1238
In vivo demonstration of arbitrary ROI shaping and B0 shimming with MC-ECLIPSE for applications in human brain proton MRSI1Radiology and Biomedical Imaging, Yale University, New Haven, CT, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: New Devices, Spectroscopy
ECLIPSE is a pulsed second order gradient insert that allows unparalleled extracranial lipid suppression over an elliptical ROI for applications in human brain proton MRSI. While ECLIPSE provides excellent axial slice coverage for brain shapes that closely resemble an ellipse, coverage is compromised for head shapes that are asymmetrical. We recently constructed an ECLIPSE gradient coil in combination with a 54-channel multi-coil array (MC-ECLIPSE) for human brain ROI shaping and B0 shimming. Here we demonstrate >95% axial slice coverage with ROI shaping over challenging head shapes, in addition to improved B0 shimming capabilities relative to second order spherical harmonic shims.Introduction
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Imaging (MRSI) is a powerful technique, able to spatially map the metabolic profile non-invasively. Extracranial lipid contamination, however, is a major hindrance that limits the widespread use of MRSI in clinical and research settings with routine MRI. Over the last five years we have developed highly effective extracranial lipid suppression methods with a second order gradient insert (ECLIPSE1) utilizing both inner volume selection (IVS) and outer volume suppression (OVS) methods2-3. While ECLIPSE provides > 100-fold in lipid suppression with modest RF power requirements, axial coverage is reduced for highly asymmetrical head shapes. In this work we demonstrate the utility of MC-ECLIPSE, a pulsed second order gradient coil with Z2 and X2Y2 fields, combined with a 54-channel multi-coil array (MC), for arbitrary ROI shaping to allow full-axial slice coverage, in addition to MC-based B0 field shimming of the brain4, for applications in proton MRSI in vivo.Methods
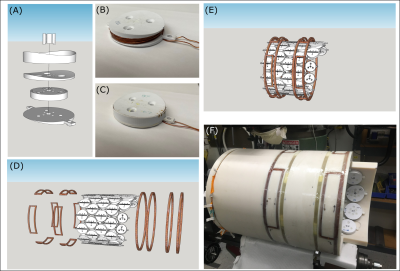
Components and construction of the MC-ECLIPSE system is illustrated in Figure 1 as previously described5. All MR experiments were performed on a 4 T 94 cm Medspec scanner (Bruker corporation. Ettlingen, Germany) with gradients capable of switching 30 mT/m in 1150 µs. The ECLIPSE gradient coil is driven by Techron 7780 amplifiers (AE Techron, Elkhart, IN, USA) with 130V and 100A each. The 54-channel MC-array is driven by 54 MXA current amplifiers capable of 2A per channel (Resonance Research Inc., MA, USA). The MC-ECLIPSE system is controlled by a home-built multi-channel gradient controller6. B0 shimming and arbitrary ROI shaping capabilities were evaluated using the MC-ECLIPSE setup on two healthy volunteers each. Two individuals with highly asymmetrical axial head shapes were selected to demonstrate ROI shapes that significantly deviate from an ellipse. ROI shaping experiments in vivo were performed using an ECLIPSE-OVS based MRSI method3, modified with a readout gradient to allow an MRI acquisition in 4 minutes. The ECLIPSE-OVS method is performed with GOIA-HS (4-2,5) pulses with 15 kHz bandwidth. As such, the ECLIPSE gradients, system gradients, and MC array currents waveforms were gradient modulated as per the GOIA algorithm7 to allow ROI shaping.Results
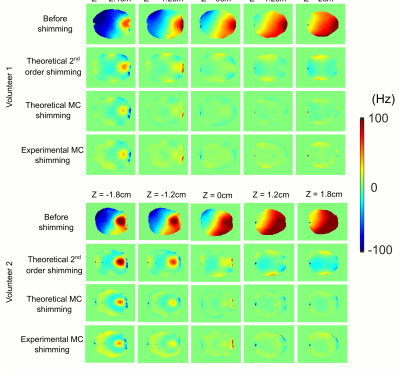
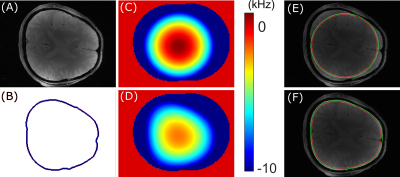
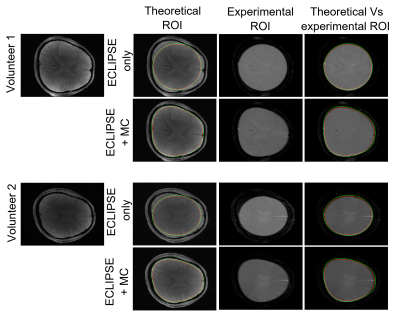
Figure 2 compares theoretical and experimental B0 maps following shimming over a 4.4 cm slab and 3.6 cm slab for volunteer 1 and volunteer 2, respectively. For the two volunteers, the standard deviation associated with the B0 inhomogeneity over the slab prior to shimming, and following theoretical second order, theoretical MC, and experimental MC shimming were 55 Hz, 14.6 Hz, 10.0 Hz, and 12.8 Hz, respectively. Similarly, the B0 spread for 90% of the voxels for the four cases were 173 Hz, 37 Hz, 18.7 Hz, 21.3 Hz, respectively. Comparing the theoretical MC vs experimental MC shimming results demonstrate high accuracy of the theoretical model. Figure 3 demonstrates the process used for ROI shaping. The contour in Figure 3B is produced by tracing the brain edge in (A) following skull stripping. To achieve a high level of localization, three layers of contours are drawn (not visible in (B)) with B0 values assigned to produce a desired chemical shift displacement at the ROI edge. Similar to a B0 fitting approach used for magnetic field shimming, this generated contoured B0 field is fitted using the basis fields of the MC, Z2, and X2Y2 fields. The fitted MC-ECLIPSE B0 field with only ECLIPSE (Z2 and X2Y2 fields only) and with both ECLIPSE + MC is illustrated in (C), and (D) respectively. The corresponding ROI shape generated with fields in (C) and (D) are illustrated in (E) and (F) respectively. The process of skull stripping and ROI generation are automated processes with allowance to manually adjust the ROI size, which can be completed in ~ 2 minutes. Figure 4 illustrates axial slice coverage with ECLIPSE only, and ECLIPSE + MC configurations in theory and experimentally. For volunteer 1, ECLIPSE provides 82.5% axial coverage, and MC-ECLIPSE closely provides 96.3% axial coverage. Similarly for volunteer 2, ECLIPSE alone and MC-ECLIPSE provide 84.0% and 95.8% axial coverage, respectively.Discussion
The near-full axial coverage achievable with ROI shaping, >100-fold in lipid suppression achievable with ECLIPSE, and superior axial slab shimming relative to second order harmonics, allows artifact free and high quality MRSI evaluations including the entire cortical surface, that has significant value in a wide range of neurological and psychiatric conditions. The flexibility in ROI shaping negates the requirement for the subject to be properly placed in the magnet, as any rotation can also be accounted for.In the current demonstration, Z2/X2Y2 gradient coil amplitudes and MC array amplitudes were limited to 45% and 60% of full amplitude, respectively with the addition of a total current cost-function imposed on the MC array. The inclusion of this cost function avoids the optimizer from converging on high current solutions with negligible gain. The developed ROI shaping enables a high level of localization in terms of CSDE and TW effects at the ROI edge, however further improvements will be gained by moving to highly localized asymmetrical GOIA pulses8, and increasing the ECLIPSE and MC array current amplitudes during optimization.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by NIH grant R01- EB014861.References
[1] de Graaf RA, Brown PB, De Feyter HM, McIntyre S, Nixon TW. Elliptical localization with pulsed second-order fields (ECLIPSE) for robust lipid suppression in proton MRSI. NMR in biomedicine 2018;31(9):e3949.
[2] Kumaragamage C, De Feyter HM, Brown P, McIntyre S, Nixon TW, de Graaf RA. Robust outer volume suppression utilizing elliptical pulsed second order fields (ECLIPSE) for human brain proton MRSI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2020; 83(5):1539-1552.
[3] Kumaragamage C, De Feyter HM, Brown P, McIntyre S, Nixon TW, de Graaf RA. ECLIPSE utilizing gradient-modulated offset-independent adiabaticity (GOIA) pulses for highly selective human brain proton MRSI. NMR in Biomedicine 2020; 34:e4415.
[4] Juchem C, Nixon TW, McIntyre S, Boer VO, Rothman DL, de Graaf RA. Dynamic multi-coil shimming of the human brain at 7 T. Journal of Magnetic Resonance. 2011; 212:280-288.
[5] Kumaragamage C, Brown P, McIntyre S, Nixon T, De Feyter H, de Graaf R., “MC-ECLIPSE for arbitrary ROI shaping and whole brain shimming for 3D MRSI”, 30th Annual meeting ISMRM Conference, 2022.
[6] Nixon TW, McIntyre S, de Graaf RA. The design and implementation of a 64 channel arbitrary gradient waveform controller. Proc Int Soc Magn Reson Med. 2017;25:969.
[7] Tannus A, Garwood M. Adiabatic Pulses. NMR in Biomedicine 1997;10:423-434.
[8] Kumaragamage C, Coppoli A, Brown P, McIntyre S, Nixon T, De Feyter H, Mason G, de Graaf R., “Short symmetric and highly selective asymmetric first and second order gradient modulated offset independent adiabaticity (GOIA) pulses for applications in clinical MRS and MRSI”, Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 341(2022) 107247, 2022.
Figures