0777
MPc-RAGE: Simultaneous MP-RAGE and Phase Contrast Angiography Acquisition1Philips, Cleveland, OH, United States, 2Department of Radiology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, United States, 3Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, Rochester, MN, United States, 4Dent Neurologic Institute, Amherst, NY, United States, 5Department of Neurosurgery, University at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Blood vessels, Blood vessels
The 3D magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo (MP-RAGE) and 3D phase contrast angiography (PCA) are widely used sequences in both clinical and research settings, due to high spatial resolution, excellent contrast, and clinically feasible scan time. Recent image acceleration techniques, such as compressed sensing and artificial intelligence reconstruction can drastically reduce scan times, allowing to create multi-domain imaging approaches. Here we introduce MPc-RAGE, a simultaneous MP-RAGE and PCA acquisition that combines the benefits of these two sequences in a single scan. Furthermore, we explore the possibility of the MPc-RAGE as a potential black blood technique for use in vessel wall imaging.Introduction
The 3D magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo (MP-RAGE) and 3D phase contrast angiography (PCA) are among the most widely used sequences in both clinical and research settings, due to high spatial resolution, excellent contrast, and clinically feasible scan time1. Recent image acceleration techniques, such as compressed sensing and artificial intelligence (AI) reconstruction can drastically reduce scan times, allowing to create multi-domain imaging approaches. Here we introduce MPc-RAGE, a simultaneous MP-RAGE and PCA acquisition that combines the benefits of these two sequences in a single scan. Furthermore, we explore the possibility of the MPc-RAGE as a potential black blood technique for use in vessel wall imaging.Methods
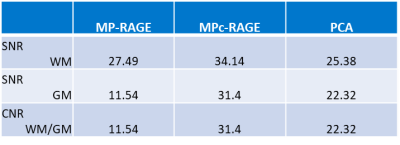
All images were acquired on a 3T Philips MRI scanner (Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands) equipped with a 15-channel head coil. Signal to noise (SNR)3 and contrast to noise (CNR)4 ratios for the MPc-RAGE (FOV= 256x256x192mm, resolution= 1x1x1mm, flip angle= 9°, TE= ms, shot interval= 2500ms, TI= 900ms, compressed SENSE=5, VENC= 50cm/s, velocity encoding directions= RL-AP-FH, scan time= 6:55) were computed and compared to the ADNI accelerated MP-RAGE (FOV= 256x256x192mm, resolution= 1x1x1mm, flip angle= 9°, TE= ms, shot interval= 2500ms, TI= 900ms, SENSE=2, scan time= 6:12) and standard 3D gradient PCA (FOV= 256x256x192mm, resolution= 1x1x1mm, flip angle= 12°, TE= 3.2ms, TR= 6ms, compressed SENSE=5, VENC= 50cm/s, velocity encoding directions= RL-AP-FH, scan time= 4:30). Images were also reviewed by radiologist to evaluate image quality and diagnostic utility. To assess the potential of MPc-RAGE as a black blood technique contrast-enhanced images were postprocessed online via subtraction (MP-RAGE – (2xPCA)).Results
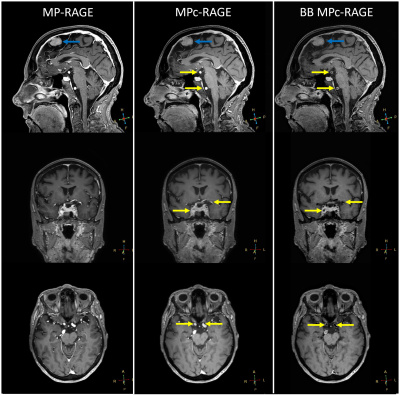
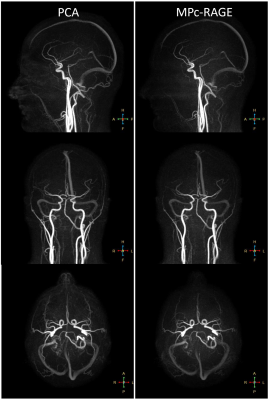
SNR and CNR calculations are reported in Table 1. Radiologist review of the MPc-RAGE for artifacts revealed no imaging artifacts, higher SNR in the MPc-RAGE but lower grey matter/white matter CNR compared to the ADNI MP-RAGE (Figure 1). Both MP-RAGE and PCA images from the MPc-RAGE resulted in sufficient diagnostic quality. Moreover, post processed MPc-RAGE images allowed for black blood appearance in smaller vessels, but incomplete blood suppression in larger vessels (Figure 2), while a flax meningioma was well visualized even after subtraction.Discussion
Here we present MPc-RAGE, a simultaneous MP-RAGE and PCA acquisition. Initial assessment shows that with advanced acceleration methods MPc-RAGE can be acquired in a clinically feasible scan time providing both parenchymal and neurovascular information. PCA has been effectively used as a luminal imaging tool for aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, and vascular stenoses in the cerebrovascular system4. Using this lumenographic information from the PCA, MPc-RAGE can potentially be used as a black blood digital subtraction technique for vessel wall imaging without the need of co-registration. Therefore, MPc-RAGE may be an appealing imaging option due to the simultaneous visualization of brain parenchyma and vasculature, with significant scan time reduction. MPc-RAGE can be further extended to acquire time resolved 3D flow imaging to allow for morphological and functional 4D neurovascular flow analysis.Conclusion
MPc-RAGE builds off the benefits and familiarity of the 3D MP-RAGE by adding a phase contrast angiography information. This provides a more complete diagnostic scan with high SNR in a reasonable scan time. Moreover, MPc-RAGE has the ability to be further explored as a potential black blood technique.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Wang, Jinghua, et al. "Optimizing the magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo (MP-RAGE) sequence." PloS one 9.5 (2014): e96899.
2. National Electrical Manufacturers Association. "Determination of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in diagnostic magnetic resonance imaging." NEMA Standards Publication MS 1-2001 (2001).
3. Brown, Robert W., et al. Magnetic resonance imaging: physical principles and sequence design. John Wiley & Sons, 2014. Wang, Jinghua, et al. "Optimizing the magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo (MP-RAGE) sequence." PloS one 9.5 (2014): e96899.
4. Turski, Patrick, et al. "Neurovascular 4DFlow MRI (Phase Contrast MRA): emerging clinical applications." Neurovascular Imaging 2.1 (2016): 1-11.
Figures