0696
One-minute 3D ky-kz Centric FFE Thoracic Aorta Imaging with Real-Time Motion-Correction and High-Resolution Deep Learning Reconstruction
Hideki Ota1, Satoshi Higuchi1, Yoshiaki Morita2, Takashi Nishina3, Sho Tanaka3, Yuichi Yamashita3, Yoshimori Kassai3, Tasuo Nagasaka1, Mitsue Miyazaki4, and Kei Takase1
1Tohoku University Hospital, Sendai, Japan, 2National Cardiovascular Research Center, Osaka, Japan, 3Canon Medical Systems, Otawara, Japan, 4University of California, San Diego, San Diego, CA, United States
1Tohoku University Hospital, Sendai, Japan, 2National Cardiovascular Research Center, Osaka, Japan, 3Canon Medical Systems, Otawara, Japan, 4University of California, San Diego, San Diego, CA, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Vessels, Vessels, workflow, deep learning reconstruction
Efficiency of 3D ky-kz centric fast field echo (FFE) acquisition was acquired using 100% efficiency of real-time motion correction in the sagittal oblique acquisition and compared with conventional 3D FFE acquisition. The thoracic aorta was acquired within 1 minute using centric ky-kz FFE and reconstructed with high-resolution deep learning reconstruction (HR-DLR), providing good image quality. Regular FFE with conventional reconstruction provides fair image quality with prominent noise and artifacts.Introduction
In general, the thoracic aorta (TA) is acquired using fast field echo (FFE) with respiratory gating or diaphragm navigator echoes using real-time motion correction (RMC). A total scan time, therefore, depends on the efficacy of the subject’s diaphragm motion range, and it may often take a long acquisition time. A past study introduced the 3D centric ky-kz FFE acquisition and obtained 100% efficiency in a 30-mm navigator echo range, as compared to conventional acquisition with a 5-mm navigator echo range, resulting in an efficacy of about 60%.[1] Considering the growing demand for images in vascular diseases and efficient clinical workflow, fast acquisition while keeping reasonable image quality is desired. Further reduction of scan time may be achieved with high-resolution deep learning reconstruction (HR-DLR). The purpose of this study was to develop time-efficient high-resolution TA imaging by applying HR-DLR and compare it with conventional 3D FFE acquisition.Methods
The study was approved by our institutional review board. All non-contrast-enhanced MR imaging data were obtained with a clinical 3-T MR imager (Vantage Centurian 3T, Canon Medical Systems, Japan; gradient amplitude: 100 mT/m; slew rate: 200 mT/m/s) in 6 healthy subjects.Acquisition parameters of our proposed method are TR/TE=3.6/1.4 ms, 488 Hz bandwidth (BW), 204x256 matrix, 18 slices, 1.7-mm slice thickness, 2-3 segments, and centric ky-kz 3D FFE using an RMC band of 30 mm.
Acquisition parameters of the conventional method are TR/TE=5/1.9 ms, 326 Hz BW, 206x256 matrix, 18 slices, 1.7-mm slice thickness, 2-3 segments, and sequential 3D FFE using the RMC band of 30 mm with 90-180 deg. navigator echoes.
HR-DLR (Figure 1): The first process is a denoising block followed by the second process of an up-sampling block. The acquired k-space data is transformed into a complex image with coil data combined and Fourier transform. The complex-valued image is input to the neural network (NN) for denoised images. Then, the denoised images are enlarged and zero-fill interpolation (ZIP) to provide higher-resolution images.
Image evaluation: The image quality was evaluated by consensus reading of two experienced cardiovascular radiologists. A 5-point scale was used: non-diagnostic=1, fair =2, moderate=3, good=4 and excellent=5.
The scan time of all acquisitions was measured. Statistical analysis was performed using Wilcoxon signed-rank test or paired t-tests. A p<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results and Discussion
Figure 2 shows the acquisition summary of both acquisitions. Using RMC with a 30-mm threshold allowing a 100% efficiency of collecting all echo signals, the centric ky-kz acquisition time was less than 60 seconds and the conventional acquisition time was ~90 seconds (p<0.05).Figure 3 shows typical sagittal oblique TA images and multiplanar reformatted images at the level of the sinus of Valsalva of 3D centric ky-kz FFE with HR-DLR and conventional FFE. The 3D centric ky-kz FFE with HR-DLR offers high-resolution images without sacrificing signal intensity and contrast with a scan time of less than 60 seconds. The sharpness of vessel structures is obtained with HR-DLR. On the other hand, conventional FFE images scanned within 90 seconds are suffered from phase-encoded motion artifacts and noises. Image quality was higher in the proposed method than in the conventional method (mean, 4.0 vs. 2.4, p<0.05).
In conclusion, the centric ky-kz FFE with 100% efficiency in RMC combined with the HR-DLR provides good image quality of TA within 60 seconds of the scan time. The proposed method has a potential to improve the clinical workflow.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Morita Y, Ota H, Masuda A, et al., ISMRM 2020 p1323.Figures
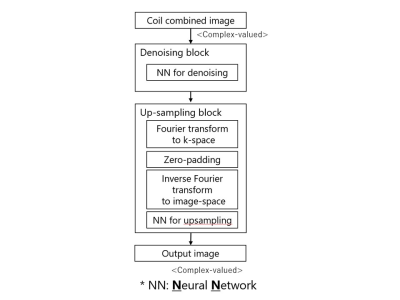
Whole Reconstruction Pipeline with
High-Resolution DLR
Acquisition summary table
3D centric ky-kz fast field echo (FFE) images with high-resolution deep learning reconstruction (a, c) and conventional FFE images (b, d). Sagittal oblique images (a, b) and multiplanar reconstruction images at the level of the sinus of Valsalva (c, d). LMT = left main trunk, RCA = right coronary artery.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/0696