1091
QRAGE - Multi-Echo MPnRAGE and Model-Based Reconstruction for Quantitative MRI of Water Content, T1, T2* and Magnetic Susceptibility at 7T
Markus Zimmermann1, Zaheer Abbas1, Yannic Sommer1, Alexander Lewin1, Shukti Ramkiran1, Ana-Maria Oros-Peusquens1, Seong Dae Yun1, and N. Jon Shah1,2,3,4
1Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine 4, INM-4, Forschungszentrum Jülich, Germany, Jülich, Germany, 2Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine 11, INM-11, JARA, Forschungszentrum Jülich, Germany, Jülich, Germany, 3JARA - BRAIN - Translational Medicine, Aachen, Germany, Aachen, Germany, 4Department of Neurology, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany, Aachen, Germany
1Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine 4, INM-4, Forschungszentrum Jülich, Germany, Jülich, Germany, 2Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine 11, INM-11, JARA, Forschungszentrum Jülich, Germany, Jülich, Germany, 3JARA - BRAIN - Translational Medicine, Aachen, Germany, Aachen, Germany, 4Department of Neurology, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany, Aachen, Germany
Synopsis
Keywords: Sparse & Low-Rank Models, Image Reconstruction, Brain, Relaxometry, Quantitative Susceptibility mapping
The development of fast, accurate, and robust methods for multiparametric quantitative MRI (qMRI) at ultrahigh field strength remains an important topic of research. Here, we present a novel qMRI technique for the simultaneous quantification of water content, T1, T2*, and magnetic susceptibility, termed QRAGE. The proposed method combines a highly undersampled multi-echo MPnRAGE sequence with a model-based reconstruction approach. It acquires 171 different contrasts with full brain coverage and 1 mm isotropic resolution within 7:20 min from which the parametric maps are estimated. The accuracy and precision of QRAGE are demonstrated by comparison to gold-standard reference methods.Introduction
Multiparametric quantitative MRI of water content CW, T1, and T2* provides insight into a multitude of neuropathological changes, such as brain edema and white matter hyperintensities1,2. Established methods to map CW are based on the variable flip angle (VFA) protocol, which acquires several multi-echo gradient-echo sequences with different flip angles. It additionally yields estimates for T1 and T2* but is slow and sensitive to the B1+ inhomogeneity that occurs at ultra-high field strength3,4.The ME-MP2RAGE sequence acquires multiple gradient echoes at two different inversion time points to simultaneously obtain information about T1, T2*, and the magnetic susceptibility χ5–7. The signal evolution at each voxel position can be described using a two-dimensional multi-exponential model, with the two dimensions being T1 and T2* relaxation and the multi-exponential nature originating from the various microstructural environments inside each voxel. It is robust against B0 and B1+ inhomogeneity and has a low SAR burden, making it well-suited for application at 7T. However, measurement time limits the number of inversion and echo times, thereby limiting the achievable accuracy and precision of parametric estimates.
We propose a novel, robust, single-scan image acquisition, and model-based reconstruction method, termed QRAGE, to provide parametric estimates of CW, T1, T2*, and χ at ultrahigh field strength with high accuracy and within a clinically acceptable measurement time. The QRAGE sequence is an extension of the ME-MP2RAGE sequence and measures 19 inversion and 9 echo time points. It uses a highly undersampled radial readout and a model-based reconstruction technique to reduce acquisition time. The proposed algorithm is based on locally low-rank Hankel and Casorati matrices8–10. It produces accurate and robust parametric estimates even at high acceleration factors by incorporating the analytical temporal signal model without approximation errors, taking partial volume effects and multi-compartment behavior into account, and providing a convex problem formulation.
Methods
The proposed model-based reconstruction technique reconstructs the images x from the k-space data d acquired at multiple inversion and echo times, with respect to the temporal signal model by solving$$$\min_\mathbf{x}\frac{1}{2}\left\lVert\mathbf{Ax}-\mathbf{d}\right\rVert_2^2+\lambda_\mathrm{W}\left\lVert\mathbf{Wx}\right\rVert_{1,2}+\lambda_\mathrm{H}\left\lVert \mathbf{Hx}\right\rVert_{*,1}+\lambda_\mathrm{C}\left\lVert \mathbf{Cx}\right\rVert_{*,1}$$$
with the encoding operator A, the Wavelet operator W, the Hankel operator H, the Casorati operator C, and the regularization weights λW, λH and λC. The concept of locally low-rank Hankel and Casorati matrices is depicted in Figure 1.
All experiments were conducted using a commercial 7T scanner (MAGNETOM Terra, Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany) and the 32-element NOVA coil. Following prior, written, informed consent, MR data was acquired from four healthy volunteers (male, aged 26-32). A spatiotemporally incoherent golden-angle stack-of-stars sampling trajectory was used, consisting of eight spokes per contrast, where each partition had the same k-space undersampling pattern11. Furthermore, QRAGE was accelerated along the partition dimension by acquiring only every second partition with a 32-partition keyhole.
Missing k-space data along the partition dimension was recovered by first using GRAPPA12 applied individually to every spoke. Data was then Fourier transformed along the partition direction, which allowed further data processing in a slice-by-slice fashion. Geometric coil compression13 was used to compress the data to eight virtual channels. Gradient-delay was corrected using RING14. Coil sensitivities were estimated using SAKE15 to reconstruct a calibration area, followed by ESPIRiT16. Data was then reconstructed offline using model-based reconstruction. The reconstruction time was approximately 8 hours on the JURECA-DC system of the Jülich Supercomputing Center, where all slices were reconstructed in parallel. The regularization parameters were empirically set to λW=0.001, λH=0.1, and λC=0.01.
To provide reference data, the following measurements were performed: two GRE2D sequences for the VFA method3, a GRE3D sequence for susceptibility mapping, the TAPIR17 sequence for T1 mapping, a TSE sequence for transmit field inhomogeneity correction, and an MP2RAGE sequence18. The parameters of all sequences measured are given in Table 1. After QRAGE reconstruction, quantitative parameter maps were estimated using a two-dimensional mono-exponential model. For QRAGE and reference data, water content and magnetic susceptibility maps were computed according to the VFA and TGV-QSM methods, respectively3,19.
Results
Figure 2 shows quantitative maps and the T1-weighted image of QRAGE in native space for a single subject. Figure 3 shows a histogram analysis of the QRAGE and reference methods in MNI space for the same subject. Good agreement can be observed for water content, T1 and magnetic susceptibility. T2* appears to be slightly lower for QRAGE as compared to the reference method. Table 2 shows the median of water content, T1 and T2* for all four subjects in grey and white matter and is in agreement with the literature3,20. Absolute deviations between QRAGE and reference methods are ≤0.7% for water content, ≤21 ms for T1 and ≤2 ms for T2* across all subjects.Discussion and conclusions
QRAGE is a novel approach to fast, accurate and robust multi-parametric MRI at ultrahigh field strength. It produces parametric maps with a resolution of 1 mm3 and full brain coverage within an acquisition time of 7:20 min, which is comparable to a qualitative MP-RAGE scan. As a side product, QRAGE also provides a T1-weighted image with contrast comparable to that of the MP2RAGE sequence, making it suitable as a drop-in replacement. As the MP2RAGE sequence is used in almost every neuroscientific research protocol, ready acceptance of the QRAGE method is anticipated.Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) – 446320670.
The authors gratefully acknowledge the computing time granted through JARA on the supercomputer JURECA21 at Forschungszentrum Jülich.
References
- Ayata, C. & Ropper, A. H. Ischaemic brain oedema. J. Clin. Neurosci. 9, 113–124 (2002).
- Iordanishvili, E. et al. Quantitative MRI of cerebral white matter hyperintensities: A new approach towards understanding the underlying pathology. NeuroImage 202, 116077 (2019).
- Abbas, Z. et al. Analysis of proton-density bias corrections based on T1 measurement for robust quantification of water content in the brain at 3 Tesla. Magn. Reson. Med. 72, 1735–1745 (2014).
- Abbas, Z., Gras, V., Möllenhoff, K., Oros-Peusquens, A.-M. & Shah, N. J. Quantitative water content mapping at clinically relevant field strengths: A comparative study at 1.5T and 3T. NeuroImage 106, 404–413 (2015).
- Metere, R., Kober, T., Möller, H. E. & Schäfer, A. Simultaneous Quantitative MRI Mapping of T1, T2* and Magnetic Susceptibility with Multi-Echo MP2RAGE. PLOS ONE 12, e0169265 (2017).
- Caan, M. W. A. et al. MP2RAGEME: T 1 , T 2 * , and QSM mapping in one sequence at 7 tesla. Hum. Brain Mapp. 40, 1786–1798 (2019).
- Sun, H. et al. Extracting more for less: multi‐echo MP2RAGE for simultaneous T 1 ‐weighted imaging, T 1 mapping, mapping, SWI, and QSM from a single acquisition. Magn. Reson. Med. 83, 1178–1191 (2020).
- Zhang, T., Pauly, J. M. & Levesque, I. R. Accelerating parameter mapping with a locally low rank constraint. Magn. Reson. Med. 73, 655–661 (2015).
- Peng, X. et al. Accelerated exponential parameterization of T2 relaxation with model-driven low rank and sparsity priors (MORASA): Accelerated T2 Mapping with MORASA. Magn. Reson. Med. 76, 1865–1878 (2016).
- Zimmermann, M., Abbas, Z., Dzieciol, K. & Shah, N. J. Accelerated Parameter Mapping of Multiple-Echo Gradient-Echo Data Using Model-Based Iterative Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37, 626–637 (2018)
- Winkelmann, S., Schaeffter, T., Koehler, T., Eggers, H. & Doessel, O. An optimal radial profile order based on the golden ratio for time-resolved MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 26, 68–76 (2007).
- Griswold, M. A. et al. Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn. Reson. Med. 47, 1202–1210 (2002).
- Zhang, T., Pauly, J. M., Vasanawala, S. S. & Lustig, M. Coil compression for accelerated imaging with Cartesian sampling. Magn. Reson. Med. 69, 571–582 (2013).
- Rosenzweig, S., Holme, H. C. M. & Uecker, M. Simple auto‐calibrated gradient delay estimation from few spokes using Radial Intersections (RING). Magn. Reson. Med. 81, 1898–1906 (2019).
- Shin, P. J. et al. Calibrationless parallel imaging reconstruction based on structured low-rank matrix completion. Magn. Reson. Med. 72, 959–970 (2014).
- Uecker, M. et al. ESPIRiT - An eigenvalue approach to autocalibrating parallel MRI: Where SENSE meets GRAPPA. Magn. Reson. Med. 71, 990–1001 (2014)
- S. Steinhoff, K. Z., M. Zaitsev & Shah, N. J. Fast T1 Mapping With Volume Coverage. Magn. Reson. Med. 46, 131–140 (2001).
- Marques, J. P. et al. MP2RAGE, a self bias-field corrected sequence for improved segmentation and T1-mapping at high field. NeuroImage 49, 1271–1281 (2010).
- Langkammer, C. et al. Fast quantitative susceptibility mapping using 3D EPI and total generalized variation. NeuroImage 111, 622–630 (2015).
- Olsson, H., Andersen, M., Kadhim, M. & Helms, G. MP3RAGE: Simultaneous mapping of T 1 and B1+ in human brain at 7T. Magn. Reson. Med. 87, 2637–2649 (2022)
- Jülich Supercomputing Centre. JURECA: Data Centric and Booster Modules implementing the Modular Supercomputing Architecture at Jülich Supercomputing Centre Journal of large-scale research facilities, 7, A182 (2018)
Figures
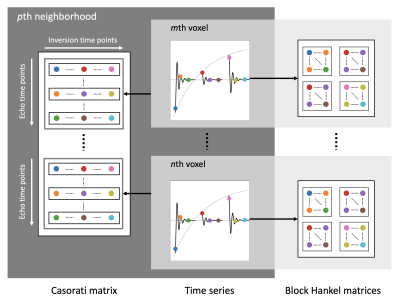
Figure 1: Concept of the proposed model-based reconstruction algorithm. The time series is reorganized into a Block Hankel matrix at every voxel position. Additionally, the time series within a 5 × 5 local neighborhood are stacked along the echo time dimension to form a Casorati matrix at every voxel position. The rank of the Hankel and Casorati matrices corresponds to the number of tissue compartments within each voxel and local neighborhood, respectively. The algorithm minimizes the rank of all Hankel and Casorati matrices by minimizing the sum of their nuclear norms.
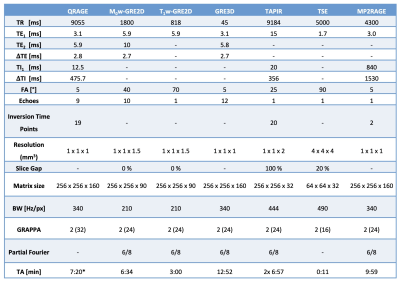
Table 1: Sequence parameters of the QRAGE sequence, the VFA protocol used for water content and T2* mapping, consisting of a M0-weighted and a T1-weighted GRE2D sequence, the GRE3D sequence used for magnetic susceptibility mapping, the TAPIR sequence used for T1 mapping, a Turbo-Spin-Echo (TSE) sequence used for B1+ mapping and an MP2RAGE sequence.
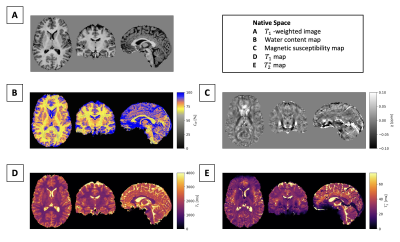
Figure 2: In vivo results in native space. (A) T1-weighted image from QRAGE. (B-D) Water content map CW, magnetic susceptibility map χ, T1 map and T2* map from QRAGE.
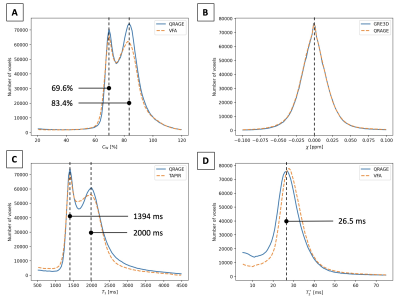
Figure 3: Histogram analysis of in vivo results in MNI space. (A) Water content map CW from VFA and QRAGE. Mean water content of grey and white matter corresponds to the peaks in the histogram for both VFA and QRAGE. (B) Magnetic susceptibility map χ from GRE3D and QRAGE. (C) T1 map from TAPIR and QRAGE. Mean T1 of grey and white matter corresponds to the peaks in the histogram for TAPIR and QRAGE. (D) T2* map from VFA and QRAGE.
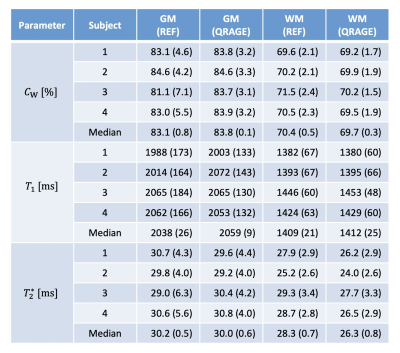
Table 2: Median water content, T1 and T2* values
in grey and white matter provided by QRAGE and the reference methods
are given for all measured subjects and across subjects, with the median
absolute deviation given in parenthesis. As reference methods, VFA was
used for water content and T2* while TAPIR was used for T1 mapping.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/1091