1192
Brain PET Synthesis from MRI Using Joint Probability Distribution of Diffusion Model at Ultrahigh Fields1Inner Mongolia University, Hohhot, China, 2Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot, China, 3Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences, shenzhen, China, 4Guangdong Laboratory of Artificial Intelligence and Digital Economy (SZ), shenzhen, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Nerves, Multimodal, Ultrahigh Field, Artificial Intelligence, Multimodal
MRI and PET are important modalities and can provide complementary information for the diagnosis of brain diseases because MRI can provide structural information of brain and PET can obtain functional information of brain. However, PET is usually missing. Especially, simultaneous PET and MRI imaging is not achievable at ultrahigh field in the current. Thus, synthetic PET using MRI at ultrahigh field is essential. In this paper, we synthetic PET using MRI as a guide by joint probability distribution of diffusion model (JPDDM). Meanwhile, We utilized our model in ultrahigh fields.Introduction
Diagnosing the disease of brain disorder, (e.g. Alzheimer’s disease (AD)) jointed Positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) become a popular and useful method because they can offer various information [1-3]. MRI and PET include complementing information for enhancing the accuracy of AD diagnosis [4-5]. However, many patients will to receive MRI scans and to reject PET scans. And ultrahigh field MRI (e.g.5T MRI and 7T MRI) can offers images which is higher resolution and high signal-to-noise ratio. But corresponding PET of ultrahigh field cannot be obtained. Missing PET scans be synthesized urgently in order to make effective use of the multi-modality medical data, especially for PET at ultrahigh field. In recent years, diffusion model have remarkable advances comparable to GANs [6]. The model of score-based generative solving the stochastic differential equation (SDE) [7] unified framework of SMLD [8] and DDPM [9]. SDE diffuses a data point into random noise continuously and then reverse the process for molding randomnoise into raw data [7]. This paper's core task is synthesizing PET data from MRI data. Therefore, we need to estimate the probability distribution of PET $$$($$$ $$$x_{PET}$$$ $$$)$$$ conditioned on MRI $$$($$$ $$$x_{MRI}$$$ $$$)$$$ , i.e., $$$p(x_{PET}|x_{MRI})$$$. However, it is not easy to estimate. In the framework of diffusion models described above, we only need to estimate $$$\nabla_{x_{PET}}\ \ p(x_{PET}|x_{MRI})$$$. Given $$$\nabla_{x_{PET}}\ \ p(x_{PET}|x_{MRI})=\nabla_{x_{PET}}\ \ p(x_{PET}, x_{MRI})$$$, we will construct an MRI and PET joint diffusion model and learn its joint distribution to achieve conditional generation. We applied the proposed model at ultrahigh fields. Because MRI scanner and PET scanner is based on Physiology and Pathology of the human body. Our model that generate PET from 5T MRI or 7T MRI is reasonable.Methods
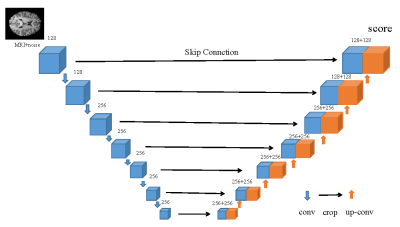
Diffusion modeling is a crucial method in the generating process. The method forecasts the score, namely the gradient of the log probability density with respect to original data, not the data distribution directly. The purpose of this paper is to synthetic PET by MRI as a guidance. We provided appropriate conditions as a guidance for the model in order to get the expected results. The joint probability distribution of diffusion model (JPDDM) has two processes that are diffusion process and sample process. Schematic diagram of joint distribution in this study is showed in Fig. 1. The diffusion process is forward SDE. The diffusion process is as follows\begin{equation*}X_{i+1} = X_{i} + \sigma_{min} \left( \frac{\sigma_{max}}{\sigma_{min}} \right) ^{t} z, i=1,2,...,N-1,\end{equation*} $$$X_{i}$$$ is the $$$i-th$$$ joint perturbed data $$$($$$e.g. $$$X_{i}(x_{PET},x_{MRI},t)$$$ $$$)$$$. $$$X_{0}$$$ is joint distribution of $$$x_{PET}$$$ and $$$x_{MRI}$$$. $$$x_{T}$$$ obeys joint distribution of Standard Gaussian distribution and $$$x_{MRI}$$$. $$$\{\sigma_{i}\}_{i=1}^{N}$$$ is the noise scales which $$$\sigma_{min}$$$ is the minimum of the noise scales and $$$\sigma_{max}$$$ is the maximum of the noise scales. Sample process is predictor-corrector sample namely PC sample. Predictor and corrector are executed alternately. Predictor is reverse diffusion (from joint distribution of noise and MRI to the distribution of PET) for the sample that can be described as\begin{equation*}X_{i} = X_{i+1} - f_{i+1}(X_{i+1}) + g_{i+1}(X_{i+1})g_{i+1}(X_{i+1})^{T} s_{\theta^{*}} \left (X_{i+1},i+1 \right) + g_{i+1}(X_{i+1})z_{i+1}.\end{equation*}Where $$$f_{i}$$$ denotes the drift coefficient of $$$X_{i}$$$. $$$g_{i}$$$ denotes the diffusion coefficient of $$$X_{i}$$$. $$$s_{\theta^{*}(X_{i+1},i+1)}$$$ is to estimate $$$\nabla_{X_{i}}\log p_{t}(X_{i})$$$. $$$p_{t}(X_{i})$$$ is the distribution of $$$X_{i}$$$. $$$s_{\theta^{*}}(X_{i+1},i+1)$$$ is obtained by deep learning of UNet that is showed in Fig. 2 and objection function is\begin{equation*}L(\theta; \sigma)=\frac{1}{2}\mathbb{E}_{p_{t}(X)}\left[\left\| \sigma_{min} \left(\frac{\sigma_{max}}{\sigma_{min}}\right)^{t} s_{\theta}(X_{i+1},\sigma)+z\right\|_{2}^{2} \right].\end{equation*}In this study, $$$f_{i}=0$$$, $$$g_{i}=\sqrt{\sigma_{i}^{2}-\sigma_{i-1}^{2}}$$$.Corrector is Langevin dynamics. Langevin method can computes the sample by\begin{equation*}X_{i} = X_{i+1} + \varepsilon s_{\theta}(X, i+1) + \sqrt{2\varepsilon} z,\end{equation*}Where $$$\varepsilon=2 \alpha_{i}\left(r\lVert z\rVert_{2} / \lVert s_{\theta}\rVert_{2}\right)$$$ denotes step size.The study utilized the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) dataset [10]. 14440 pairs image of MRI and PET had registered. All image are reshaped to 128 * 128.Results
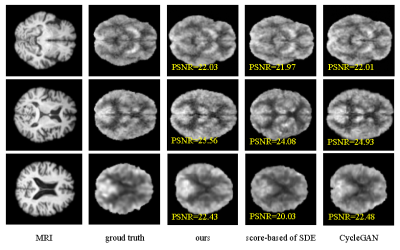
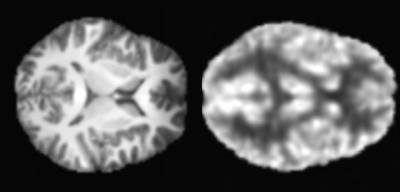
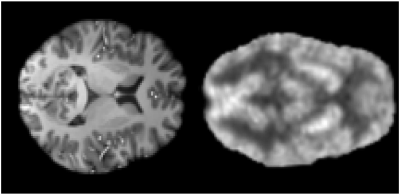
In this study, Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) were used to assess image quality. Our model, CycleGAN [11] and score-based of SDE model [7] are contrasted for synthesis PET using MRI in our study. The experimental results are shown in Fig. 3. Efficiency of our model is better and PSNR of our model is higher than others. We applied the trained model to the 5T MRI images acquired by a 5T MRI scanner (uMR Jupiter, United Imaging, Shanghai, China) and the 7T MRI images acquired by a 7T MRI scanner (MAGNETOM Terra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany). All of the protocols were approved by our Institutional Reviews Board (IRB). The results of synthesis PET from 5T MRI show in Fig. 4. The results of of synthesis PET from 7T MRI show in Fig. 5.Conclusions and Discussion
This study synthetic PET from MRI using joint probability distribution of diffusion model. It not only improves the stability of the generation model but also enables more accurate recovery of PET from MRI. The method has high potential for cross-modal synthesis. However, the disadvantage of our method is the slow of imaging speed. In future research, accelerated imaging speed is one of the research directions.Acknowledgements
Taofeng Xie and Chentao Cao contributed equally to this work. This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61871373, 62271474, 81830056, U1805261, 81729003, 81901736, 12026603, 12026603 and 81971611), the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB25000000 and XDC07040000), the High-level Talent Program in Pearl River Talent Plan of Guangdong Province (2019QN01Y986), the Key Laboratory for Magnetic Resonance and Multimodality Imaging of Guangdong Province (2020B1212060051), the Science and Technology Plan Program of Guangzhou (202007030002), the Key Field R&D Program of Guangdong Province (2018B030335001), the Shenzhen Science and Technology Program, Grant Award (JCYJ20210324115810030), the Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (Grant No. KQTD20180413181834876, and KCXF20211020163408012), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants Nos. 12061052), Young Talents of Science and Technology in Universities of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (NJYT22090), the National Key R&D Program of China under Grant (2020YFA0712200), the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant (61771463, 81830056, U1805261, 61671441, 81971611, 12026603, 62106252 and 62206273), the Zhiyuan Talent of Inner Mongolia Medical University (ZY0301025), “111 project” of higher education talent training in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region and the Independent scientific research project of Inner Mongolia University.References
1.K. A. Johnson et.al., "Brain imaging in alzheimer disease," Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine, 2(4):a006213, 2012.
2.X. Y. Zhang et.al., "Pet/mr imaging: new frontier in alzheimer’s disease and other dementias," Frontiers in molecular neuroscience, 10:343, 2017.
3.D. Cheng et.al., "Cnns based multi-modality classification for ad diagnosis," In 2017 10th international congress on image and signal processing, biomedical engineering and informatics (CISP-BMEI), pages 1–5. IEEE, 2017.
4.V. D. Calhoun et al., "Multimodal fusion of brain imaging data: a key to finding the missing link (s) in complex mental illness," Biological psychiatry: cognitive neuroscience and neuroimaging, 1 (3):230–244, 2016.
5.M. Liu et.al., "Multi-hypergraph learning for incomplete multimodality data," IEEE journal of biomedical and health informatics, 22(4):1197–1208, 2017.
6.I. Goodfellow et.al., "Generative adversarial networks," Communications of the ACM, 63(11):139–144, 2020.
7.Y. Song et.al., “Score-based generative modeling through stochastic differential equations,” in International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2021, OpenReview.net, 2021.
8.Y. Song et.al., “Generative modeling by estimating gradients of the data distribution,” in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 32:11918–11930, 2019.
9.J. Ho et.al., "Denoising diffusion probabilistic models," Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 33:6840–6851, 2020.
10. C. R. Jack Jr et.al., The alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative (adni):Mri methods. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: An Official Journal of the InternationalSociety for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 27(4):685–69, 2008.
11.J. Y. Zhu et.al., "Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks," In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pages: 2223–2232, 2017.
Figures