0935
Phase-Contrast MRI with Hybrid One- and Two-sided Simultaneous Three Directional Flow-Encoding and Velocity SPectrum SepAration (HOTSPA+)
Wenjian Liu1, Junpu Hu2, Jiayu Zhu2, Jian Xu3, Zijian Zhou1, Haikun Qi1,4, and Peng Hu1,4
1School of Biomedical Engineering, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, China, 2United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 3UIH America, Inc., Houston, TX, United States, 4Shanghai Clinical Research and Trial Center, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, China
1School of Biomedical Engineering, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, China, 2United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 3UIH America, Inc., Houston, TX, United States, 4Shanghai Clinical Research and Trial Center, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Flow, Velocity & Flow
Phase contrast MRI (PC MRI) has been widely used to quantify blood flow and velocity. Four-dimensional (4D) flow PC MRI needs to acquire the FC data and three-directional (3D) FE data interleaved within each cardiac k-space segment. In this work, we propose a more efficient flow encoding strategy for PC MRI using a temporal modulation technique and we showed the preliminary feasibility of quadrupling the temporal resolution or reducing the scan time by 70% compared with conventional 4D flow by redesigning and adjusting the temporal modulation strategy for under-sampled M1 space.INTRODUCTION
Phase contrast MRI (PC MRI) has been widely used to quantify blood flow and velocity. In conventional PC MRI, the flow-compensated (FC) and flow-encoding (FE) data are acquired in an interleaved fashion. Four-dimensional (4D) flow PC MRI needs to acquire the FC data and three-directional (3D) FE data interleaved within each cardiac k-space segment.1 A temporal modulation technique with simultaneous two-directional flow-encoding (HOTSPA) has been used in PC MRI for accelerating blood velocity measurement.2 In this work, we extend this concept and propose a PC MRI strategy that simultaneous encodes the velocity in three directions, dubbed HOTSPA+.METHODS
The temporal sampling period of the conventional reference 4D flow PC-MRI is 4*TR*views-per-segment (VPS). In the HOTSPA+ technique, we assume that that the FC background phase data do not temporally change as fast as the FE data3. We first acquire a shared FC segment and then start to acquire the simultaneous three-directional FE data. The temporal sampling period of three FE data is shorted to 1*TR*VPS. This is achieved by applying two-sized FE both in the y-direction and x-direction (i.e. Z+Y+X, Z-Y+X, Z+Y-X, and Z-Y-X directions) in four cardiac phases as shown in Fig 1. The entire acquisition process shares the FC data, and we apply filters in the temporal frequency domain to extract the temporal flow signal curve for each of the X, Y, and Z directions. As shown in Fig. 2, if we apply a temporal Fourier transform to the FE data, we can see that the velocity spectra in the three directions (X, Y, and Z) share the large spectral bandwidth BW1 corresponding to a temporal sampling rate of one TR, which is typically about 4ms, rather than 4 TRs in a conventional 4D flow acquisition. The spectral bandwidth allocation for each of the three orthogonal directions can be retrospectively determined after the MRI scan on a voxel-by-voxel basis. Given the FE encoding used shown in Fig. 1, the Y velocity spectrum is shifted by half of BW1, the X spectrum is shifted by a quarter of BW1 and split, while the Z spectrum remains intact. Therefore, the three spectra can be separated from each other using filters. Such temporal modulated FE strategy accelerates PC MRI by encoding three-directional (3D) velocities using only 1 TR (Z+Y±X, and Z-Y±X) with a shared FC instead of 4TRs (four M1 space encoding steps including FC and three-directional FE).To test our hypothesis, a volunteer was scanned at the common carotid arteries (CCAs) using three sequences: 1) the HOTSPA strategy with 2D spatial encoding.2 2) our HOTSPA+ strategy with 2D spatial encoding. 3) conventional 4D flow FC/3FE with 2D spatial encoding. HOTSPA’s TE/TR=4.14/14.1 ms, VPS=2, 4, and 6, HOTSPA+’s TE/TR=4.16/7.1 ms, VPS=2, 4, and 6, and 4D flow’s TE/TR=4.1/28 ms, VPS=1, 2, and 4. The common sequences parameters were: flip angle=15°, VENC=170 cm/s, FOV=270*270 cm²,acquired matrix size=192*192, slice thickness=6 mm.
RESULTS
Figures 3 and 4 show examples of through-plane mean velocity and peak velocity (average and maximum within the vessel lumen) of the CCA comparing three strategies. Fig.3 shows the 4-VPS conventional 4D flow FC/3FE, the 4-VPS HOTSPA , and 4-VPS HOTSPA+. The velocity information can be clearly shown in the figure. The comparison between HOTSPA and HOTSPA+ shows that HOTSPA+ retains more velocity information due to its higher temporal resolution. Fig.4 shows the 2-VPS conventional 4D flow FC/3FE, the 4-VPS HOTSPA, and 6-VPS HOTSPA+. The 6-VPS HOTSPA+ still retains good velocity profile information compared with 2-VPS 4D flow FC/3FE, but the acquisition was three times faster. compared with 4-VPS HOTSPA, 6-VPS HOTSPA+ also retains good velocity information but achieves faster acquisition.DISCUSSION
In this work, we propose a more efficient flow encoding strategy for PC MRI using a temporal modulation technique and we showed the preliminary feasibility of quadrupling the temporal resolution or reducing the scan time by 70% compared with conventional 4D flow by redesigning and adjusting the temporal modulation strategy for under-sampled M1 space. Our strategy can be combined with conventional acceleration techniques, such as parallel imaging, k-t acceleration methods, and compressed sensing, to further shorten the scan time of PC MRI.CONCLUSION
The proposed HOTSPA+ technique achieves nearly quadruple the temporal resolution or triple acceleration of 4D PC MRI while maintaining accuracy for through-plane mean velocity and peak velocity quantification.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Soulat G, McCarthy P, Markl M. 4D Flow with MRI. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2020;22:103-126. doi:10.1146/annurev-bioeng-100219-110055
2. Wang D, Shao J, Ennis DB, Hu P. Phase-contrast MRI with hybrid one and two-sided flow-encoding and velocity spectrum separation. Magn Reson Med. 2017;78(1):182-192. doi:10.1002/mrm.26366
3. Wang D, Shao J, Rapacchi S, Middione MJ, Ennis DB, Hu P. Phase contrast MRI with flow compensation view sharing. Magn Reson Med. 2015;73(2):505-513. doi:10.1002/mrm.25133
Figures
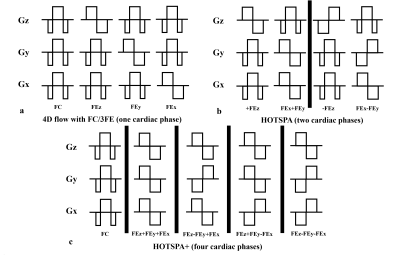
Figure
1. Sequence diagrams of a) conventional 4D flow FC/3FE, b) HOTSPA, c) HOTSPA+.
4D flow with FC/3FE is encoded four times to acquire one cardiac phase. HOTSPA
is encoded four times to acquire two cardiac phases. HOTSPA+ is encoded four
times to acquire four cardiac phases except for the shared FC.
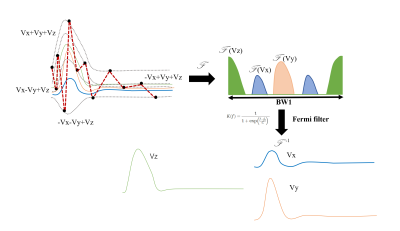
Figure
2. Three-directional velocities separation process of HOTSPA+. Firstly, the acquisition
process of three-directional velocities. And then the result of
three-directional velocities after the Fourier transform. Separation of
velocities peaks in three directions. With the Fermi filter, the velocities in
three directions are separated after the inverse Fourier transform.
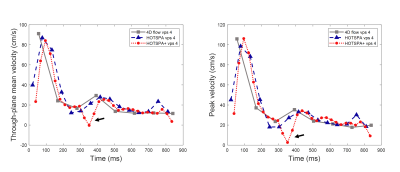
Figure
3. Through-plane mean velocity and peak velocity profiles from conventional 4D
flow, HOTSPA and HOTSPA+. The three techniques had the same data acquisition
time, but HOTSPA+ provided higher temporal resolution compared to the other two
techniques. Consequently, HOTSPA+ is able to show more features of the velocity
curve (arrow) that was not identified using the other two methods.
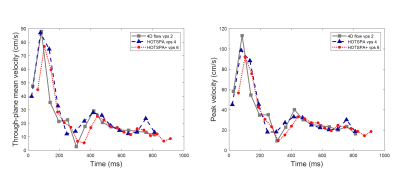
Figure
4. Through-plane mean velocity and peak velocity are shown separately. 2-VPS 4D
flow FC/3FE, 4-VPS HOTSPA, and 6-VPS HOTSPA+ show that HOTSPA+ can still
maintain good velocity information when it has a higher VPS.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/0935