1339
A Novel MR Sequence of 3D-ZOOMit Real Inversion Recovery Imaging Improves Endolymphatic Hydrops Detection in Patients with Ménière’s Disease
Jinye Li1, Lixin Sun2, Na Hu2, Mengxiao Liu3, Linsheng Wang2, and Chuanting Li2
1shangdong provincial ENT hospital, Jinan, China, 2Shandong Provincial ENT Hospital, Jinan, China, 3Siemens healthineers, Shanghai, China
1shangdong provincial ENT hospital, Jinan, China, 2Shandong Provincial ENT Hospital, Jinan, China, 3Siemens healthineers, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Head & Neck/ENT, Head & Neck/ENT
In order to visualize endolymphatic hydrops in Ménière’s disease better, we compared the conventional 3D real IR and ZOOMit 3D real IR sequence. Results suggest that visualization of the endolymphatic space might be higher by zs-3D real IR compared with t-3D real IR, especially in the cochlea.BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
As a chronic disease, the incidence of Ménière’s disease (MD) reaches 200-500 cases per 1000,000 people1 and seriously affect the quality of patients’ life. What’s more, endolymphatic hydrops (EH) is the main pathological manifestation of MD 2. Magnetic resonance contrast provides a completely new examination method for MD diagnosis, however the detection rate of premortem MRI EH is lower than that of postmortem autopsy EH, indicating that current MR technique may underestimate the Ménière’s disease. So, we prospectively investigated whether a novel high-resolution MR imaging technique, the 3D-ZOOMit real inversion recovery, improves endolymphatic hydrops detection compared with conventional 3D-TSE inversion recovery.BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Fifty patients (22 male, 28 female, average age ± SD: 53.06 ± 13.28 years, affected side:21right, 29 left) with definite unilateral Ménière’s disease were enrolled from December 2020 to October 2021. All patients were scanned on a 3T MR system (MAGNETOM Prisma, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) with 64 channel head coil. Conventional 3D real IR and 3D-ZOOMit real IR were performed after 6 h gadolinium injection with a double dose(0.4 0.4 ml/kg body weight; ProHance). The parameters of conventional 3D real IR is as below: TR 5300ms, TE 191ms, TI 1850, FOV 220mm×220mm, voxel size 0.6mm×0.6mm and scan time 16min47s; The parameters of ZOOMit 3D real IR is as below: TR 8000ms, TE 491ms, TI 2250, FOV 160mm×80mm, voxel size 0.6mm×0.6mm and scan time 15min12s. The endo- and perilymph spaces were scored separately by 2 radiologists independently. Scores for the separate visualization of the cochlear and vestibular endolymph were as follows: 1, impossible to recognize; 2, some can be recognized; 3, most can be recognized; and 4, all can be recognized 26. The contrast-to-noise ratio, SNR, and signal intensity ratio of the two sequences were respectively calculated using the following equations:CNR = (SIperi − SIendo)/SDnois [Eq. 1]
SNR = SIperi/SDnoise [Eq. 2]
SIR = SIperi/SIlmcp [Eq. 3]
Where, SIperi, SIendo and SIlmcp present the signal intensity of the cochlear basal turn’s center, the endolymph and the left middle cerebellar peduncle of the images. SDnoise is the standard deviation in the artifact-free air area. And the presence of endolymphatic hydrops was evaluated in patients.
For quantitative and qualitative analysis, we used the paired samples t-test or Wilcoxon signed ranked test. Statistical significance was set at P values < 0.05(SPSS25.0, IBM, Chicago, IL, USA).
RESULTS
The visualization of 3D ZOOMit real IR in endolymphatic space of cochlea and vestibule is better than conventional 3D-TSE real IR (P < .001). For the visualization of endolymphatic space in the cochlea, all images from ZOOMit 3D real IR performed well (score ≥ 3) and 37 patients scored 4. For 3D TSE real IR, there are 5 patients’ score ≤2, and only 17 patients scored 4. Meanwhile, for the recognition of the endolymphatic space in the vestibule, most images can perform well in both sequences (49 patients’ score ≥ 3), but the number of score4 in ZOOMit 3D real IR is 40 and the number is 27 in 3D TSE real IR. For asymptomatic side, the performance of ZOOMit 3D real IR is also better than 3D TSE real IR (table 1). The CNR, SNR, and SIR values of 3D-ZOOMit real IR images were statistically higher than those of conventional 3D-TSE inversion recovery images (all P < .001), the details are shown in table 2.DISCUSSION
In our study, CNR, SNR, and SIR values, endo- and perilymph image quality scores by ZOOMit 3D real IR were higher than those by 3D TSE real IR. For ZOOMit is a technique with an independent parallel transmission (pTX) system, thus can provide less image blur and artifacts, higher spatial resolution, and faster screening time.CONCLUSIONS
3D-ZOOMit real IR sequence is superior to conventional 3D-TSE IR sequence in visualizing the endolymphatic space, detecting endolymphatic hydrops, and discovering contrast permeability.Acknowledgements
NoneReferences
1. Havia M, Kentala E, Pyykko I. Prevalence of Meniere's disease in general population of Southern Finland. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2005;133:762-768.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2005.06.015
2. Lopez-Escamez JA, Carey J, Chung WH, et al. Diagnostic criteria for Meniere's disease. J Vestib Res 2015;25:1-7.https://doi.org/10.3233/VES-150549
Figures
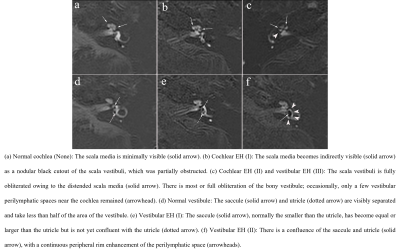
Fig.1.
Zoomed imaging technique with parallel transmission Space real inversion
recovery images of different degrees of cochlear and vestibular endolymphatic
hydrops (EH) in patients with Ménière’s disease.
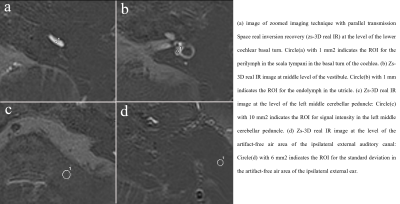
Fig.2. ROI for different areas.
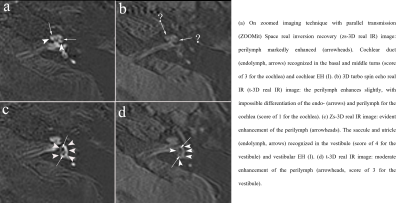
Fig.3. A 32-year-old woman
suspected with left endolymphatic hydrops (EH).
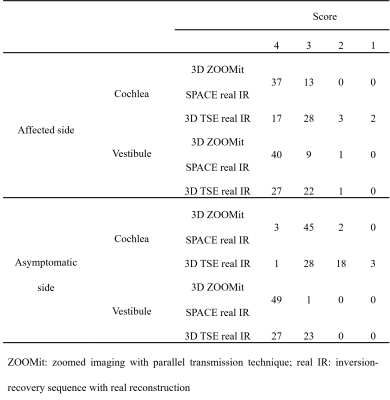
Table
1 Scores for separate visualization
of endolymphatic space in the cochlea and vestibule by 2 pulse sequences in 50
patients of Ménière’s
disease
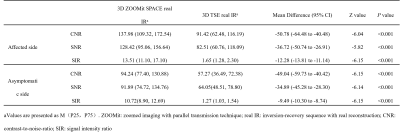
Table
2 The CNR, SNR and SIR values in the cochlea by 2 pulse sequences in 50
patients with Ménière’s disease
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/1339