1102
Nine-Fold Acceleration of Multi-Parametric Imaging of the Brain through Joint Sparsity regularized Wave-SPIRiT reconstruction
Sen Jia1, Lixian Zou1, Zhilang Qiu2, Yongquan Ye3, Haifeng Wang1, Chao Zou1, Ye Li1, Jian Xu3, Xin Liu1, Hairong Zheng1, and Dong Liang1,4
1Paul C. Lauterbur Research Center for Biomedical Imaging, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Shenzhen, China, 2Biomedical Engineering, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, United States, 3UIH America, Houston, TX, United States, 4Medical AI Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Shenzhen, China
1Paul C. Lauterbur Research Center for Biomedical Imaging, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Shenzhen, China, 2Biomedical Engineering, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, United States, 3UIH America, Houston, TX, United States, 4Medical AI Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Shenzhen, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Quantitative Imaging, Relaxometry, Susceptibility
The MULTIPLEX technique could quantify the T1/T2*/PD/Susceptibility maps in a single 3D scan but leads to a long scan time due to the dual-TR, dual-flip angle, and multi-echo signal acquisition strategy. Wave-CAIPI acceleration with SENSE reconstruction is limited by noise amplification at high acceleration factors and is susceptible to artifacts from inaccurate coil sensitivity maps. This work develops a L1 regularized Wave-SPIRiT reconstruction to achieve 9-fold accelerated MULTIPLEX imaging in 3 minutes. The L1 regularized coil-by-coil reconstruction also benefits the Multi-Dimensional Integration (MDI) quantification to achieve comparable accuracy and robustness as the reference scan with 55% reduction of scan time.Introduction
The MULTI-Parametric MR imaging with fLEXible design technique (MULTIPLEX) could quantify the T1/T2*/PD/susceptibility maps and produces qualitative augmented T1/susceptibility-weighted images (aT1w/SWI) jointly in a single 3D scan 1. However, the dual-TR, dual-flip angle and multi-echo signal acquisition strategy leads to a long scan time and limits the achievable spatial resolution 1. The Wave-CAIPI acceleration with SENSE reconstruction could reduce undersampled artifacts and reconstruction noise for highly accelerated 3D imaging 2,3. However, its noise reduction capability is determined by the applied wave gradient amplitude, which is strictly limited by the maximum slew rate of the gradient system, especially in the high-resolution imaging scenarios with high bandwidth readout 3,4. Moreover, the SENSE reconstruction for Wave-CAIPI is vulnerable to artifacts induced by the calibration errors and phase nonlinearity in the coil sensitivity maps (CSM) 5,6.Methods
This work develops a joint sparsity/L1 7 regularized, coil-by-coil SPIRiT 8 reconstruction model for Wave-CAIPI sampling (i.e., L1-Wave-SPIRiT) to achieve 9-fold accelerated MULTIPLEX imaging without the need of estimating CSM:$$\min_{x_i, i=1:R_z}||(G_i-I)x_i||_2^2 + \alpha||A{F_x}^{-1}{{P_{sf}}^i}{F_x}x_i-I_a||_2^2+\mu\sum_{i=1}^{R_z}||Wx_i||_{\bf{Joint}\bf{\it{l}_1}}$$
where $$$x_i, i=1:R_z$$$ denote the unknown multi-coil images of $$$R_z$$$ slices which are aliased together by the $$$R_z$$$-fold undersampling in the $$$k_z$$$ dimension, $$$G_i$$$ denotes the image domain SPIRiT kernel of each aliased slice, $$$I$$$ denotes the identity operator, $$${P_{sf}}^i$$$ denotes the point spread function (PSF) characterizing the Wave sampling, $$$F_x$$$ and $$${F_x}^{-1}$$$ denote the Fourier transform (FT) along the $$$k_x$$$ dimension and its inverse, $$$A$$$ represents the image aliasing induced by CAIPI undersampling in the $$$k_y$$$ and $$$k_z$$$ dimensions, $$$I_a$$$ denotes the aliased image calculated by inverse FT of the Wave-CAIPI accelerated k-space data, $$$W$$$ denotes the 2D Wavelet transform (Daubechies is utilized in this work), and $$${\parallel\cdot\parallel}_{\bf{Joint}\it{l_1}}$$$ denotes the joint sparsity model for multi-coil images. The L1-Wave-SPIRiT model is solved iteratively by the ADMM algorithm. The regularization weight of data consistency term is set to $$$\alpha =0.6$$$, while the sparsity regularization weight $$$\mu$$$ varies between 1.8e-3 and 2.6e-3 according to the different signal-to-noise levels of multi-echo images. The coil-by-coil reconstruction with noise alleviation by L1 regularization also benefits the subsequent multi-dimensional integration (MDI) 9 quantification strategy by fully utilizing the dimensional orthogonality of multi-dimensional MR signals, improving the quantification accuracy and robustness. 1,9,10
In-vivo experiments were IRB-approved, with written informed consent obtained from three healthy volunteers. All 9-fold Wave-CAIPI accelerated MULTIPLEX scans (TA = 3 min 3 sec) were performed on a 3T scanner (uMR 790, United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai) with a 32-channel head coil. Each subject also underwent a 4-fold CAIPI accelerated MULTIPLEX scan (TA = 6 min 52 sec), serving as the reference for image quality evaluation. The SPIRiT kernel and Wave PSF were estimated from the calibration data acquired separately in 3 seconds. The other scan parameters were reported in Figure 1. The reconstructed multi-coil images were fed into the MDI quantification framework to obtain quantitative T1/T2*/R2*/QSM maps and qualitative SWI/aT1w images.
Results
Figure 2 illustrates that the proposed L1-Wave-SPIRiT model could effectively reduce the noise amplification in the multi-echo images of the 9-fold accelerated MULTIPLEX data. Figure 3 demonstrates the improvement by L1-Wave-SPIRiT on the quantification accuracy of T1/T2*/R2*/Susceptibility maps, and on the visual signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) of qualitative aT1w/SWI images. In Figure 4, the T2* mapping by MDI with coil-uncombined complex images outperforms MDI with images combined by SENSE or sum-of-squares, and the conventional two-parameter T2* exponential fitting, especially in the low SNR region. Finally, Figure 5 demonstrates that the proposed L1-Wave-SPIRiT reconstruction with MDI quantification for the 9-fold accelerated MULTIPLEX data could achieve comparable quantification accuracy and qualitative image SNR as the reference scan, reducing the scan time by 55%.Discussion
This work develops a L1 regularized Wave SPIRiT reconstruction model for Wave-CAIPI sampling and achieves 9-fold acceleration of the MULTIPLEX scan with remarkable reduction of reconstruction noise. The coil-by-coil image reconstruction with reduced noise further benefits the subsequent multi-dimensional integration based multi-parametric quantification by fully utilizing the dimensional orthogonality. The proposed L1-Wave-SPIRiT acceleration could achieve comparable quantification accuracy and qualitative signal-to-noise ratio as the reference MULTIPLEX scan with a 55% reduction of scan time.Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81830056) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81801691).References
- Ye Y, Lyu J, Hu Y, Zhang Z, Xu J, Zhang W. MULTI-parametric MR imaging with fLEXible design (MULTIPLEX). Magn Reson Med. 2021; 87: 658– 673.
- Bilgic B, Gagoski BA, Cauley SF, et al. Wave-CAIPI for highly accelerated 3D imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2015, 73: 2152-2162.
- Polak D, Cauley S, Huang SY, et al. Highly-accelerated volumetric brain examination using optimized wave-CAIPI encoding. J Magn Reson Imaging 2019, 50: 961-974.
- Qiu Z, Jia S, Su S, et al. Highly accelerated parallel MRI using wave encoding and virtual conjugate coils. Magn Reson Med. 2021; 86: 1345– 1359.
- Schwarz JM, Pracht ED, Brenner D, Reuter M, Stöcker T. GRAPPA reconstructed wave-CAIPI MP-RAGE at 7 Tesla. Magn Reson Med. 2018; 80: 2427– 2438.
- Jia S, Qiu Z, Zhang L, et al. Aliasing-free reduced field-of-view parallel imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2022; 87: 1574– 1582.
- Murphy M, Alley M, Demmel J, et al. Fast l1-SPIRiT Compressed Sensing Parallel Imaging MRI: Scalable Parallel Implementation and Clinically Feasible Runtime. IEEE Trans. Medical Imaging 2012, 31:1250-1262.
- Lustig M and Pauly JM. SPIRiT: Iterative self-consistent parallel imaging reconstruction from arbitrary k-space. Magn Reson Med. 2010, 64: 457-471.
- Ye Y, Lyu J, Sun W, et al. A multi-dimensional integration (MDI) strategy for MR T2* mapping. NMR in Biomedicine 2021; 34:e4529.
- Ye Y, Lyu J, Hu Y, et al. Augmented T1-weighted steady state magnetic resonance imaging. NMR in Biomedicine 2022; 35:e4729.
- Walsh DO, Gmitro AF, Marcellin MW. Adaptive reconstruction of phased array MR imagery. Magn Reson Med. 2000, 43: 682-690.
Figures
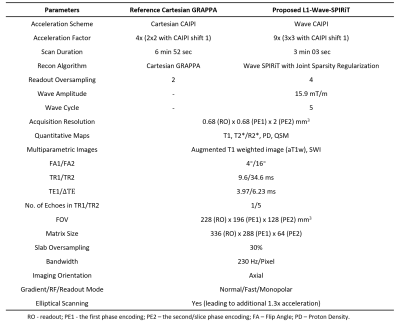
Figure 1. The imaging parameters of 9-fold Wave-CAIPI accelerated MULTIPLEX scan. The 4-fold CAIPI accelerated MULTIPLEX scan with GRAPPA reconstruction serves as the reference for image quality evaluation
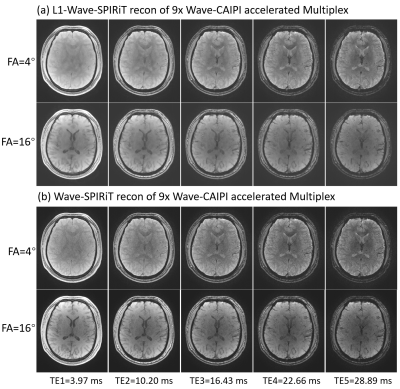
Figure 2. Comparing the multi-echo images reconstructed by L1-Wave-SPIRiT and Wave-SPIRiT for the 9-fold Wave-CAIPI accelerated MULTIPLEX data
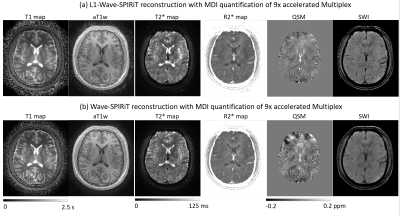
Figure 3. Comparing the quantitative T1/T2*/R2*/QSM maps and qualitative aT1w/SWI images produced by Multi-Dimensional Integration (MDI) using the multi-echo images reconstructed by L1-Wave-SPIRiT and Wave-SPIRiT respectively
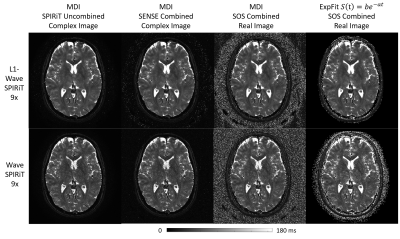
Figure 4. The effects of different reconstruction and coil combination methods on the T2* mapping by the Multi-Dimensional Integration (MDI) strategy
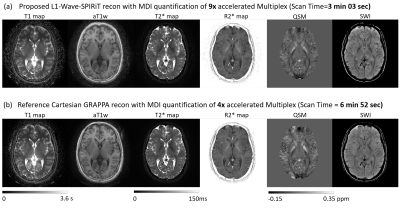
Figure 5. Comparing the quantitative maps and qualitative images produced by the L1-Wave-SPIRiT reconstruction of 9-fold Wave-CAIPI accelerated MULTIPLEX scan with the reference 4-fold CAIPI accelerated scan
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/1102