0811
EVAC: Multi-scale V-Net with Deep Feature Conditional Random Field Layers for Brain Extraction1Intelligent Systems Engineering / Neuroscience, Indiana University, Bloomington, Bloomington, IN, United States, 2Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Segmentation, Brain
Brain Extraction is a complicated semantic segmentation task. While Deep Learning methods are popularly used, they are heavily biased towards the training dataset. To reduce this dependency, we present EVAC (Enhanced V-net like Architecture with Conditional Random Fields), a novel Deep Learning model for Brain Extraction. Using V-net as a skeleton, we propose three improvements: multi-scale inputs, modified CRF layer and regularizing Dice Loss. Results show that these changes not only increase accuracy but also the efficiency of the model as well. Compared to the state-of-the-art methods, our model achieves high and stable accuracy across datasets.Introduction
Brain Extraction (also known as Skullstripping) is one of the most challenging problems in medical image segmentation. Multiple methods have been proposed to solve this problem, both traditional and Deep Learning based1. However, there is still a large window for improvement.Traditional methods mainly fail because brain and nearby non-brain tissues have similar intensities. Deep Learning models should in theory resolve such issues given enough training data and ground truth segmentations. The true brain masks, however, are mostly results from an arbitrary method with refinement. Thus, Deep Learning models trained on such data can share potential biases or errors from the traditional methods. Previously, Fully Connected Conditional Random Fields(CRF)2 have been a popular choice for correcting such errors.
However, there are two reasons CRFs are not used as much as they could in medical imaging. First, it is computationally heavy to fully connect all the voxels. Second, CRFs often use color channels as features, which many medical images lack. One could simply use a single channel, but previous studies have shown this to be ineffective3.
In this work, we propose EVAC (Enhanced V-net like Architecture with Conditional Random Fields). The model uses multi-scale information with improved Conditional Random Field layers to fine-tune the method for semantic segmentation of medical images.
Methods
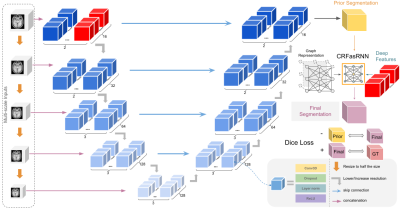
We propose three improvements to V-net4, a variant of U-net5 for 3D medical image segmentation. First, we utilize multi-scale raw inputs to reinforce multi-scale feature usage of the architecture, which were proven to be effective in medical image segmentation tasks 6,7. While this alone is not new, ablation studies provided below show a synergistic effect with our other improvements.Next, we modify the previously proposed CRFasRNN8 layers. While the Recurrent Layer solves the efficiency problem, there is still the single channel problem. We propose to solve the lack of features by providing features from the last layer of the original scale along with the intensities. Reinforced by the multi-scale inputs, the CRF layer utilizes precise smaller features of the image, which are important for fine-tuning the segmentation results.
Finally, we propose a significant change to the loss function. We introduce an additional regularizing Dice Loss4 between the segmentation results of the main architecture and the CRF layer. Adding a negative Dice Loss forces the CRF layer to be a prominent step in the segmentation process. Fig. 1 shows a summary of the model architecture.
Results
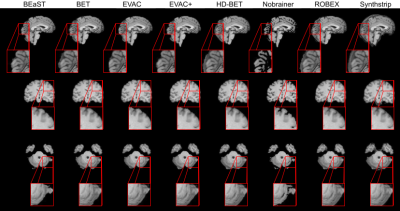
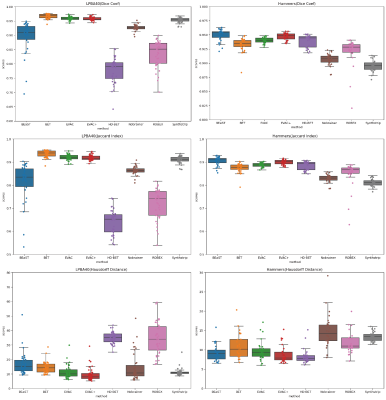
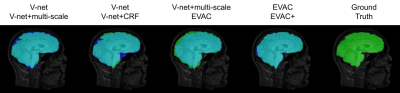
Fig. 2 shows a comparison of our model with different state-of-the-art available methods 9-14. Methods were selected based on accessibility. We have added our model with and without the special loss to emphasize its effectiveness. Our model without the additional loss already performs well by removing the dura mater and CSF, while minimizing errors in the cerebellum.Fig. 3 provides scores on public datasets, LONI Probabilistic Brain Atlas (LPBA40)15 and adult brains of Hammers Atlas Database 16,17. Dice Coefficient, Jaccard Index and Hausdorff Distance were chosen for evaluation. While other methods have unstable results depending on the dataset, our models have a stable high score in all metrics regardless of the data.
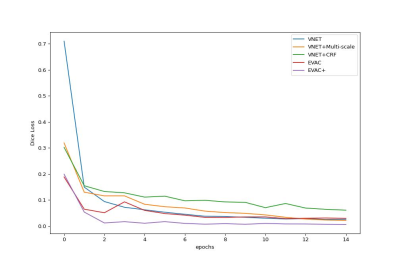
Finally, we provide ablation studies of our proposed changes. Fig. 4 shows the original Dice Loss change per epoch. It is clear that each enhancement we propose provides an advantage in training efficiency-wise. It is worth noting that the additional loss function is still more effective in the original Dice Loss, even though the additional Dice Loss function of the model works as a regularizer. Fig. 5 shows the increase in accuracy as we add the proposed changes to the architecture.
Discussion
We propose a Brain Extracting model that utilizes a combination of multi-scale inputs, CRF layer with model features and an additional Dice Loss. Results show that the model has high accuracy compared to other state-of-the-art methods, and the proposed changes both alone and together increase accuracy and efficiency, even though it was trained with public datasets with potential biases.In Fig. 3 there are some metrics where our model without the proposed loss function works better than the one with it. We believe it to be a result of the difficulty of the data. If the data is easier to segment, there can be occasions of the CRF layer adding more errors rather than going closer to the truth. However, many raw T1 modality images are not perfect, which the additional loss can be beneficial.
For years BEaST9 has been the top method outperforming both traditional and Deep Learning methods, which is clearly visible in Fig. 2. Nevertheless, the template matching process of BEaST is very time consuming, preventing the usage of the method. The results suggest that our method can achieve higher accuracy while significantly reducing the time complexity given that it is a Deep Learning method.
Conclusion
We suggest three changes which are beneficial for Skullstripping tasks. Our results indicate that our trained model is stable with high accuracy, regardless of the testing dataset. They also show that the changes increase training efficiency. We believe this additionally provides an insight into the effect CRFs can have in medical image semantic segmentation. The model and code will be provided open source in DIPY18.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
Rehman, H. Z. U., Hwang, H., & Lee, S. (2020). Conventional and deep learning methods for skull stripping in brain MRI. Applied Sciences, 10(5), 1773.
Krähenbühl, P., & Koltun, V. (2011). Efficient inference in fully connected crfs with gaussian edge potentials. Advances in neural information processing systems, 24.
Monteiro, M., Figueiredo, M. A., & Oliveira, A. L. (2018). Conditional random fields as recurrent neural networks for 3d medical imaging segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.07464.
Milletari, F., Navab, N., & Ahmadi, S. A. (2016, October). V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In 2016 fourth international conference on 3D vision (3DV) (pp. 565-571). IEEE.
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., & Brox, T. (2015, October). U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention (pp. 234-241). Springer, Cham.
Mehta, R., & Sivaswamy, J. (2017, April). M-net: A convolutional neural network for deep brain structure segmentation. In 2017 IEEE 14th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2017) (pp. 437-440). IEEE.
Xu, Y., Gong, M., Fu, H., Tao, D., Zhang, K., & Batmanghelich, K. (2018, September). Multi-scale masked 3-D U-net for brain tumor segmentation. In International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop (pp. 222-233). Springer, Cham.
Zheng, S., Jayasumana, S., Romera-Paredes, B., Vineet, V., Su, Z., Du, D., ... & Torr, P. H. (2015). Conditional random fields as recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 1529-1537).
Eskildsen, S. F., Coupé, P., Fonov, V., Manjón, J. V., Leung, K. K., Guizard, N., ... & Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. (2012). BEaST: brain extraction based on nonlocal segmentation technique. NeuroImage, 59(3), 2362-2373.
Smith, S. M. (2000). BET: Brain extraction tool. FMRIB TR00SMS2b, Oxford Centre for Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain), Department of Clinical Neurology, Oxford University, John Radcliffe Hospital, Headington, UK.
Isensee, F., Schell, M., Pflueger, I., Brugnara, G., Bonekamp, D., Neuberger, U., ... & Kickingereder, P. (2019). Automated brain extraction of multisequence MRI using artificial neural networks. Human brain mapping, 40(17), 4952-4964.
Hoopes, A., Mora, J. S., Dalca, A. V., Fischl, B., & Hoffmann, M. (2022). SynthStrip: Skull-Stripping for Any Brain Image. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.09974.
Cullen, N. C., & Avants, B. B. (2018). Convolutional neural networks for rapid and simultaneous brain extraction and tissue segmentation. In Brain Morphometry (pp. 13-34). Humana Press, New York, NY.
Speier, W., Iglesias, J. E., El-Kara, L., Tu, Z., & Arnold, C. (2011, September). Robust skull stripping of clinical glioblastoma multiforme data. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (pp. 659-666). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Shattuck, D. W., Mirza, M., Adisetiyo, V., Hojatkashani, C., Salamon, G., Narr, K. L., ... & Toga, A. W. (2008). Construction of a 3D probabilistic atlas of human cortical structures. Neuroimage, 39(3), 1064-1080.
Hammers, A., Allom, R., Koepp, M. J., Free, S. L., Myers, R., Lemieux, L., ... & Duncan, J. S. (2003). Three‐dimensional maximum probability atlas of the human brain, with particular reference to the temporal lobe. Human brain mapping, 19(4), 224-247.
Gousias, I. S., Rueckert, D., Heckemann, R. A., Dyet, L. E., Boardman, J. P., Edwards, A. D., & Hammers, A. (2008). Automatic segmentation of brain MRIs of 2-year-olds into 83 regions of interest. Neuroimage, 40(2), 672-684.
Garyfallidis, E., Brett, M., Amirbekian, B., Rokem, A., Van Der Walt, S., Descoteaux, M., ... & Dipy Contributors. (2014). Dipy, a library for the analysis of diffusion MRI data. Frontiers in neuroinformatics, 8, 8.
IXI Dataset – Brain Development. (n.d.). https://brain-development.org/ixi-dataset/
Figures