0719
The GRAPH-CRAFITY Score: a novel prognostic tool for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with targeted therapy and immunotherapy
Ying Xu1, Lu Li1, Yi Yang1, Lizhi Xie2, Sicong Wang2, Feng Ye1, and Xinming Zhao1
1Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China, 2GE Healthcare, China, Beijing, China
1Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China, 2GE Healthcare, China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Liver, Treatment, Targeted Therapy, Immunotherapy, Prognostic Prediction ·
One-hundred and sixty-six patients (55.6±10.4 years) treated with lenvatinib plus anti-PD-1 antibody were included in training cohort and 77 patients (55.4±10.7 years) treated with lenvatinib or bevacizumab plus anti-PD-1 antibody were included in validation cohort. Based on independent risk factors (Gender, intRatumoral fAt, enhancing tumor caPsule, gross growtH type and CRAFITY Score) identified by the multivariate analysis, a novel prognostic tool named GRAPH-CRAFITY Score was developed to predict OS. GRAPH-CRAFITY Score by integrating Gender, MR features and laboratory tests is an effective and user-friendly tool to predict OS of HCC patients treated with targeted therapy and immunotherapy.Objectives
To establish an optimized model by integrating magnetic resonance (MR) features and CRAFITY score to predict overall survival (OS) of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients treated with targeted therapy and immunotherapy.Methods
This retrospective study included patients with HCC who received targeted therapy and immunotherapy at two hospitals in China from August 2018 to February 2022. The clinical variables and MR features were assessed by univariate and multivariate Coxregression analyses.Results
One-hundred and sixty-six patients (55.6±10.4 years) treated with lenvatinib plus anti-PD-1 antibody were included in training cohort and 77 patients (55.4±10.7 years) treated with lenvatinib or bevacizumab plus anti-PD-1 antibody were included in validation cohort. Based on independent risk factors (Gender, intRatumoral fAt, enhancing tumor caPsule, gross growtH type and CRAFITY Score) identified by the multivariate analysis, a novel prognostic tool named GRAPH-CRAFITY Score was developed to predict OS. The OS was significantly different among the 3 groups according to GRAPH-CRAFITY score (≤3.2, 3.3-6.1, ≥6.2; p<0.001) and C index of GRAPH-CRAFITY Score was 0.74 in both training cohort and validation cohort. Area under the time-dependent receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) for discrimination at 6, 12, 18, 24 months were 0.80, 0.79, 0.77, 0.72 and 0.87, 0.75, 0.73, 0.78 in training cohort and validation cohort, respectively.Conclusions
GRAPH-CRAFITY Score by integrating Gender, MR features and laboratory tests is an effective and user-friendly tool to predict OS of HCC patients treated with targeted therapy and immunotherapy, which may help oncologists for decision-making.Acknowledgements
None.References
1 Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A et al (2021) Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 7:62 Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M et al (2020) Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N Engl J Med 382:1894-19053 Zhang W, Gong C, Peng X et al (2022) Serum Concentration of CD137 and Tumor Infiltration by M1 Macrophages Predict the Response to Sintilimab plus Bevacizumab Biosimilar in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Clin Cancer Res 28:3499-35084 Ren Z, Xu J, Bai Y et al (2021) Sintilimab plus a bevacizumab biosimilar (IBI305) versus sorafenib in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (ORIENT-32): a randomised, open-label, phase 2-3 study. Lancet Oncol 22:977-9905 Finn RS, Ikeda M, Zhu AX et al (2020) Phase Ib Study of Lenvatinib Plus Pembrolizumab in Patients With Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 38:2960-29706 Xu J, Shen J, Gu S et al (2021) Camrelizumab in Combination with Apatinib in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma (RESCUE): A Nonrandomized, Open-label, Phase II Trial. Clin Cancer Res 27:1003-10117 Llovet JM, Castet F, Heikenwalder M et al (2022) Immunotherapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 19:151-1728 Sangro B, Melero I, Wadhawan S et al (2020) Association of inflammatory biomarkers with clinical outcomes in nivolumab-treated patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 73:1460-14699 Scheiner B, Pomej K, Kirstein MM et al (2022) Prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with immunotherapy - development and validation of the CRAFITY score. J Hepatol 76:353-36310 Yang Y, Ouyang J, Zhou Y, Zhou J, Zhao H (2022) The CRAFITY score: A promising prognostic predictor for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitor and immunotherapy combinations. J Hepatol 77:574-57611 Lee S, Kim SH, Lee JE, Sinn DH, Park CK (2017) Preoperative gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI for predicting microvascular invasion in patients with single hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 67:526-53412 Wu TH, Yu MC, Chen TC et al (2012) Encapsulation is a significant prognostic factor for better outcome in large hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Oncol 105:85-9013 Siripongsakun S, Lee JK, Raman SS, Tong MJ, Sayre J, Lu DS (2012) MRI detection of intratumoral fat in hepatocellular carcinoma: potential biomarker for a more favorable prognosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199:1018-102514 Sheng R, Zeng M, Jin K, Zhang Y, Wu D, Sun H (2021) MRI-based Nomogram Predicts the Risk of Progression of Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Combined Lenvatinib and anti-PD-1 Antibody Therapy. Acad Radiol. 10.1016/j.acra.2021.09.00415 Heimbach JK, Kulik LM, Finn RS et al (2018) AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 67:358-38016 KANAI,T. (1987) Pathology of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Proposal for a New Gross Classification. Cancer 60:810-81917 Conforti F, Pala L, Bagnardi V et al (2018) Cancer immunotherapy efficacy and patients' sex: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol 19:737-74618 Wallis CJD, Butaney M, Satkunasivam R et al (2019) Association of Patient Sex With Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Overall Survival in Advanced Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol 5:529-53619 Sieghart W, Pinter M, Hucke F et al (2013) Single determination of C-reactive protein at the time of diagnosis predicts long-term outcome of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 57:2224-223420 Mori S, Kita J, Kato M, Shimoda M, Kubota K (2015) Usefulness of a new inflammation-based scoring system for prognostication of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. Am J Surg 209:187-19321 Duvoux C, Roudot-Thoraval F, Decaens T et al (2012) Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a model including α-fetoprotein improves the performance of Milan criteria. Gastroenterology 143:986-994.e983; quiz e914-98522 Hatanaka T, Kakizaki S, Hiraoka A et al (2022) Prognostic impact of C-reactive protein and alpha-fetoprotein in immunotherapy score in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab: a multicenter retrospective study. Hepatol Int. 10.1007/s12072-022-10358-z23 Rhee H, Chung T, Yoo JE et al (2020) Gross type of hepatocellular carcinoma reflects the tumor hypoxia, fibrosis, and stemness-related marker expression. Hepatology International 14:239-24824 Murai H, Kodama T, Maesaka K et al (2022) Multiomics identifies the link between intratumor steatosis and the exhausted tumor immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 10.1002/hep.3257325 Zhu AX, Dayyani F, Yen CJ et al (2022) Alpha-Fetoprotein as a Potential Surrogate Biomarker for Atezolizumab + Bevacizumab Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 28:3537-354526 Llovet JM, Montal R, Villanueva A (2019) Randomized trials and endpoints in advanced HCC: Role of PFS as a surrogate of survival. J Hepatol 70:1262-127727 Kudo M, Montal R, Finn RS et al (2022) Objective Response Predicts Survival in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Systemic Therapies. Clin Cancer Res 28:3443-345128 Bruix J, Chan SL, Galle PR, Rimassa L, Sangro B (2021) Systemic treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: An EASL position paper. J Hepatol 75:960-974Figures
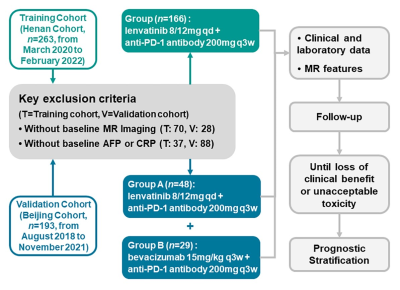
Figure1.
Flowchart of the study.
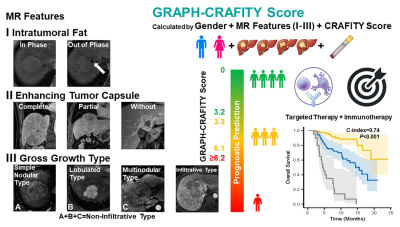
Figure
2. Development of GRAPH-CRAFITY Score.
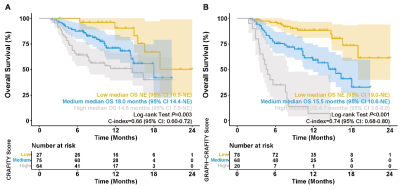
Figure
3. Kaplan-Meier survival curves based on CRAFITY
Score (A) and GRAPH-CRAFITY Score (B) in training cohort.
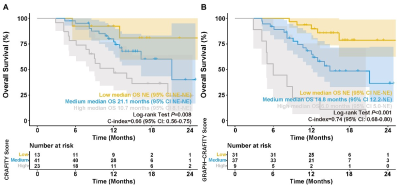
Figure
4. Kaplan-Meier survival curves based on CRAFITY
Score (A) and GRAPH-CRAFITY Score (B) in validation cohort.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/0719