1075
Automatic identification of Moyamoya disease based on time-of-flight MR angiography
Zheng Tan1, Mingming Lu2, Shuai Liu1, Shitong Liu2, Hongtao Zhang2, Xiaoying Tang1, Jianming Cai2, and Fei Shang1
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Life Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, China, 2Department of Radiology, The Fifth Medical Center of PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Life Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, China, 2Department of Radiology, The Fifth Medical Center of PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Vessels, Stroke
Moyamoya disease (MMD) is a rare chronic progressive cerebrovascular disease that causes strokes. For the diagnosis of MMD, time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography (TOF-MRA) can be an alternative to digital subtraction angiography (gold standard) owing to its non-invasive and radiation-free attributes. In this study, the deep learning method (ResNet-50) was used for MMD automatic diagnosis on the maximum intensity projection images from 3D TOF-MRA, and five-fold cross-validation was used for validation. The method exhibits the accurate ability (AUC: 0.990 ± 0.008, accuracy: 0.933 ± 0.063) to identify MMD and has the potential to improve the clinical management of MMD.INTRODUCTION
Moyamoya disease (MMD) is a cerebrovascular disease characterized by chronic progressive stenosis or occlusion in the terminal portions of the bilateral internal carotid artery1. Early diagnosis of MMD can facilitate its treatment and prognosis. Although digital subtraction angiography (DSA) was seen as the gold standard in MMD diagnosis2, time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography (TOF-MRA) has been widely used due to its non-invasive and radiation-free imaging3. This study aimed to automatically detect the MMD by deep learning on TOF-MRA.METHODS
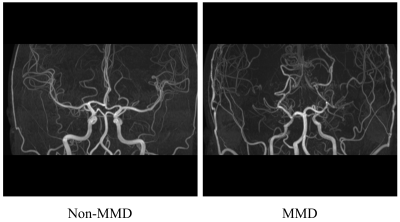
Materials: Sixty MMD patients (36.13 ± 16.45 years old, 30 females) diagnosed by DSA and sixty controls without MMD (47.67 ± 7.37 years old, 20 females) were recruited in the present study. Each subject underwent head 3D TOF-MRA scan (TR/TE = 20.00 ms/3.43 ms, flip angle = 18°) on a 3.0 T MR scanner (AWP45571, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany). Image process: A maximum intensity projection (MIP) was used on the 3D TOF images to generate the MIP-TOF image. The MIP-TOF image was resized to 512 × 512 by cropping and padding with 0 (Figure 1), and the image intensities were normalized to [0, 255] by the linear normalization. Next, horizontal flip and rescale [0.9, 1.1] was applied in data augmentation. Model building: ResNet-50 with cross-entropy loss function and Adam optimizer (learning rate = 0.0001) was used to distinguishing MMD in the present study4. Five-fold cross-validation was conducted (training set: test set = 4: 1). The models were trained for 200 epochs with a batch size was 15, and were built by PyTorch 1.11.0 on a computer equipped with Intel i7-9700F CPU, 16 GB RAM and Nvidia RTX 2070S graphic cards (8 GB memory). Evaluation metrics: F1 score, accuracy, sensitivity and specificity were calculated to assess the classification performance of the model. The analysis of receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the classification ability, and the area under the curve (AUC) was also provided.RESULTS
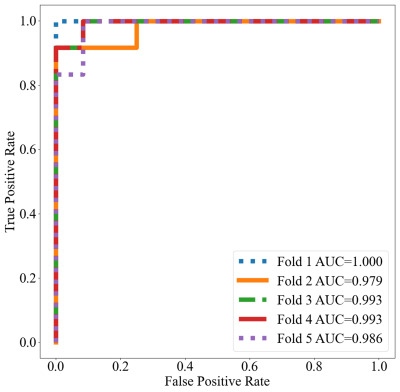
The method achieved a high average diagnosis performance (AUC: 0.990 ± 0.008, F1 score: 0.936 ± 0.058, accuracy: 0.933 ± 0.063, sensitivity: 0.950 ± 0.046, specificity: 0.917 ± 0.102). The ROC curves of five-fold cross-validation were shown in Figure 2.DISCUSSION
In this study, we investigated the performance of deep learning in distinguishing MMD on TOF images. Five-fold cross-validation was used to validate the robustness of the model. The model built by ResNet-50 can accurately identify patients with MMD. MIP-TOF images can be acquired in a patient-friendly manner. The models didn't demand a massive computing resource in view of MIP-TOF images. Our result exhibited the potential of non-invasive and automatic diagnosis for MMD using deep learning on MIP-TOF images.CONCLUSION
The use of deep learning on TOF images allows for non-invasive and accurate automatic diagnosis of MMD and has the potential for clinical application.Acknowledgements
None.References
- Ihara M, Yamamoto Y, Hattori Y, et al. Moyamoya disease: diagnosis and interventions. Lancet Neurol. 2022;21(8):747-758.
- Hwang I, Cho WS, Yoo RE, et al. Revascularization Evaluation in Adult-Onset Moyamoya Disease after Bypass Surgery: Superselective Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion MRI Compared with Digital Subtraction Angiography. Radiology. 2020;297(3):630-637.
- Ren S, Wu W, Su C, et al. High-resolution compressed sensing time-of-flight MR angiography outperforms CT angiography for evaluating patients with Moyamoya disease after surgical revascularization. BMC Med Imaging. 2022;22(1):64.
- He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2016;770-778.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/1075