1222
The value of amide proton-weighted imaging and diffusion kurtosis imaging in predicting Her-2 expression in endometrial cancer
Xiwei Li1, Shifeng Tian1, Changjun Ma1, Nan Wang1, Jiazheng Wang2, and Ailian Liu1
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare,Beijing, Beijing, China
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare,Beijing, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Cancer, Body
Endometrial cancer (EC) is one of the three major malignant tumors in women, and its commonly used treatment is mainly surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy and hormone therapy . However, some patients still have low response to the above treatments. However, molecular therapy targeting Her-2 gene has significant value in the clinical diagnosis and improving the prognosis. Amide proton weighted imaging (APTw) and diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI)can be used for the diagnosis of diseases by reflecting the level of molecular metabolism and cellular microstructure. This study explored the value of the above two sequences in quantitative prediction of HER-2 gene expression levels.Synopsis
Endometrial cancer (EC) is one of the three major malignant tumors in women, and its commonly used treatment is mainly surgery, supplemented by radiotherapy, chemotherapy and hormone therapy . However, some patients still have low response to the above treatment and are prone to relapse. However, molecular therapy targeting Her-2 gene has significant value in the clinical diagnosis and improving the prognosis. Amide proton weighted imaging (APTw) and diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI)can be used for the diagnosis of diseases by reflecting the level of molecular metabolism and cellular microstructure. This study explored the value of the above two sequences in quantitative prediction of Her-2 gene expression levels.Summary of Main Findings
In this study,we evaluated the value of APT, MD and MK measurements in expression of Her-2 in EC. It was found that the measurements of APT in HER-2 positive group was higher than the negative one. The measurements of MD in Her-2 positive group was lower than that the negative group. In addition, the combined APT and MD measurements improved the prediction efficiency of the two groups.Introduction
Her-2 can stimulate the occurrence, invasion and metastasis of cancer cells through gene amplification and protein overexpression. At present, immunohistochemistry is commonly used to detect the expression of Her-2 in clinical practice, but it is an invasive examination, and the accuracy of its results is affected by the standardization of technical personnel and the subjectivity of pathologists' interpretation. In addition, the results have a certain lag. In this study, the APT, MK and MD measurements of APTw and DKI sequences were measured to predict the expression of Her-2 in EC .Methods
52 patients with EC who underwent pelvic 3.0T MRI (including APTw and DKI sequences) scans (Table 1) (Ingenia CX, Philips, the Netherlands)were retrospectively collected and divided into 22 cases in the Her-2 positive expression group (group A) and 30 cases in the Her-2 negative expression group (group B). Two observers measured APT values, mean kurtosis (MK) and mean diffusivity (MD) of the two groups of lesions at the level of the largest tumour entity on display.The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was used to assess the consistency of each measured parameter between the two observers. The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to test the normality of the distribution of the parameters. Independent samples t-test or Mann-Whitney U-test was used to assess the differences in the values of each parameter between the two groups of cases. The Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve(ROC) was used to assess the diagnostic efficacy of the differential parameters and to record the Area Under the Curve (AUC) , sensitivity, specificity and threshold of each parameter to differentiate between the two groups. Logistic regression was used to calculate the predictive values of the joint model with differential parameters. The De-Long test was used to assess the diagnostic efficacy of the discrepant parameters.Results
The measurements of the two observers are in good agreement(Table 2). APT values were higher in the Her-2 positive expression group than in the Her-2 negative expression group, with a statistically significant difference [(2.99±0.32)% vs (2.41±0.46)%, t =4.999,P<0.05]. MD values were lower in the Her-2 positive expression group than in the Her-2 negative expression group, with a statistically significant difference [(0.72± 0.19)μm2/ms vs (0.86±0.12)μm2/ms, t=-2.771, P<0.05]. There was no statistical difference in MK values between the Her-2 positive expression group and the negative one (t=-0.195, P>0.05)(Table 3). the AUC values, sensitivity and specificity of APT values, MD values and the combination of both (APT+MD) to identify the two groups of disease were 0.854, 90.91%, 70.00%, 2.45%, 0.716, 81.80%, 56.70%, 0.82 μm2/ms and 0.858, 95.45%, 66.67% respectively(Table 4,Figure 2). The AUC of MD values were significantly different from the APT-MD model (p=0.0417).Discussion
The APT values of in Her-2 positive group was higher than that of the negative group, which may be attributed to the following reasons. Firstly ,with the increase of tumor aggressiveness, the tumor tissue metabolism became more vigorous, Resulting in increased protein and peptide content, so the APT value increased. In addition, the serious degree of tumor hypoxia also made the higher APT values. The MD values of in Her-2 positive group was lower than that of the negative group, which may be attributed to the following reason. With the increase of tumor invasiveness, the increased tumor cell density made the lower MD values. There was no difference in MK values between the two groups, indicating that Her-2 was not valuable in distinguishing tumor heterogeneity in thisstudy.Conclusion
Both APT and MD values are significantly different between Her-2 positive group and negative group,and the combination of the two parameters improves the diagnostic efficiency. These two sequences all provide novel techniques for predicting Her-2 expression in EC from the aspect of molecules and cells respectively.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2021 [published correction appears in CA Cancer J Clin. 2021 Jul;71(4):359]. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(1):7-33. doi:10.3322/caac.21654
[2] Zhou J, Payen JF, Wilson DA, Traystman RJ, van Zijl PC. Using the amide proton signals of intracellular proteins and peptides to detect pH effects in MRI. Nat Med. 2003;9(8):1085-1090. doi:10.1038/nm907
[3] Li J, Lin L, Gao X, Li S, Cheng J. Amide Proton Transfer Weighted and Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Imaging in Evaluation of Prognostic Factors for Rectal Adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. 2022;11:783544. Published 2022 Jan 3. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.783544
Figures
Table 1. Scan parameter table
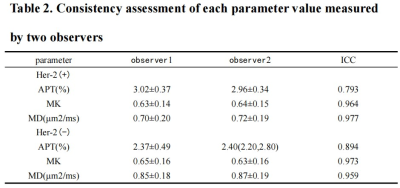
Table 2. Consistency assessment of each parameter value measured by two observers
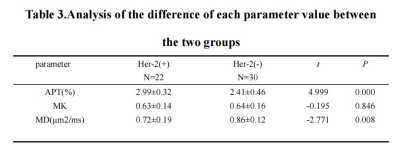
Table 3.Analysis of the difference of each parameter value between the two groups
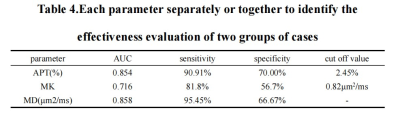
Table 4.Each parameter separately or together to identify the effectiveness evaluation of two groups of cases
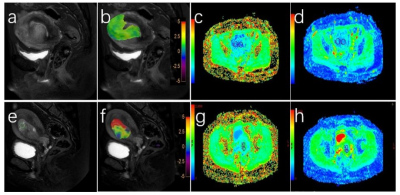
Figure 1. (A-D) a 54-year-old patient with positive expression of EC Her-2. T2WI (a), T2WI and APT fusion (b), MK (c) and MD (d) showed endometrial mass. The values of APT, MD and MK values were 2.1%, 0.65 and 1.05μm2/ms, respectively. (e-h) A 51-year-old patient with negative EC Her-2 expression. T2WI (a), T2WI and APT fusion (b), MK (c) and MD (d) showed endometrial mass. The values of APT, MD and MK were 2.85%, 0.746 and 0.82μm2/ms, respectively.
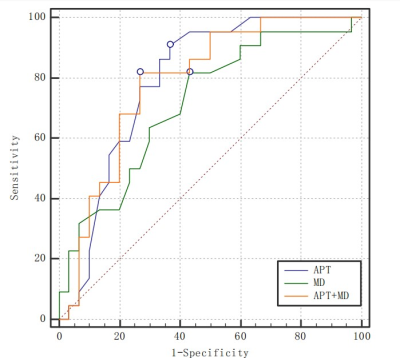
Figure 2. Diagnostic efficacy of APT value, MD value and their combination to distinguish two groups of diseases
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/1222