0848
Improving Quantification of Hyperpolarized 13C-Pyruvate Metabolism Using Pyruvate Metabolite Specific bSSFP and Variable Flip Angles1Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: MR Fingerprinting/Synthetic MR, RF Pulse Design & Fields, variable flip angle
A pyruvate-specific bSSFP protocol was defined, based on prior work, demonstrating increased signal efficiency over GRE sequences. Monte Carlo simulations evaluated signal efficiency and kinetic performance of potential flip angle schemes. A sigmoid-based flip scheme, varying from 5 to 80 degrees, showed greatest performance of kPL estimation compared to simulated GRE and constant flip angle bSSFP. Small animal studies validated the expected signal increase and kPL estimation, with resulting kinetic parameter maps showing consistency among methods and qualitative noise reduction.
Introduction
Hyperpolarized (HP) carbon 13 (13C) imaging is a powerful non-invasive tool to study metabolic processes in real time. One application of interest is the measurement of pyruvate-to-lactate (kPL) conversion as an indicator of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) expression and tumor aggressiveness.1 Previously, our group has demonstrated the advantages of Balanced Steady-State Free Precession (bSSFP) based acquisition of lactate signal to increase sensitivity compared to conventional GRE-based methods,2,3 due to leveraging bSSFP’s inherent high SNR efficiency. In this work, we build upon these ideas to further improve sensitivity, specifically by extending the bSSFP framework to both pyruvate and lactate detection, implementation of variable RF flip angle excitation schemes, and parameter estimation using a MR Fingerprinting (MRF) dictionary matching based approach.Methods
Following prior 3D Metabolite Specific bSSFP (MS-bSSFP) methods, pyruvate bSSFP sequence was implemented with 3D stack-of-spiral acquisition (Figure 1a).2,3 bSSFP imaging parameters for both lactate and pyruvate imaging were performed using 4 spiral interleaves, FOV = 8 x 8 x 33.6 cm, matrix size 32 x 32 x 16, at TR of 15.3 ms using metabolite specific RF excitation. Different flip angle excitation schemes of the MS-bSSFP sequence for pyruvate were explored, including constant flip angle schemes (Figure 1b), and variable flip angle strategies, including linearly-ramped flip angle strategies, as well as a sigmoid-ramped flip angle strategy, or “sigmoid-MRF” (Figure 1b).Monte Carlo simulations were used to assess the relative performance of implemented acquisition schemes. Simulated signal evolutions for both MRF dictionary quantification and Monte Carlo simulation experiments were calculated from the 2-pool Bloch-McConnell equations. For Monte Carlo experiments, bootstrap complex noise was added to simulated ground truth signal evolutions (kPL=0.025 1/s, T1, PYR = T1, LAC = 30s, T2, PYR = T2, LAC = 0.5s). Parameter estimation was performed using complex inner product template matching against pre-constructed dictionaries of signal evolutions varying across different kPL values.
Animal studies were performed using previously described experimental setups2,3 on a clinical 3T MRI scanner with a 1H/13C transceiver single channel birdcage coil on adult Sprague Dawley rats.
Results
Monte Carlo simulation results (Figure 2) show kPL measurement precision improved up to 2.2 fold through constant flip angle pyruvate MS-bSSFP acquisition compared to GRE, and up to 2.6 fold improvement using sigmoid-MRF.In vivo dynamic images (Figure 3) illustrate the higher SNR maintained by bSSFP based pyruvate acquisitions compared to GRE based acquisition. The signal curves in the kidneys show approximately 2-fold SNR increase in pyruvate. Additionally, pyruvate contrast is shown to be altered by the bSSFP sequence, showing higher relative signal in the blood vessels.
Figures 4 and 5 show dynamic images and kinetic model fits comparing pyruvate GRE to pyruvate bSSFP with constant and the proposed MRF variable flip angle strategy. Expected distributions of the estimated parameters are observed between all methods, with relatively homogenous low level kPL, but with relatively high lactate flux within the kidneys compared to other organs. Qualitatively, sigmoid-MRF strategy kinetics appear less noisy, consistent with simulation results.
Discussion & Conclusion
In this work, we demonstrate the potential of a novel bSSFP based acquisition of pyruvate and lactate signal to increase sensitivity for lactate dehydrogenase metabolism. Simulation experiments show substantial parameter estimation precision increases compared to previous methods, and this is further enhanced using a variable flip angle scheme using a sigmoid scheme.Many parameter estimation methods have been investigated for HP-13C analysis. Although AUC methods have previously been shown to be robust and accurate for conventional GRE based methods,4 the same underlying assumptions for AUC methods have not been similarly established for variable flip angle bSSFP methods. In the current work, MRF dictionary based parameter estimation scheme was used for parameter estimation due to its flexibility, however optimal quantification methods is an area of active investigation.
In vivo methods show prominently increased signal within acquired dynamic images within voxels with substantial blood pool such as renal parenchyma, based on the substantial SNR efficiency advantages of bSSFP methods for long T2 moieties. Resulting quantified kPL and lactate flux maps appear high quality, although some spiral artifacts can be noted, particularly around high flow voxels. Overall, these results are promising, and suggest that these methods may be leveraged for higher spatial resolution and improved sensitivity and characterization of pathology.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
- Sriram R, Van Criekinge M, DeLos Santos J, et al. Elevated Tumor Lactate and Efflux in High-grade Prostate Cancer demonstrated by Hyperpolarized 13C Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of Prostate Tissue Slice Cultures. Cancers. 2020;12(3):537. doi:10.3390/cancers12030537
- Tang S, Bok R, Qin H, et al. A metabolite-specific 3D stack-of-spiral bSSFP sequence for improved lactate imaging in hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate studies on a 3T clinical scanner. Magn Reson Med. 2020;84(3):1113-1125. doi:10.1002/mrm.28204
- Liu X, Tang S, Mu C, et al. Development of specialized magnetic resonance acquisition techniques for human hyperpolarized [ 13C, 15N 2 ]urea + [ 1-13C ]pyruvate simultaneous perfusion and metabolic imaging. Magn Reson Med. Published online May 8, 2022:mrm.29266. doi:10.1002/mrm.29266
- Larson PEZ, Chen H, Gordon JW, et al. Investigation of analysis methods for hyperpolarized 13C-pyruvate metabolic MRI in prostate cancer patients. NMR Biomed. 2018;31(11). doi:10.1002/nbm.3997
Figures
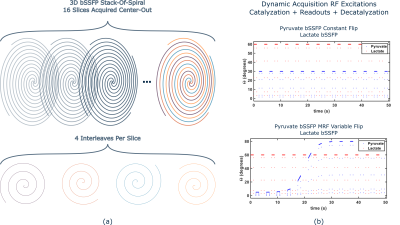
Figure 1: (a) Depiction of interleaved, stack-of-spiral readout demonstrated in MS-bSSFP acquisitions of lactate and pyruvate.2,3 (b) RF excitation flip angles for alternating dynamic acquisitions of pyruvate and lactate. The design of the MRF variable flip scheme is based on a sigmoid.
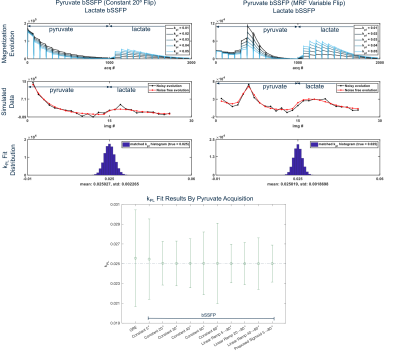
Figure 2: Simulated magnetization evolution and signal dynamics comparing pyruvate bSSFP constant flip angle and MRF flip acquisitions. The top row shows the simulated transverse magnetization for various pyruvate-to-lactate conversion rates (kPL), the middle row shows simulated data, and the bottom row shows Monte Carlo simulation results for fitting kPL with noise. The Monte Carlo results show expected improvements using bSSFP and a variable MRF flip schedule.
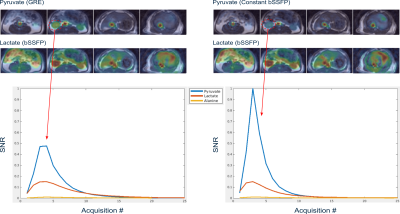
Figure 3: Comparison of pyruvate GRE and pyruvate bSSFP in rat kidneys. The top row shows AUC metabolite images. The ROI plots show similar lactate dynamics and signal amplitude, but approximately 2-fold higher pyruvate SNR with bSSFP, consistent with the high SNR efficiency shown in prior bSSFP based approaches.2,3
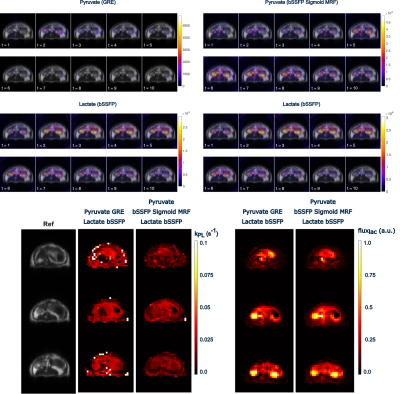
Figure 4: Comparison of pyruvate GRE and pyruvate bSSFP kinetics in rat kidneys. The dynamic images are noticeably different with the bSSFP sigmoid-MRF variable flip. The rate constants and fluxes computed from this data are also very similar between the two approaches.
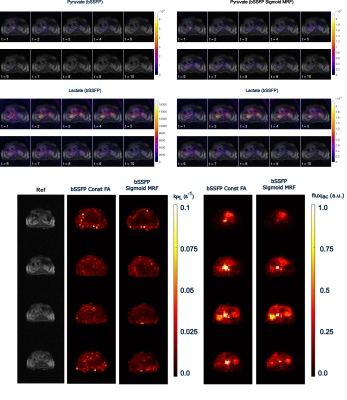
Figure 5: Comparison of pyruvate bSSFP with a constant flip angle to bSSFP sigmoid-MRF variable flip angle strategies. The dynamic images are noticeably different with bSSFP sigmoid-MRF variable flip. The kinetic model fits computed from this data show a similar distribution, but the sigmoid-MRF variable flip has a smoother, less noisy appearance.