0701
Identification of high-risk basilar artery plaque with HR-VWI-based radiomics and machine learning1Shanxi Cardiovascular Hospital, Taiyuan, China, 2MR Research China,GE Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Blood vessels, Atherosclerosis, Radiomics;Machine Learning
The stability of plaques is the key cause of cerebral ischemic in patients with basilar atherosclerosis. High-resolution vessel wall imaging (HR-VWI) is a useful technique for study of plaques. Radiomics are widely used in recently years to discover the radiographic information of diseases and to improve diagnostic performance. In this study, we constructed six machine learning models based on radiomics features from HR-VWI to predict the stability of plaques of the basilar artery, finding support vector machine has the best performance.
Introduction
Posterior circulation ischemic stroke is the cerebral infarction that occurs in the vertebrobasilar artery blood supply area, accounting for 20%~25% of all ischemic strokes. The basic artery is the largest vessel in the posterior circulation and an important responsible vessel for posterior ischemic stroke. Atherosclerotic stenosis is the main cause of posterior circulation ischemic stroke. Whether cerebral ischemic events occur in patients with basilar atherosclerosis mainly depends on the stability of plaques. With the emergence and application of high-resolution vessel wall imaging, the study of the stability of basilar atherosclerosis plaques has gradually become a research hotspot in recent years. Radiomics are used to extract features from radiographic images and to deeply explore tissue information. This study aimed to identify high-risk plaques of the basilar artery based on radiomics features from high-resolution vessel wall imaging (HR-VWI).Methods
A total of 54 patients with basilar artery stenosis who underwent HR-VWI scanning were recruited in this study and were divided into training group and validation group with a ratio of 8:2. The horizontal axial images of basilar artery plaque in HR-VWI of each patient were selected for manual segmentation and radiomics features extraction. Plaque segmentation for radiomics analysis was performed with an open-source software ITK-SNAP (version 3.8.0,www.itk-snap.org) (Figure 1). The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) was used for dimension reduction of the radiomics features. Combined with the characteristics of screening, the selected features were applied to establish prediction models including support vector machine (SVM), k-nearest neighbor (KNN), logical regression (LR), decision tree (DT), random forest (RF), and XGBoost to predictunstable patches. At the end,the accuracy of all the six models were compared.Results
Forty-three patients were included in the training group and 11 in the validation group. In the total 54 patients, there are 28 stable plaques and 26 unstable plaques. After LASSO regression, 108 radiomics features were quantitatively extracted from the plaque including 2 features of GLSZM and GLDM(Figure 2,3). The accuracy of SVM and KNN exceeds 65% among the six machine learning models, which are the best of all models(Figure 4). The areas under the ROC curve of the training group and the validation group in the KNN model was 0.763 and 0.667 respectively. The area under the ROC curve of the training group and the validation group in the SVM model was 0.713 and 0.867 respectively. The SVM has the best performance(Figure 5).Conclusion
Based on HR-VWI, we have established six prediction models for the stability prediction of basilar atherosclerotic plaques by using radiomics and machine learning algorithms. Among them, SVM model show the best performance, which is helpful to predict the stability of basilar atherosclerotic plaques and provide reference for clinical intervention.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Zhang R, Zhang Q, Ji A, et al. Identification of high-risk carotid plaque with MRI-based radiomics and machine learning. Eur Radiol. 2021 May;31(5):3116-3126.
2. Xu X, Zhang J, Yang K, et al. Prognostic prediction of hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage using CT radiomics and machine learning. Brain Behav. 2021 May;11(5):e02085.
Figures
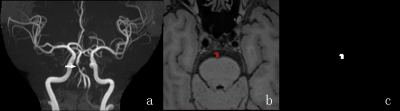
Figure 1: The procedure of radiomics segmentation:a TOF showed basilar artery stenosis. b In one patient with the regions of interest (ROIs) outlining the basilar artery plaque on T1WI-SPACE images. c The segmentations extracted from the ROIs corresponding to the images on b.
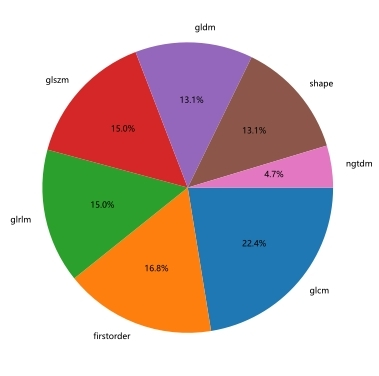
Figure 2: The distribution of 108 radiomics features extracted from plaque.
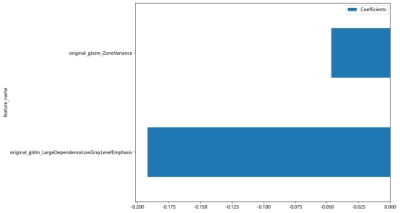
Figure 3: Features finally selected for prediction after the LASSO regression analysis.
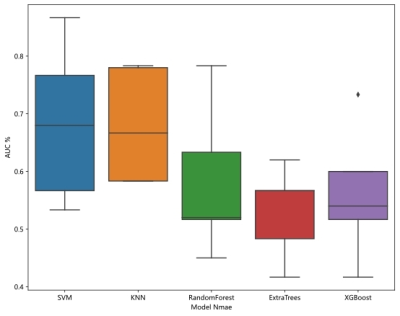
Figure 4: Six models including support vector machine (SVM), k-nearest neighbor (KNN), logical regression (LR), decision tree (DT), random forest (RF) and XGBoost, among which the accuracy of support vector machine (SVM) and k-nearest neighbor (KNN) is greater than 65%.
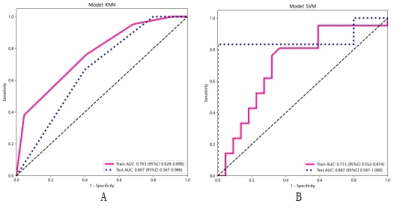
Figure 5:The area under ROC curve of k-nearest neighbor (KNN) and support vector machine (SVM) models. The area under the ROC curve of the KNN model training group was 0.763, and the area under the ROC curve of the validation group was 0.667(A); The area under the ROC curve of the SVM model training group was 0.713, and the area under the ROC curve of the validation group was 0.867(B).