0534
MR Sampling Patterns Learned with Variational Information Maximization1Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 2Radiology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Data Acquisition, Data Sampling
Variational information maximization allows joint optimization of MR data sampling and reconstruction and improves reconstruction quality upon the heuristically designed sampling patterns. Here, we analyze the learned sampling patterns with respect to changes in acceleration factor, measurement noise, anatomy, and coil sensitivities in order to provide some interpretation. We show that all of these factors contribute to the optimization result by impacting the sampling density, k-space coverage and point spread functions of the learned sampling patterns.Introduction
Recently, end-to-end deep learning methods have been proposed for learning undersampling patterns for MRI reconstruction problems1-12. These techniques attempt to optimize both the sampling pattern and the reconstruction network using data-driven methods to improve the reconstruction performance upon heuristically designed patterns such as variable density and poisson disc sampling methods. In particular, 1,2 presents a novel variational information maximization method that allows continuous optimization of k-space samples along with reconstruction networks and reports improved reconstruction quality upon the prevailing variable-density sampling.In this work, we further analyze the learned/optimized sampling patterns from the mutual information maximization framework with respect to the changes in acceleration factor, measurement noise, anatomy of interest and coil sensitivity maps. Our findings indicate that the optimized patterns have a strong dependence on each of the factors we investigated. In particular, the noise amount and acceleration factor influences sampling density and k-space extent. In addition, we find that the learned sampling patterns adapt to the coil sensitivities, requiring completely different patterns for single-coil and multi-coil scenarios.
Methods
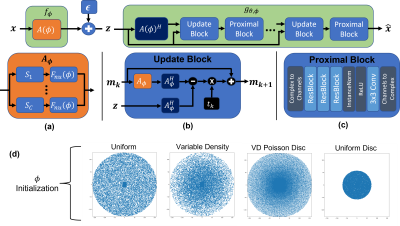
Joint Optimization via Variational Information Maximization: We consider the 3D acquisition scenario where the two phase encoding axes are undersampled and the readout axis is fully sampled. Following the variational information maximization framework 1,2,13, the final loss function for the joint optimization can be expressed as: $$\mathcal{L}(\phi,\theta;\mathcal{D})=\max_{\phi,\theta}\sum_{x\in\mathcal{D}}\mathbb{E}_{q_\phi(Z|x)}[\log p_\theta(x|z)]$$where $$$\phi$$$ is the vector of k-space sample coordinates and $$$\theta$$$ correspond to the reconstruction network weights. $$$z\in\mathbb{C}^M$$$ is the k-space signal according to the MR signal model under the additive white complex Gaussian noise
$$z=f_\phi(x)+\epsilon=A_{\phi}x+\epsilon=\big[(F_{nu}(\phi)S_1)^H\cdots(F_{nu}(\phi)S_C)^H\big]^Hx+\epsilon$$
where $$$\epsilon\sim\mathcal{N}_c(0,\sigma^2I)$$$ is the measurement noise, $$$S_i \in \mathbb{C}^{N\times N}$$$ contains coil sensitivity profiles for coil $$$i$$$, and $$$F_{nu}(\phi): \mathbb{C}^N\rightarrow\mathbb{C}^{M/C}$$$ is the nuFFT operator at sampling locations $$$\phi$$$.
Note that a different set of $$$\phi$$$ and $$$\theta$$$ must be learned for each dataset and the learned sampling pattern is fixed at inference time. Our overall network architecture and initializations we used for $$$\phi$$$ are illustrated in Fig. 1.
Datasets: Our primary dataset is "Stanford Fully Sampled 3D FSE Knees" dataset available in mridata.org14 which contains 8-coil 3D knee scans with 14, 2 and 3 subjects for training, validation and test, respectively. Two different sets of sensitivity maps were estimated using ESPIRiT15 and JSENSE16 algorithms for multi-coil sensitivity map experiments. To show the sampling pattern differences on a different anatomy, we also used the 12-coil 3D T2 CUBE Brain dataset available in 17 where 4 subjects are used for training and 1 subject is used for testing. The coil sensitivities for the brain dataset were estimated using ESPIRiT.
Experiments and Results
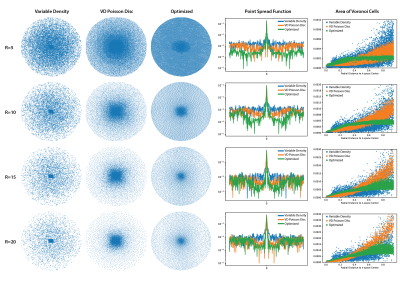
We perform 4 main experiments that investigate the effect of acceleration factor (R), measurement noise, anatomy of interest and coil sensitivity maps on the learned sampling patterns. Pattern characteristics were analyzed using point spread functions (PSF) and radial distribution of Voronoi cell areas which is a measure for the sampling density18. Unless specified otherwise, the experiments were performed on the multicoil knee dataset with ESPIRiT maps and $$$\sigma$$$=1e-4.Acceleration Factor (R): We considered R={5, 10, 15, 20} and compared the learned patterns with Variable Density (VD) Sampling19 , and VD Poisson Disc Sampling20-22. As shown in Fig. 2, for all acceleration factors, the learned sampling patterns avoid clustering the samples and the PSF sidelobes are reduced, improving the reconstruction quality. In addition, the learned patterns are more uniformly distributed compared to the VD and VD Poisson Disc patterns. Optimized patterns show 4.4dB, 2.0dB, 0.75dB, 0.7dB pSNR improvement over reconstruction with Poisson Disc masks in the test set for R=5, 10, 15, 20, respectively.
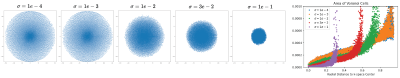
Measurement Noise: We considered five different noise levels: $$$\sigma$$$={1e-4, 1e-3, 1e-2, 3e-2, 1e-1} with R=10 and compared the Voronoi cell area distributions. As shown in Fig. 3, as the SNR decreases, the optimal sampling patterns get concentrated to the center due to the fact that the highly noise corrupted outer k-space deteriorates reconstruction performance.
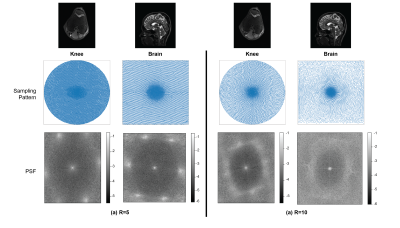
Anatomy: Fig. 4 illustrates the differences between learned sampling patterns with the knee and brain datasets for R={5,10}. The sampling patterns and hence the PSFs show different characteristics due to the differences in image energy spectrums and k-space supports in the two datasets.
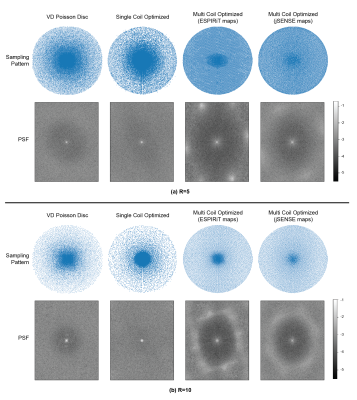
Coil Sensitivities (Single vs Multi-Coil): For single coil experiments, we treated the SENSE24 combined images as ground truths (as in multi-coil experiments) and removed the coil sensitivity dependence in the forward signal model. For the multi-coil scenario we compared the resulting patterns trained with ESPIRiT and JSENSE estimated maps. Fig. 5 demonstrates the differences between single-coil and multi-coil optimized patterns. Single-coil optimized patterns conform more to a variable density distribution, whereas the samples in multi-coil patterns are distributed more uniformly.
Discussion and Conclusion
This work analyzes the effects of acceleration factor, measurement noise, dataset and coil sensitivities on the learned/optimized sampling patterns obtained with the variational information maximization framework. Our results indicate that the learned sampling patterns adapt to each of these factors by adjusting the sampling density, k-space coverage and point spread functions.Future work can utilize the demonstrated dependency on the coil sensitivity maps by conditioning the sampling patterns on the information from autocalibration regions and sensitivity maps that are typically acquired with low resolution scans in clinical settings.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by NIH U01-EB029427 and NIH R01-EB009690.References
1. Alkan C, Mardani M, Vasanawala S, Pauly JM. Joint Data Driven Optimization of MRI Data Sampling and Reconstruction via Variational Information Maximization. ISMRM 2021 Annual Meeting Proceedings.
2. Alkan C, Mardani M, Vasanawala S, Pauly JM. Learning to Sample MRI via Variational Information Maximization. NeurIPS 2020 Workshop on Deep Learning and Inverse Problems.
3. Kyong Hwan Jin, Michael Unser, and Kwang Moo Yi. Self-supervised deep active accelerated mri. arXiv preprint arXiv:1901.04547, 2019.
4. Zizhao Zhang, Adriana Romero, Matthew J Muckley, Pascal Vincent, Lin Yang, and Michal Drozdzal. Reducing uncertainty in undersampled mri reconstruction with active acquisition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 2049–2058, 2019.
5. L. Pineda, S. Basu, A. Romero, R. Calandra, and M. Drozdzal, “Active mr k-space sampling with reinforcement learning,” in International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, 2020, pp. 23–33
6. Cagla Deniz Bahadir, Adrian V Dalca, and Mert R Sabuncu. Learning-based optimization of the under-sampling pattern in mri. In International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging, pages 780–792. Springer, 2019.
7. Iris AM Huijben, Bastiaan S Veeling, and Ruud JG van Sloun. Learning sampling and model-based signal recovery for compressed sensing mri. InICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pages 8906–8910. IEEE, 2020.
8. Hemant Kumar Aggarwal and Mathews Jacob. J-modl: joint model-based deep learning for optimized sampling and reconstruction. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing,14(6):1151–1162, 2020.
9. Tomer Weiss, Ortal Senouf, Sanketh Vedula, Oleg Michailovich, Michael Zibulevsky, and Alex Bronstein. Pilot: Physics-informed learned optimal trajectories for accelerated mri. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.05773, 2019.
10. C. G R, Z. Ramzi and P. Ciuciu, "Hybrid Learning of Non-Cartesian K-Space Trajectory and Mr Image Reconstruction Networks," 2022 IEEE 19th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), 2022, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1109/ISBI52829.2022.9761408.
11. G. Wang, T. Luo, J. -F. Nielsen, D. C. Noll and J. A. Fessler, "B-Spline Parameterized Joint Optimization of Reconstruction and K-Space Trajectories (BJORK) for Accelerated 2D MRI," in IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol. 41, no. 9, pp. 2318-2330, Sept. 2022, doi: 10.1109/TMI.2022.3161875.
12. Zibetti, M.V.W., Herman, G.T. & Regatte, R.R. Fast data-driven learning of parallel MRI sampling patterns for large scale problems. Sci Rep 11, 19312 (2021).
13. Aditya Grover and Stefano Ermon. Uncertainty autoencoders: Learning compressed representations via variational information maximization. In The22nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, pages 2514–2524, 2019
14. F Ong, S Amin, SS Vasanawala, and M Lustig. An open archive for sharing mri raw data. In ISMRM & ESMRMB Joint Annual Meeting, page 3425, 2018.
15. Martin Uecker, Peng Lai, Mark J Murphy, Patrick Virtue, Michael Elad, John M Pauly, Shreyas S Vasanawala, and Michael Lustig. Espirit—an eigenvalue approach to autocalibrating parallel mri: where sense meets grappa. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 71(3):990–1001, 2014.
16. Ying, L., & Sheng, J. (2007). Joint image reconstruction and sensitivity estimation in SENSE (JSENSE). Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 57(6), 1196-1202.
17. H. K. Aggarwal, M. P. Mani and M. Jacob, "MoDL: Model-Based Deep Learning Architecture for Inverse Problems," in IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol. 38, no. 2, pp. 394-405, Feb. 2019, doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2865356.
18. Rasche V, Proksa R, Sinkus R, Börnert P, Eggers H. Resampling of data between arbitrary grids using convolution interpolation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1999 May;18(5):385-92. doi: 10.1109/42.774166. PMID: 10416800.
19. Michael Lustig, David Donoho, and John M Pauly. Sparse mri: The application of compressed sensing for rapid mr imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 58(6):1182–1195, 2007.
20. Robert Bridson. Fast poisson disk sampling in arbitrary dimensions. SIGGRAPH sketches, 10(1):1, 2007.
21. SS Vasanawala, MJ Murphy, Marcus T Alley, P Lai, Kurt Keutzer, John M Pauly, and Michael Lustig. Practical parallel imaging compressed sensing mri: Summary of two years of experience in accelerating body mri of pediatric patients. In 2011 ieee international symposium on biomedical imaging: From nano to macro, pages 1039–1043. IEEE, 2011.
22. Michael Lustig and John M. Pauly. Spirit: Iterative self-consistent parallel imaging reconstruction from arbitrary k-space. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 64(2):457–471, 2010.
23. Christopher M Sandino, Joseph Y Cheng, Feiyu Chen, Morteza Mardani, John M Pauly, and Shreyas S Vasanawala. Compressed sensing: From research to clinical practice with deep neural networks: Shortening scan times for magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine,37(1):117–127, 2020
24. Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P. SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1999 Nov;42(5):952-62. PMID: 10542355.
Figures