1424
First QSM of an ex vivo human brain on the Iseult 11.7T whole-body system using parallel transmission and virtual coil reconstruction1Institut du Cerveau – Paris Brain Institute – ICM, INSERM, CNRS, Sorbonne Université, Paris, France, 2CENIR - Centre for NeuroImaging Research, Sorbonne University, Paris, France, 3Hôpital Pitié-Salpêtrière, AP-HP, Paris, France, 4CEA, CNRS, BAOBAB, NeuroSpin, University of Paris-Saclay, Gif-sur-Yvette, France
Synopsis
Keywords: High-Field MRI, Quantitative Susceptibility mapping
This work presents the first QSM images obtained on the 11.7T whole body Iseult system, using tailored parallel transmission kT-point pulses and a virtual coil approach for coil combination, on a post mortem brain.introduction
QSM at ultra-high field presents strong benefits due to an enhancement of the susceptibility effect [1]. However, B0 and B1 field inhomogeneity make full exploitation difficult. Here we show the first QSM images obtained on an ex vivo brain and with the whole-body 11.7T Iseult magnet, using tailored parallel transmission kT-point pulses and a virtual coil approach for coil combination.Materials & Methods
Brain extraction was approved by the national biomedicine agency (Agence de la Biomédecine) and the French ministry of Health. The encephalon was imaged using the 11.7T Iseult MRI with Siemens VE12U software. An 8/32-channel custom built pTX head coil was used for signal emission and reception. Before imaging, the ex vivo brain was transferred to a vial containing Fluorinert (Sigma, Germany) to decrease the magnetic susceptibility mismatch between the samples and the buffer. MR images were acquired using a 3D Multi Echo Gradient Echo sequence with an isotropic resolution of 700 µm. Parameters were: FOV= 192*192*134 mm, Mtx= 280*280*192, TR = 30 ms, TEs ranging from 2.00 to 23.44 ms with a ΔTE of 2.68 ms (9 echoes acquired). Flip angle was 10° and only one Nex was acquired. A 2*2 GRAPPA scheme was used to speed up the acquisition, leading to a scan time of 5 minutes 28 s. Flip angle homogenization was performed using tailored parallel transmission kT-point pulses [2] generated offline in Matlab (The Mathworks, NA, MA, USA) following the acquisition of B0- and B1-maps. Raw data was saved for further processing. Magnitude and Phase images were generated offline and coil combination was performed using a Virtual Coil approach [3] again using Matlab. Images of multiple echoes were combined using a root mean square along time dimension, thus providing both high SNR and T2*-contrasted images. Brain mask was obtained using ITK-SNAP software and a combination of morphological operations (closing and erosion). Transversal relaxation rate (R2*) was evaluated using a nonlinear fitting method in Matlab. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) images were reconstructed using several functions from the MEDI Toolbox [4-5] for both background field removal and dipole inversion, using respectively Laplacian Boundary Value (LBV) and a GPU modified L1-MEDI function.Results
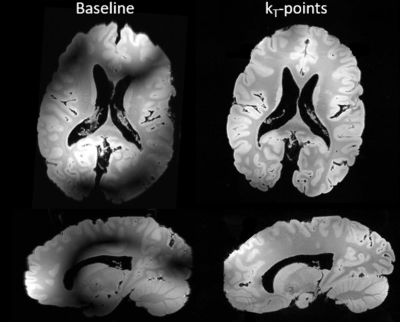
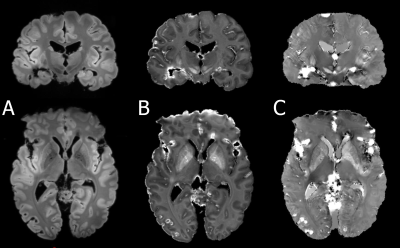
Figure 1 presents the images obtained from the ex vivo brain with and without the use of kT-point pulses. B1 signal inhomogeneities are clearly seen on images without kT-point pulses and vanish using kT-point pulses excitation. Figure 2 presents the images obtained for anatomical T2*w - SWAN, R2* and susceptibility maps. Virtual coil combination provided naturally unbiased magnitude images (no normalization used). Moreover, no clear evidence of abnormal signal inhomogeneity due to bad B1-shimming or coil combination were identified on these images. Several air bubbles were identified on R2* and susceptibility maps, thus giving raise to high susceptibility values in these regions.Discussion & Conclusions
Here we reported the first QSM images obtained at 11.7T on an ex vivo brain at 700µm isotropic resolution obtained in approximately 5 minutes. We showed the feasibility of using tailored kT-pulses and virtual coil combination for providing R2* and susceptibility maps using a limited resolution for ultra-high field strength. We now intend to push further image resolution to detect details and features that might not be visible at conventional field strength on big samples. Degassing the sample before imaging will certainly limit the presence of air bubbles within the vial and sample.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] A. Deistung et al. (2013) “Toward in vivo histology: A comparison of quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) with magnitude-, phase-, and R2⁎-imaging at ultra-high magnetic field strength.”, Neuroimage, 65 (15): 299-314 doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.09.055
[2] M. A. Cloos, et al. (2012). “kT-points: Short three-dimensional tailored RF pulses for flip-angle homogenization over an extended volume.” Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 67:72–80, doi:10.1002/mrm.22978
[3] M. Santin (2021). “Optimised generation of MRI images by a multi-antenna MRI system.”, US Patent 11,143,729
[4] Liu, T. at al. (2011). "A novel background field removal method for MRI using projection onto dipole fields". NMR in Biomedicine. 24 (9): 1129–36. doi:10.1002/nbm.1670. PMC 3628923. PMID 21387445.
[5] de Rochefort et al. (2010). “Quantitative susceptibility map reconstruction from MR phase data using bayesian regularization: validation and application to brain imaging.”, Magnetic Resonance in Medicine . Jan;63(1):194-206. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22187.
Figures