD groups. A, B are survival curves of high and low RV FD groups in HCM patients (cutoff value at RV global FD=1.290). C, D are survival curves of high and low LV FD groups in HCM patients (cutoff value at LV max apical FD=1.347). A, C for primary end point, B, D for secondary end point.